Dive into the captivating history of the internet in our article, [- A History of the Internet in a Nutshell: Unraveling the Evolution of the Digital World]. Discover the pioneering moments, groundbreaking innovations, and influential figures that shaped the digital landscape we know today. From the inception of the World Wide Web to the rise of social media, explore the remarkable journey of the internet and its profound impact on our societies, cultures, and economies.
Key Takeaways:
The internet’s roots can be traced back to the 1950s and 1960s, when scientists and engineers developed computer networks for communication and research.
The first successful message over the internet was sent in 1969 between two computers at UCLA and Stanford Research Institute.
The internet took shape in the 1970s and 1980s with the development of email, Usenet newsgroups, and the World Wide Web.
The commercialization of the internet in the 1990s led to a surge in usage and the development of new technologies like e-commerce, online banking, and social media.
The internet’s evolution has continued in the 21st century with the rise of mobile devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
History Of The Internet In A Nutshell
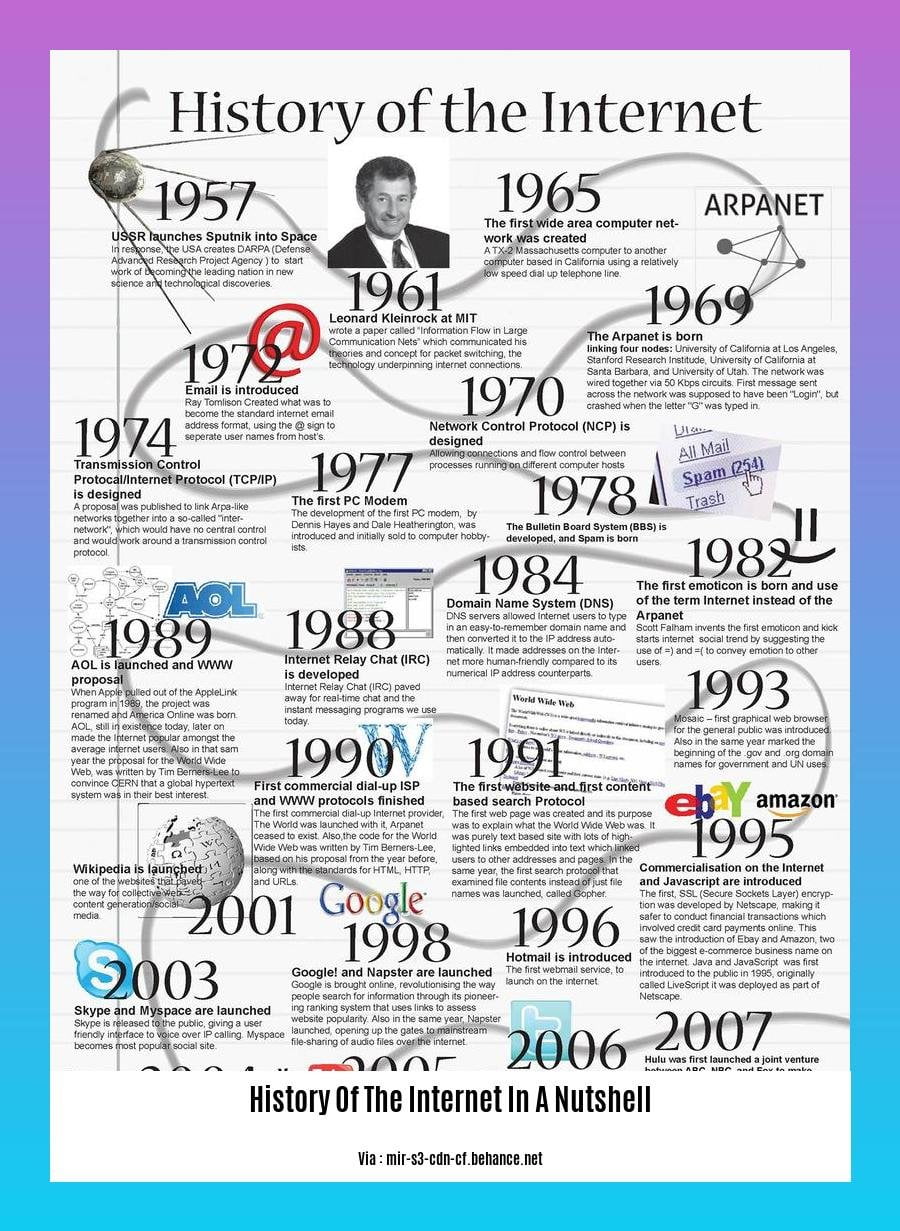
From humble beginnings in the mid-20th century to its current status as an indispensable global network, the history of the internet is a fascinating tale of innovation, collaboration, and societal transformation.
The Early Days: A Network’s Genesis
The origins of the internet can be traced back to the 1950s and 1960s, when scientists and engineers sought to develop computer networks for communication and research purposes. In 1969, the first successful message was transmitted over the ARPANET, a network developed by the US Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). This marked a pivotal moment in the development of the internet.
The 1970s and 1980s: Paving the Way for the World Wide Web
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed significant advancements in networking technology. Email, Usenet newsgroups, and the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) suite were born during this period, laying the foundation for the interconnected global network we know today.
The 1990s: The Internet Goes Mainstream
The commercialization of the internet in the 1990s marked a turning point in its history. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) emerged, making the internet accessible to businesses and households. This era also saw the advent of web browsers, notably Mosaic and Netscape Navigator, which made navigating the World Wide Web an intuitive experience.
The 21st Century: A Digital Revolution
The 21st century has witnessed the exponential growth of the internet. Mobile devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have transformed how we interact with the digital world. Social media platforms, e-commerce, and online streaming services have become ubiquitous, revolutionizing communication, business, and entertainment.
The Internet’s Impact: A Double-Edged Sword
The internet has undoubtedly revolutionized our lives. It has fostered global connectivity, democratized information access, and empowered businesses and individuals alike. However, it has also brought forth challenges, including concerns about data privacy, misinformation, and the digital divide.
The history of the internet is an ongoing narrative, filled with twists, turns, and constant evolution. As technology continues to progress, we can expect the internet to continue shaping our world in profound ways.
Witness the evolution of technology through ages in the history of the internet and wifi, from its humble beginnings to its modern-day omnipresence.
Dive into the annals of the internet and social media in our comprehensive History Of The Internet and Social Media, chronicling the rise of virtual connectivity and its impact on our world.
Embark on a journey through time as we explore the History of the Internet in the 2000s, an era marked by groundbreaking innovations and a surge in global connectivity.
Delve into the captivating History of Internet Access, tracing its roots from dial-up modems to high-speed broadband, and witnessing the transformative impact on information exchange.
Explore the definitive resource on the History Of The Internet Wikipedia, an exhaustive exploration of the origins, evolution, and cultural significance of the internet, curated by a global community of knowledge seekers.
The Dot-Com Boom and Bust: A Tale of Innovation, Excess, and Transformation

Imagine a time when the internet wasn’t a household staple but a promising frontier, brimming with possibilities. The 1990s witnessed a phenomenon that forever changed the landscape of technology and business: the dot-com boom.
Key Takeaways:
The dot-com boom was a period of rapid growth and investment in internet-based companies during the late 1990s and early 2000s.
Fueled by the internet’s increasing popularity and widespread adoption, tech companies experienced a surge in valuations, often without substantial profits to back them up.
The speculative frenzy led to the rise of dot-com companies, many of which focused on e-commerce, internet services, and technology hardware.
Investors poured money into these companies, hoping to capitalize on the perceived limitless potential of the internet.
The dot-com bubble burst in the early 2000s, resulting in a sharp decline in stock prices of many tech companies, leading to significant financial losses for investors.
This period highlighted the risks associated with investing in emerging industries and the importance of careful evaluation before making investment decisions.
The Rise of Dot-Com Companies:
The dot-com boom was characterized by the emergence of numerous internet-based companies, often referred to as dot-coms. These companies ranged from online retailers and search engines to social media platforms and e-commerce businesses.
With the rapidly growing internet user base, dot-coms saw a massive influx of investment and attention. Investors, eager to be a part of the digital revolution, flocked to these companies, driving up their valuations to astronomical levels.
The Speculative Frenzy:
The dot-com boom was fueled by a speculative frenzy, where investors disregarded traditional valuation metrics and placed their bets on the future potential of these internet companies. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) of dot-coms were highly sought-after, with investors hoping to get a piece of the seemingly endless pie.
This speculative behavior led to unrealistic valuations and unsustainable growth, setting the stage for the inevitable market correction that followed.
The Dot-Com Bubble Bursts:
The unsustainable growth and speculative nature of the dot-com boom could not be sustained indefinitely. In the early 2000s, the bubble burst, resulting in a sharp decline in the stock prices of many dot-com companies.
Several factors contributed to the bursting of the bubble, including the lack of profitability of many dot-coms, the rising interest rates by the Federal Reserve, and the aftermath of the 9/11 terrorist attacks.
The bursting of the dot-com bubble had a significant impact on the global economy, leading to job losses, financial instability, and a loss of confidence in the tech industry. However, it also served as a cautionary tale, highlighting the importance of prudent investment decisions and the inherent risks associated with investing in emerging industries.
Lessons Learned:
The dot-com boom and bust left a lasting legacy, shaping the way we view technology investments and market valuations. It underscored the importance of careful analysis, realistic expectations, and the need for sustainable business models in the tech industry.
The lessons learned from this period continue to guide investors and entrepreneurs today, reminding them of the cyclical nature of markets and the importance of balancing innovation with sound financial practices.
Sources:
Dot-Com Bubble Explained | Story of 1995-2000 Stock Market – Finbold
The Dot-Com Bubble – CHM Revolution
The evolution of social media and Web 2.0: The emergence of platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube, and the shift towards user-generated content and social interaction.
In the early days of the internet, websites were static and one-directional. Users could only consume content, not create it. But with the advent of social media and Web 2.0, that all changed.
Key Takeaways:
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube have revolutionized the way people communicate and interact with each other.
Web 2.0 has empowered users to create and share their own content, leading to a more interactive and dynamic online experience.
User-generated content has become a powerful force in shaping public opinion and driving online trends.
Social media platforms allow users to connect with friends and family, share photos and videos, and express their opinions on a variety of topics. They have also become powerful tools for businesses to reach and engage with customers.
Web 2.0 is a term used to describe the second generation of the internet, which is characterized by user-generated content, social networking, and the ability for users to interact with each other. Web 2.0 has made the internet a much more dynamic and interactive place, and it has led to the rise of new forms of online entertainment and communication.
User-generated content has become a major part of the online experience. People now share everything from photos and videos to blog posts and podcasts. This content can be a valuable source of information and entertainment, and it can also help to connect people with similar interests.
The evolution of social media and Web 2.0 has had a profound impact on the way we live our lives. It has changed the way we communicate, the way we consume information, and the way we interact with businesses. It has also led to the rise of new industries and the creation of new jobs.
Sources
The Evolution of Social Media | Pew Research Center
Web 2.0: A New Wave of Innovation for Teaching and Learning | Edutopia
The Internet of Things and the future of connectivity: The growing network of physical devices connected to the Internet and the impact on various industries and aspects of daily life.
As we look into the crystal ball of technological advancements, the Internet of Things (IoT) gleams as a radiant star. Let’s venture into a world where physical devices intertwine with the digital realm, reshaping our industries and transforming daily life.
Key Takeaways:
IoT encompasses a vast array of interconnected devices equipped with sensors, software, and internet connectivity. These devices seamlessly gather, transmit, and process data to automate tasks, enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and create intelligent environments.
IoT’s impact spans numerous industries, including healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and energy. This interconnected ecosystem fosters automation, remote monitoring, real-time analytics, and enhanced customer experiences. Imagine smart homes that adjust lighting and temperature based on your preferences, or self-driving cars communicating with traffic systems to optimize commutes.
IoT can revolutionize healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring, wearable health trackers, and AI-powered diagnostics. These innovations empower individuals to take proactive control of their health and facilitate timely interventions by healthcare providers.
IoT’s integration into agriculture promises increased crop yields, efficient water management, and precision farming techniques. Farmers can monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health in real-time, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing environmental impact.
Manufacturing embraces IoT to streamline production processes. Factory floors equipped with smart sensors can identify inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, and optimize supply chains. This results in enhanced productivity, reduced downtime, and improved product quality.
IoT’s potential in the energy sector lies in smart grids, smart meters, and energy-saving devices. These technologies optimize energy distribution, reduce wastage, and enable consumers to make informed choices about their energy consumption.
As we delve deeper into the realm of IoT, challenges emerge. Security concerns loom as the sheer number of interconnected devices expands the attack surface. Ensuring the privacy and integrity of sensitive data becomes paramount. Balancing convenience with data protection will be a delicate dance.
The digital divide, a persistent issue in the realm of connectivity, poses a challenge to IoT’s widespread adoption. Narrowing this gap will require concerted efforts from governments, telecom providers, and community initiatives to ensure equitable access to IoT’s benefits.
Conclusion:
The Internet of Things is poised to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us. With its transformative potential across industries and aspects of daily life, IoT holds the key to a future where connectivity and intelligence seamlessly blend to enhance our experiences and empower us in unprecedented ways.
Source:
– What is IoT and How Does it Work? – Oracle
– How IoT Is Changing Industries for the Better | SAS
FAQ
Q1. How did the internet come into existence?
A1. The internet’s origins can be traced back to the 1950s and 1960s when scientists and engineers developed computer networks to promote communication and research.
Q2. What marked the beginning of the internet as we know it today?
A2. The first successful message over the internet was sent in 1969 between two computers at UCLA and Stanford Research Institute, laying the foundation for the modern internet.
Q3. What were the key factors driving the growth of the internet in the 1970s and 1980s?
A3. The development of email, Usenet newsgroups, and the World Wide Web in the 1970s and 1980s fueled the internet’s growth and set the stage for its widespread adoption.
Q4. When did the internet become a commercialized entity, and what were the consequences?
A4. The commercialization of the internet in the 1990s led to a surge in internet usage and the development of new technologies and services like e-commerce, online banking, and social media.
Q5. How has the internet evolved in recent years, and what are its current applications?
A5. The 21st century has witnessed the rapid evolution of the internet, marked by the rise of mobile devices, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), which have transformed communication, business, and everyday life.
- Crypto Quotes’ Red Flags: Avoid Costly Mistakes - June 30, 2025
- Unlock Inspirational Crypto Quotes: Future Predictions - June 30, 2025
- Famous Bitcoin Quotes: A Deep Dive into Crypto’s History - June 30, 2025





![A Journey Through the History of Computing: From Its Humble Origins to Modern Innovations [history of computing ss1] history-of-computing-ss1_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/history-of-computing-ss1_2-150x150.jpg)










