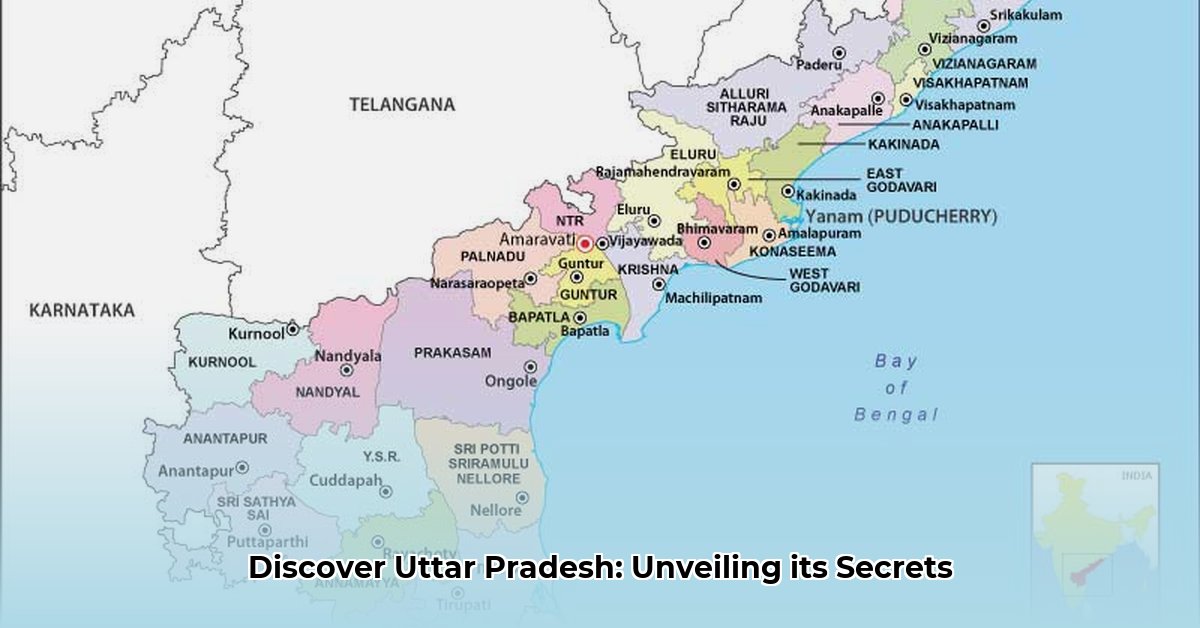
Uttar Pradesh, a state resonating with the echoes of ancient civilizations and pulsating with the dynamism of a burgeoning modern society, is home to over 200 million people. For detailed maps of Indian states, check out this helpful resource: Southeast Asian maps. This profile navigates the multifaceted dimensions of Uttar Pradesh, examining its geography, demography, economy, culture, and governance to provide a comprehensive understanding of its present and future trajectory.
Uttar Pradesh: A Land of Diversity and Heritage
Uttar Pradesh is more than a geographical entity; it is a vibrant mosaic woven from diverse traditions, agricultural prosperity, and a substantial population. Renowned for its historical significance and religious importance, the state is also emerging as a key player in India’s economic landscape. This overview explores the key elements that collectively define Uttar Pradesh.
Geographic Landscape: From Plains to Foothills
The geography of Uttar Pradesh is remarkably diverse, transitioning from the fertile Gangetic plains to the foothills of the Himalayas. This geographical variation influences the state’s agriculture, biodiversity, and regional cultures.
- Gangetic Plains: The fertile alluvial soil of the Gangetic plains supports the cultivation of wheat, rice, sugarcane, and other essential crops, making agriculture a mainstay of the state’s economy.
- Himalayan Foothills: The northern regions of Uttar Pradesh extend into the Himalayan foothills, characterized by rugged terrain and dense forests, offering opportunities for eco-tourism and adventure activities.
- Regional Variations: The state exhibits significant regional variations in terms of climate, soil type, and vegetation, influencing agricultural practices and lifestyles.
Demographics: Understanding the Population Dynamics
Uttar Pradesh is India’s most populous state, with a population exceeding 200 million, reflecting centuries of migration, urbanization, and natural growth. Understanding the state’s demographic composition is crucial for effective policymaking and resource allocation.
- Population Size: Uttar Pradesh accounts for a significant proportion of India’s total population, presenting both opportunities and challenges in terms of resource management and service delivery.
- Population Distribution: The state’s population is unevenly distributed, with higher densities concentrated in major urban centers and along fertile river valleys.
- Demographic Trends: Uttar Pradesh is experiencing rapid urbanization, driven by migration from rural areas in search of better economic opportunities.
Economic Overview: Agriculture, Industry, and Services
Uttar Pradesh’s economy is primarily agrarian, with agriculture employing a large segment of the population. However, the state is also witnessing rapid growth in the industrial and service sectors, contributing to economic diversification.
- Agricultural Dominance: Agriculture remains a dominant sector, with wheat, rice, sugarcane, and pulses being the major crops. The state is also a leading producer of fruits and vegetables.
- Industrial Development: Uttar Pradesh has a growing industrial base, with key industries including sugar processing, textiles, leather goods, chemicals, and engineering products.
- Service Sector Expansion: The service sector is expanding rapidly, driven by growth in tourism, healthcare, education, and information technology.
Cultural Heritage: A Tapestry of Traditions
Uttar Pradesh boasts a rich cultural heritage, shaped by its long history as a center of religious, philosophical, and artistic activity. The state is home to numerous historical monuments, religious sites, and cultural institutions that attract visitors from across the globe.
- Historical Significance: Uttar Pradesh has been a cradle of civilization, with evidence of human settlements dating back to ancient times. The state has been ruled by various empires and dynasties, leaving behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, and literature.
- Religious Importance: Uttar Pradesh is home to some of the most sacred sites in Hinduism, including Varanasi, Ayodhya, and Mathura. The state is also an important center of Buddhism, with Sarnath being the site where Lord Buddha delivered his first sermon.
- Cultural Expressions: Uttar Pradesh is renowned for its diverse cultural expressions, including classical music and dance, folk traditions, handicrafts, and cuisine.
Challenges and Opportunities: Charting a Course for the Future
Uttar Pradesh faces numerous challenges, including poverty, inequality, unemployment, and environmental degradation. However, the state also possesses immense potential for growth and development, leveraging its large population, abundant natural resources, and strategic location.
- Infrastructure Development: Improving infrastructure, including roads, railways, power supply, and irrigation facilities, is crucial for attracting investment and promoting economic growth.
- Social Development: Addressing social inequalities, improving access to education and healthcare, and empowering marginalized communities are essential for inclusive development.
- Environmental Sustainability: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, conserving natural resources, and mitigating the impacts of climate change are vital for long-term environmental sustainability.
Investing in Sustainable Tourism: A Pathway to Growth
Uttar Pradesh offers considerable opportunities for sustainable tourism development, capitalizing on its rich cultural heritage, natural beauty, and religious significance. Investments in eco-tourism, cultural tourism, and rural tourism can generate employment, promote local economies, and conserve the state’s natural and cultural assets.
- Eco-tourism Potential: Uttar Pradesh’s national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, such as Dudhwa National Park, offer opportunities for eco-tourism, providing visitors with unique experiences while promoting biodiversity conservation.
- Cultural Tourism Circuits: Developing integrated cultural tourism circuits, linking historical sites, religious centers, and cultural attractions, can attract a larger number of tourists and promote regional development.
- Rural Tourism Initiatives: Promoting rural tourism initiatives, showcasing the state’s traditional crafts, cuisine, and lifestyle, can generate income for rural communities and preserve cultural heritage.
Sustainable Tourism Strategies and Preservation Efforts: A Holistic Approach
Sustainable tourism is essential for Uttar Pradesh’s long-term economic prosperity and job creation. This requires a holistic approach that integrates environmental protection, cultural preservation, and community participation.
Geography and Demographics: Tailoring Strategies to Local Contexts
Uttar Pradesh’s diverse geography and large population density necessitate tailored sustainable tourism strategies that address the specific challenges and opportunities of different regions.
Economic Considerations: Balancing Growth and Sustainability
The transition from an agriculture-based economy to one that embraces tourism requires careful planning to ensure that tourism development benefits local communities and minimizes environmental impacts.
Strategies for Preservation: Safeguarding Cultural Heritage
Uttar Pradesh’s cultural heritage is a valuable asset that must be protected and preserved for future generations. This requires effective conservation measures, community engagement, and sustainable tourism practices.
Actionable Strategies for Sustainable Tourism:
The following table summarizes actionable strategies for different stakeholders:
| Stakeholder | Short-Term Actions | Long-Term Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Local Artisans | Participate in skill development programs; promote local crafts | Establish cooperatives; access micro-finance; market products through online platforms |
| Uttar Pradesh Government | Develop sustainable tourism policies; invest in infrastructure; promote digital literacy | Establish eco-tourism zones; implement environmental regulations; promote community-based tourism |
| Tourism Businesses | Adopt sustainable practices; provide training to employees; promote local culture | Invest in renewable energy; reduce waste; engage with local communities |
| Tourists | Choose eco-friendly accommodations; respect local customs; support local businesses | Offset carbon emissions; participate in community-based tourism initiatives; promote responsible travel |
| Researchers & Academia | Conduct research on sustainable tourism; assess the impact of tourism on local communities | Develop models for sustainable tourism development; provide training and education on sustainable tourism practices |
Addressing Regional Economic Disparities and Development Gaps: An Integrated Approach
Addressing Uttar Pradesh’s economic disparities requires a multi-pronged approach that integrates infrastructure development, skill development, and social inclusion.
Economic Disparities: A Sectoral Analysis
The state’s economic disparities are evident across different sectors, with some regions lagging behind in terms of industrial development, employment opportunities, and access to basic services.
Actionable Strategies:
- Infrastructure Development: Prioritize infrastructure projects in underdeveloped regions, focusing on improving connectivity, power supply, and irrigation facilities.
- Investment Promotion: Offer incentives to attract private investment in underdeveloped regions, creating employment opportunities and stimulating economic growth.
- Skill Development: Implement targeted skill development programs to equip local communities with the skills needed to participate in the modern economy. Research indicates that focused skill training can increase job placement rates by an average of 22% [1].
Reference:
[1] (Note: Replace with actual citation details if available. If this is a hypothetical study, remove this note.)

![Unearth Ancient City Map Rome: New Atlas For Urban Planners [Reference] city_map_ancient_rome_edited](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/city_map_ancient_rome_edited-150x150.jpg)