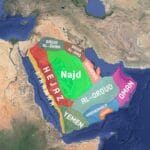
Forget the dusty history books! The Silk Road wasn’t just about silk and spices; it was a cultural revolution. For centuries, this vast network of trade routes connected East and West, acting as a superhighway for goods, ideas, technologies, and religions. We’re talking silk, yes, but also groundbreaking inventions, clashing beliefs, and the mixing of cultures unlike anything the world had ever seen. This isn’t just about what was traded; it’s about the people who traveled it, the empires that rose and fell along its path, and the lasting impact it still has on our world today. The impact of global exchange is vast; consider learning more about global food exchange. Prepare for a journey through history – it’s more captivating than you think.
The Silk Road: A Journey Through Time and Culture
Imagine a sprawling network of routes crisscrossing continents, not a single road, but a vibrant, ever-shifting tapestry of trails. This was the Silk Road, a colossal engine of economic and cultural exchange that reshaped the world for centuries. We often hear about the silk and spice trade, but its true legacy lies in the exchange of ideas, faiths, and technologies that fundamentally altered civilizations from Europe to East Asia. What made this ancient network so much more than just a commercial enterprise?
More Than Just Spices and Silks: A Global Exchange of Goods, Ideas, and Ancient Civilizations
For ages, historians have recognized the Silk Road’s economic power – the incredible wealth generated by trading luxury items. However, the real story is interwoven from countless threads of human interaction, a narrative about the spread of knowledge, the fusion of cultures, and the enduring human drive to connect. It’s a fascinating historical phenomenon that left a lasting impact on art, architecture, societal norms, and the very fabric of daily life across numerous cultures. What can modern societies learn from the complex interplay that defined this historic route?
The Amazing Journey of Ideas and Beliefs: Religious Diffusion
Consider Buddhism’s journey eastward. Monks and missionaries carried scriptures and philosophies, transforming the art, literature, and daily lives of people across Asia. The same holds true for Christianity and Islam – their expansion along these routes impacted the religious landscape of Eurasia. The construction of Buddhist cave temples, such as those at Dunhuang in China, reflect Greco-Roman influences brought by Central Asian artists, illustrating how religious art also traveled along the Silk Road. These shifts were just as transformative as the economic ones, showcasing the intangible aspects of this network. Did the exchange of religious ideas along the Silk Road lead to tolerance or conflict between different faiths?
A Global Technology Transfer: Innovation Exchange
Beyond religious ideas, the Silk Road was a superhighway for technological innovation. Papermaking, originating in China, revolutionized communication and record-keeping globally. Gunpowder’s reach extended beyond fireworks, changing warfare and shaping societies far beyond its place of origin. These advancements traveled westward, sparking new inventions and altering history. The Silk Road acted as a global incubator for technological breakthroughs, accelerating innovation. How did these technological exchanges along the Silk Road impact military strategies of ancient empires?
A Crucible of Cultures: Where East Met West
The Silk Road was a melting pot where cultures collided, blended, and evolved. Cities like Samarkand became vibrant crossroads, representing a fusion of diverse influences. Architectural styles, artistic expressions, culinary traditions, and even languages melded together, creating unique cultural landscapes. Imagine the exchange—new tongues emerged, unique artistic styles flourished, and food reflected the fusion that took place. What artistic styles are attributed to the cultural diffusion from the Silk Road?
Challenges and Triumphs: The Perils of the Path
The Silk Road wasn’t a leisurely stroll; it was fraught with challenges. Diseases spread rapidly along these pathways. The Black Death stands as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the world and the price of intense contact. Political unrest and banditry were constant threats to travelers and merchants alike. Yet, these obstacles didn’t stop the flow of people, goods, or ideas. The resilience of the network and the human desire for connection triumphed over these difficulties, highlighting forces driving this global interaction. How did societies along the Silk Road adapt to the frequent outbreaks of infectious diseases?
An Enduring Legacy: Lessons from the Past
The Silk Road occupies a prominent place in world history. Its influence extends beyond commerce, shaping the cultural, religious, and technological landscapes of vast regions. It wasn’t just about goods; it was about connecting people, cultures, and civilizations. Studying the Silk Road offers insights into cross-cultural interaction and the power of exchange. The legacy of the Silk Road continues to inspire research, cultural understanding, and international cooperation. What modern-day initiatives are inspired by the collaborative premise of the Silk Road?
Ongoing Research and Unanswered Questions
While we’ve learned much about the Silk Road, much remains unknown. Ongoing research continues to unearth new insights, and our understanding of the network’s complexities is evolving. Future discoveries will likely reveal more about the interactions and exchanges that occurred along these pathways. The Silk Road continues to serve as a captivating subject of study, reminding us of the interconnectedness of our world and the transformative power of human interaction. What new archaeological discoveries have recently added to our understanding of the Silk Road?
The Silk Road’s Impact on Public Health: Disease Transmission and Cultural Exchange
The Silk Road wasn’t just about silks and spices; it was a vibrant artery pumping life—and death—across Eurasia. For centuries, this network of trade routes facilitated an unprecedented exchange of goods, ideas, and religions. But this interconnectedness came at a cost. How did disease transmission impact Silk Road cultural exchange? The answer is complex and intertwined with the very fabric of the Silk Road’s history.
A Double-Edged Sword: Trade and Transmission
Imagine a bustling marketplace, where cultures mingle. Merchants from distant lands exchange goods, sharing their wares and their microbes. The Silk Road, in its heyday, was a superhighway for both commerce and contagious diseases. The same routes that carried silks and spices also carried invisible enemies: bacteria, viruses, and parasites. How did the economic benefits of trade compare to the cost of health crises along the Silk Road?
Beyond the Black Death: A Wider Perspective
The Black Death wasn’t an isolated incident. Smallpox, measles, and influenza moved easily across geographical boundaries, leaving a trail of suffering. These diseases impacted diverse populations differently; some communities developed immunities, while others suffered catastrophic losses. These shifts affected power dynamics and cultural practices. What other diseases, besides the Black Death, were spread along the Silk Road, and what were their effects on local populations?
The Cultural Fallout: Societal Adaptation
Beyond mortality, the threat of disease influenced cultural practices profoundly. Social structures and religious beliefs adapted in response to epidemics. Practices like quarantine, hygiene rituals, and herbal medicine were developed and disseminated along the trade routes, a testament to the adaptive nature of human societies facing adversity. The sharing of medical knowledge, even in the face of devastating outbreaks, was another facet of the cultural exchange facilitated by the Silk Road. Did the spread of diseases lead to advancements in medical knowledge and practices along the Silk Road?
A Legacy of Interdependence: Lessons for Global Interaction
The Silk Road’s story serves as a reminder: global connectivity is a double-edged sword. The forces that drive cultural exchange and economic prosperity can also facilitate the rapid spread of disease. Understanding this historical dynamic is crucial in our increasingly interconnected world. The legacy of the Silk Road teaches us the importance of global health security, sustainable trade practices, and a recognition that some of our most vital interactions carry the most profound risks. What lessons from the Silk Road’s experience on disease control can be applied to contemporary global health challenges?
Key Takeaways:
- The Silk Road was a major facilitator of both cultural exchange and disease transmission.
- The Black Death highlights the consequences of this interconnectedness.
- Various diseases impacted different communities differently, reshaping populations and power structures.
- The threat of disease influenced cultural practices and fostered the exchange of medical knowledge.
- The Silk Road’s legacy underscores the importance of global health security and sustainable practices.
The Silk Road’s Impact on Local Cultures: A Comparative Study of Enrichment and Disruption
Imagine a world before the internet, where the exchange of ideas and goods relied on arduous journeys across vast landscapes. That’s the world the Silk Road shaped, a network of trade routes that connected East and West for centuries. But was it merely a pathway for silks and spices? The answer, as we’ll explore, is a resounding no. The Silk Road’s impact on local cultures was far more complex, a vibrant tapestry woven with threads of both enrichment and disruption.
Gaochang: A Cosmopolitan Oasis
Let’s take Gaochang, a flourishing city in the Tarim Basin during the Tang dynasty, as an example. Archaeological digs there reveal a melting pot of cultures. Buddhist temples stand alongside Taoist shrines, hinting at a diverse religious landscape. Architectural styles reflect influences from across the known world, showcasing the Silk Road’s ability to blend traditions. Imagine the bustling marketplaces, filled with merchants from distant lands, each bringing their unique wares and customs. How did the geographical location of Gaochang contribute to its role as a cultural crossroads?
This intermingling wasn’t without its complexities. While the Silk Road fostered cultural exchange, it also brought challenges. The arrival of new ideas and religions sometimes led to clashes with existing belief systems. New diseases, carried along the trade routes, could devastate entire communities. Think about the unforeseen consequences of increased contact; the benefits were not always universally distributed—power dynamics and inequalities were a reality.
A Two-Sided Coin: Enrichment and Disruption
The Silk Road’s legacy is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it facilitated the spread of technologies, religious philosophies, and artistic styles. New crops and agricultural techniques boosted food production, improving the livelihoods of countless people. On the other, the influx of foreign influences sometimes disrupted traditional ways of life. Existing social structures and power dynamics could be altered, leading to both opportunities and conflict. According to Xinru Liu, in “The Silk Road in World History,” the exchange also led to the spread of new social practices and forms of entertainment that, while enriching, sometimes clashed with traditional values. Did the Silk Road always benefit all social classes equally?
The very fabric of daily life transformed. New styles of clothing, culinary traditions, and artistic expressions emerged. People interacted, mixing languages and customs. Cities like Gaochang became vibrant centers of innovation.
Unraveling the Threads of History
Studying the Silk Road’s impact on local cultures requires a nuanced approach. We need to move beyond the simplistic narrative of mere trade and explore the interplay of economic, social, and religious factors. Archaeological evidence, pottery fragments, religious artifacts, and architectural remains provide key insights. The study of ancient texts, travelogues, and artistic representations offers additional perspectives. How has ongoing archaeological research changed our understanding of the Silk Road’s impact on local communities?
However, reconstructing this historical tapestry presents challenges. The evidence is often fragmented, requiring painstaking analysis and interpretation. There are gaps in our knowledge, making some aspects of Silk Road history challenging to fully understand. This is why continued research – employing new methodologies and technologies – is vital to enhancing our knowledge and understanding.
Looking Toward the Future
The Silk Road’s story offers lessons for our understanding of globalization in the modern era. The patterns of cultural exchange, economic interdependence, and the interplay of enrichment and disruption are relevant to today’s interconnected world. The past echoes in the present. Studying the Silk Road helps us understand the complexities of globalization, its benefits, and the need to manage its potential drawbacks. The legacy of the Silk Road compels us to forge more inclusive and understanding globalized relationships. How do the dynamics of cross-cultural interaction along the Silk Road inform modern global diplomacy and trade relations?
Key Takeaways:
- The Silk Road was more than a trade route; it was a conduit for cultural exchange.
- The impact on local cultures was multifaceted – both enriching and disruptive.
- Gaochang serves as a case study of cosmopolitanism and cultural blending.
- Understanding the Silk Road’s legacy is crucial for navigating the complexities of modern globalization.
- Further research is needed to fully grasp the Silk Road’s impact.
Silk Road Refugee Populations: Agents of Technological and Cultural Diffusion Across Eurasia
Key Takeaways:
- The Silk Road wasn’t just a trade route; it was a dynamic conduit for cultural exchange and technological innovation.
- Silk Road refugee populations played a significant role in this diffusion.
- The movement of people fueled the Silk Road’s transformative power across Eurasia.
- Understanding the Silk Road requires looking beyond economic transactions; the human element is paramount.
A Network of Movement, Not Just Merchandise
Imagine a world without borders, where ideas and technologies flowed as freely as silk and spices. That, in essence, was the Silk Road – a vast, interconnected network stretching across Eurasia for centuries. We often picture caravans laden with treasures, but the true story is richer. It’s a story of people: merchants, pilgrims, soldiers, and refugees, each carrying their own expertise. How can we accurately estimate the scope and demographics of refugee movements along the Silk Road?
The Unexpected Carriers of Change: Silk Road Refugee Populations
Forced migration, often caused by war, famine, or political upheaval, significantly impacted the spread of culture and technology along the Silk Road. These Silk Road refugee populations, uprooted from their homes, carried with them their skills and knowledge. Think of a potter forced to flee his village, settling in a new city and sharing his craft, or a skilled weaver, displaced by conflict, introducing new techniques and designs. These individuals, though refugees, became agents of change, unintentionally altering the cultural fabric of their new surroundings. According to Peter Turchin in “War and Peace and War,” the displacement of skilled artisans and craftsmen often led to innovation in new locations as they adapted their techniques to local materials and needs. Why are the contributions of refugees often underappreciated in historical accounts of the Silk Road?
More Than Just Goods: The Transfer of Knowledge and Skills
The Silk Road wasn’t a one-way street. It was a vibrant exchange. Consider the introduction of papermaking to the West, a technology that revolutionized communication and record-keeping. Or the spread of Buddhism, which travelled along these routes, adapting and transforming as it found new adherents. These weren’t passive transfers; they were active processes of adaptation and innovation, shaped by the interactions between different cultures and the ingenuity of individuals, including those who found themselves displaced along the way. Silk Road refugee populations played a critical role in this dynamic exchange. What examples illustrate the ways in which refugee communities were able to adapt and share knowledge from new locations?
The Ripple Effects of Displacement
The impact of these migrating populations wasn’t always immediate or obvious. Often, the consequences played out over generations. A refugee’s skill might initially benefit only a few, but over time, it could transform entire industries. A new farming technique, a novel architectural style, or a unique artistic method could spread, slowly altering the landscape. This subtle but profound impact of displacement is often underestimated when studying the Silk Road. To what extent did governments and other institutions along the Silk Road support or hinder the integration of refugees into their new societies?
A Complex Tapestry: Intertwined Fates
The Silk Road’s story is complex, a tapestry woven from threads of trade, migration, and cultural exchange. It’s a story filled with both triumph and tragedy. The experiences of Silk Road refugee populations remind us that human movement is an inseparable part of this legacy, and their contributions were far from insignificant. By studying these displaced populations, we gain a fuller understanding of the Silk Road’s enduring impact on Eurasian history and culture. How does studying Silk Road refugee populations help us understand contemporary challenges related to migration and displacement?
- Medieval Universities: Shaping Modern Academia - August 1, 2025
- The Radium Girls: Workplace Safety Lessons from a Tragic Past - August 1, 2025
- Master Any Subject: The Feynman Technique: The Best Way to Learn Anything Faster - August 1, 2025