Embark on an extraordinary journey through the annals of computing history in [A Journey Through the History of Computing: From Its Humble Origins to Modern Innovations [history of computing ss1]] , a comprehensive narrative that unveils the fascinating evolution of computational technology. From the rudimentary mechanical marvels of the early days to the cutting-edge digital wonders of today, this exploration delves into the key milestones, influential figures, and cultural impacts that have shaped the world we live in.
Key Takeaways:
- Computing devices have evolved from ancient devices like the tally stick to modern computers.
- The abacus, slide rule, and steam engine were other early computing devices.
- The development of the computer in the late 19th and early 20th centuries revolutionized computing.
- ENIAC, developed in 1946, was the first computer.
- Transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and microprocessors led to smaller, more powerful, and more affordable computers.
- The development of the internet and the World Wide Web in the 1990s transformed communication and information sharing.
The History of Computing: From Ancient Roots to Modern Innovations

The evolution of computing, from its rudimentary beginnings to the sophisticated technology that permeates our daily lives, is a journey steeped in ingenuity, innovation, and a relentless pursuit of problem-solving. From the humble origins of tally sticks and abacuses to the advent of the internet and artificial intelligence, the history of computing is an epic narrative of human endeavor and technological revolution.
Evolution of Computing Devices
Ancient Calculators:
Tally sticks: The earliest known computing device, used since prehistoric times for record-keeping.
Abacus: A manual calculating tool using beads strung on rods, originating in ancient Mesopotamia.
Mechanical Devices:
Slide rule: A mechanical calculator for performing mathematical operations like multiplication and division, invented in the 17th century.
Difference engine: A mechanical computer designed by Charles Babbage in the 19th century to automate polynomial calculations.
Electromechanical Computers:
Analytical engine: A more advanced mechanical computer proposed by Charles Babbage, capable of performing complex mathematical operations.
- Mark I: The first electromechanical computer, built by Howard Aiken in the 1940s, used electromagnetic relays for calculations.
Electronic Computers:
Early Electronic Computers:
ENIAC: The first fully electronic computer, developed in 1946, was capable of performing complex calculations at speeds never before seen.
UNIVAC: The first commercial electronic computer, introduced in 1951, was used for business and scientific applications.
Transistors and Integrated Circuits:
Transistors: Miniaturized electronic switches that replaced vacuum tubes in computers, leading to smaller and more efficient machines.
Integrated circuits (ICs): Miniaturized electronic circuits containing transistors and other components, revolutionizing computer design.
Personal Computers:
Microprocessors: The invention of microprocessors, like the Intel 4004, made it possible to build affordable personal computers.
- IBM PC: The introduction of the IBM Personal Computer in 1981 marked the beginning of the PC revolution, making computing accessible to the masses.
The Internet and Beyond:
The Internet:
ARPANET: The precursor to the internet, developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1960s, linked computers for research and military purposes.
World Wide Web: The development of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 revolutionized communication and information sharing.
Mobile Computing:
Smartphones: The convergence of mobile phones and computing power led to the rise of smartphones, enabling a wide range of tasks on the go.
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing: The concept of storing and accessing data and applications over the internet, rather than on local devices, has transformed how we use computing resources.
Conclusion
The history of computing is a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of innovation. From ancient calculators to modern supercomputers, the evolution of computing has shaped our world in profound ways. Today, computing technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and transforming every aspect of our lives. The future of computing holds even more promise, with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and the Internet of Things poised to revolutionize the way we interact with the world around us.
Interested in tracing the evolution of computing from its humble origins to the sleek devices we carry today? Explore the fascinating history of computers for primary 2, and delve into an illuminating journey through the ages.
From the ancient abacus to the groundbreaking era of smartphones, discover the incredible history of computers from abacus to smartphone . Unravel the pivotal innovations and trailblazers who shaped the digital landscape.
Want to know the remarkable history of computers in Tamil? Immerse yourself in the rich narrative of computing in Tamil and uncover the significant contributions made by Tamil pioneers in this field.
The Role of Computing in Major Historical Events
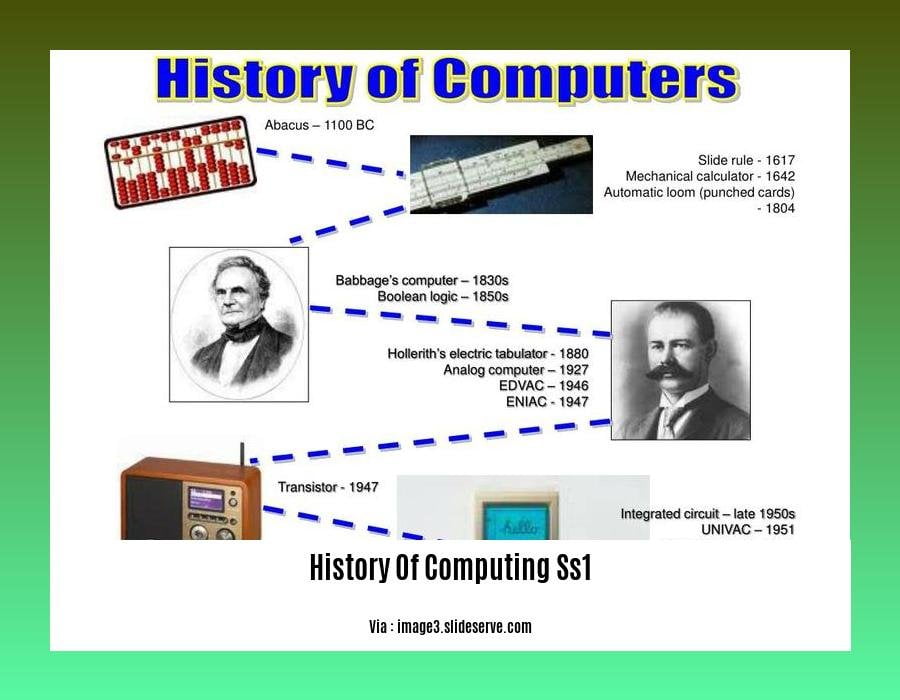
Early computing devices, like abacuses and slide rules, aided humans in record-keeping and intricate calculations, setting the stage for more complex machines.
Konrad Zuse’s creation of the Z3, the first fully functional digital computer, marked a pivotal moment in computing history. World War II’s influence on code-breaking efforts accelerated the development of electromechanical computers like the Colossus, underscoring computing’s role in warfare.
The ENIAC and UNIVAC machines heralded the era of electronic digital computers. These massive machines aided in complex calculations for scientific research and government projects, revolutionizing fields like meteorology and nuclear physics.
The invention of transistors and integrated circuits miniaturized computer components, paving the way for smaller, more powerful personal computers. The PC revolution in the 1970s democratized computing, making it accessible to individuals and small businesses.
The advent of the internet, fueled by ARPANET and the World Wide Web, connected computers globally, transforming communication, information sharing, and global collaboration.
The rise of mobile computing, exemplified by smartphones, made computing truly portable, enabling a wide range of tasks on the go, from communication to entertainment and productivity.
Cloud computing further revolutionized resource usage by allowing data and applications to be accessed over the internet, reducing the need for local storage and enhancing scalability.
Key Takeaways:
- Early computing devices aided in record-keeping and calculations.
- Electromechanical computers like the Colossus played a crucial role in World War II’s code-breaking efforts.
- Electronic digital computers like ENIAC and UNIVAC revolutionized scientific research and government projects.
- The invention of transistors and integrated circuits miniaturized computer components, leading to the PC revolution.
- The internet connected computers globally, transforming communication, information sharing, and collaboration.
- Mobile computing made computing portable, enabling various tasks on the go.
- Cloud computing revolutionized resource usage by allowing data and applications to be accessed over the internet.
Sources:
The impact of computing on society and culture
Computers have become an intricate part of our lives, influencing us in ways we may not even realize. Society’s journey from relying on physical calculators to embracing the digital realm is a story of how technology has evolved to accommodate our need to share and process information more easily.
From the invention of the printing press to the rise of the internet, technology has always played an instrumental role in driving cultural shifts. In the realm of computing, this influence is even more profound, reaching into the very fabric of society and transforming almost every aspect of our lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Computing technology has democratized culture.
- Dynamic and interconnected digital information encourages creation and sharing.
- Computers made information more accessible, enabling us to learn and experience more.
- They have strengthened global ties and forged new communities around shared interests.
- Technology has led to the emergence of new forms of entertainment and art.
Digital Revolution and Cultural Transformation:
The digital revolution has transformed how we create, share, and consume information. Traditional static and passive media, such as books and paintings, have given way to dynamic and interconnected digital information. The internet has democratized culture, allowing individuals to create and share content like never before. This cultural shift has also led to the emergence of new forms of entertainment and art, such as video games, digital art, and online performances.
Computing and Globalization:
Computing has played a major role in shrinking the world. With the rise of the internet, we can now stay connected with friends and family across the globe. Social media platforms have fostered global communities and facilitated conversations around shared interests. Cultural exchanges have become easier, promoting understanding and tolerance among people from different backgrounds.
Balancing Act: Preserving Tradition in a Digital World:
While computing has enriched our lives in many ways, it has also presented challenges in preserving traditional cultural practices. As we move towards a digital-first world, the question of how to balance the preservation of traditional culture while embracing technological advancements becomes increasingly relevant.
In conclusion, computing technology’s impact on society and culture has been profound. It has democratized culture, fueled globalization, and transformed the way we create, share, and experience information and art. As technology continues to advance, we must navigate the challenges and opportunities it presents, ensuring that cultural heritage is preserved while embracing the benefits of the digital age.
Sources:
[^1^]: Cultural consequences of computing technology
[^2^]: The impact of computing technology from a cultural perspective
The Future of Computing
Welcome to the realm of computing, where innovation knows no bounds, and the future unfolds a tapestry of possibilities. In this continuously evolving landscape, where advancements emerge at an ever-increasing pace, let’s peer into the crystal ball and explore the thrilling prospects that await us.
Key Takeaways:
Ubiquitous Computing: Technology will become an intrinsic part of our everyday lives, seamlessly blended into our environment, providing assistance and connectivity without conscious effort.
Quantum Supremacy: Harnessing the power of qubits, computers will break through computational barriers, enabling rapid drug discovery, complex financial simulations, and groundbreaking scientific research.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Blending the digital and physical worlds, these technologies promise immersive experiences in gaming, education, healthcare, entertainment, and more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Machines will learn, adapt, and make informed decisions, enhancing productivity, efficiency, and personalization across various industries.
Brain-computer Interfaces (BCIs): A direct link between the human brain and computers will enable intuitive control, enhanced communication, and even the restoration of lost abilities.
The Internet of Things (IoT): A vast network of interconnected devices will revolutionize industries, create smart cities, and empower individuals with unprecedented control over their surroundings.
Fusion Energy: By harnessing the power of nuclear fusion, we could potentially solve the world’s energy crisis, paving the way for sustainable computing and technological advancements.
Personalized Medicine: Genetic sequencing and data analytics will lead to tailored treatments, therapies, and preventive measures, revolutionizing healthcare.
Space Colonization: As we venture beyond Earth, computing will play a pivotal role in supporting life in extraterrestrial environments, enabling communication, navigation, and resource management.
Cybersecurity and Privacy: Enhanced security measures will safeguard our digital lives, protecting data, preventing cyberattacks, and ensuring privacy in the face of evolving threats.
The future of computing is an exciting frontier, where the boundaries of innovation are constantly pushed, and technological advancements continue to transform our world in unprecedented ways. As we embrace these emerging possibilities, let’s navigate the digital landscape with curiosity, adaptability, and a sense of wonder, for the journey ahead promises to be nothing short of extraordinary.
Sources:
The Future of Computing: 10 Breakthrough Technologies That Will Change the World
10 Predictions for the Future of Computing
FAQ
Q1: What were some of the earliest computing devices?
A1: Ancient civilizations used tools like the tally stick to track records and count. The abacus, the slide rule, and the steam engine are also considered early computing devices.
Q2: When was the first computer developed?
A2: The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) was created in 1946 and is acknowledged as the initial computer.
Q3: What impact has computing technology had on our lives?
A3: Computing technology has revolutionized various aspects of our lives, significantly impacting industries such as research, education, government, and scientific medicine. It has also transformed how people communicate and access information.
Q4: Can you provide some examples of the cultural impact of computing technology?
A4: Computing technology has democratized culture by enabling individuals to create and share information effortlessly. It has transformed static and passive traditional representation media into dynamic and interconnected digital information.
Q5: How did the transition from “computing machine” to “computer” occur?
A5: During the late 1940s and early 1950s, with the advent of electronic and digital computing machines, the terminology shifted from “computing machine” to “computer.”












