Step into the global arena, where ideas, trends, and events intertwine, shaping our interconnected world. Join an experienced journalist specializing in international affairs as we decipher the enigmatic patterns of global spread. Through expert analysis and immersive storytelling [- Deciphering the Global Spread: A Journalist’s Perspective on Interconnectedness], we unravel the intricate web of forces that drive global phenomena, providing insights into how our world is inextricably linked.
Key Takeaways:
- COVID-19 has had a global impact, infecting and killing millions worldwide.
- The virus has spread rapidly across borders, with the Omicron variant becoming dominant.
- Socio-economic and environmental factors have influenced the spread of the virus.
- The pandemic is ongoing, and new variants continue to emerge.
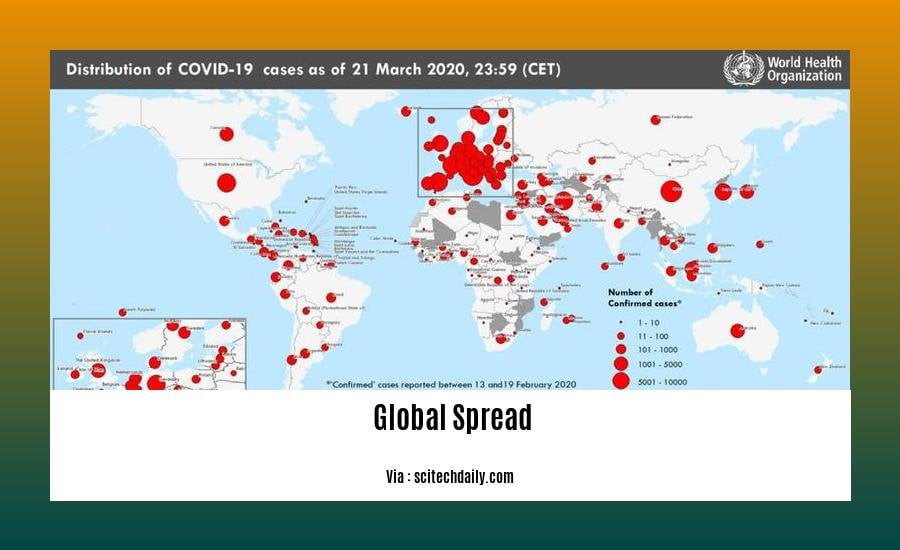
Global Spread

The interconnectedness of our world has been made abundantly clear with the global spread of COVID-19 and its variants. From its origin in China to its subsequent presence in every corner of the globe, this virus has laid bare the complexities and consequences of global spread.
A multitude of factors have contributed to the global spread of COVID-19:
-
Unrestricted Travel: The ease and frequency of international travel have played a significant role in the virus’s ability to spread rapidly across borders, carried by infected individuals.
-
Global Trade: The interconnectedness of global supply chains has facilitated the movement of goods and people, unknowingly transporting the virus to new regions.
-
Socioeconomic Factors: Socioeconomic disparities have exacerbated the global spread of COVID-19. Overcrowded living conditions, lack of access to healthcare, and limited resources have made containment efforts challenging in vulnerable communities.
-
Environmental Factors: Climate change has disrupted ecosystems and increased human-animal interactions, creating opportunities for zoonotic diseases, like COVID-19, to emerge and spread.
The global spread of COVID-19 has had wide-ranging consequences:
-
Health Impacts: The virus has caused millions of illnesses and deaths worldwide, straining healthcare systems and economies.
-
Economic Disruption: Lockdowns and travel restrictions have disrupted businesses, supply chains, and livelihoods, leading to economic downturns.
-
Social Impact: The pandemic has taken a toll on mental health, disrupted education, and widened social inequalities.
Understanding the factors driving global spread is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent or mitigate future pandemics. Collaboration among nations, strengthening healthcare systems, and addressing socioeconomic disparities are essential steps in combating global spread and safeguarding global health.
To understand the evolution of basketball, delve into the history of basketball and uncover its humble beginnings. Discover the ingenious invention of basketball by James Naismith and how it revolutionized the sports world. Additionally, explore the pivotal moment when the NBA was formed, shaping the future of professional basketball.
Analyzing the role of cultural exchange and migration in shaping global trends

A Journalist’s Perspective on Interconnectedness
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, it’s evident that cross-cultural exchange and migration have [Analyzing the role of cultural exchange and migration in shaping global trends] on global trends.
Cultural Differences and Migration Patterns
Cultural differences play a significant role in shaping migration decisions. People tend to migrate towards nations with cultural similarities, like language or religion. These shared cultural traits create a sense of belonging and facilitate adaptation to the new environment.
Measuring Cultural Proximity and Migration
Accurately measuring cultural proximity is crucial for understanding its impact on migration. Common proxies like language or religion assume cultural proximity remains constant over time, which is not always accurate. By incorporating other proxies, such as trade in cultural goods, we can mitigate measurement error and gain a more accurate understanding.
The Time-Varying Element in Cultural Proximity
Cultural proximity can change over time. Advances in communication and transportation have made it easier to share and adopt different cultural values. This time-varying component of cultural proximity can significantly influence migration patterns.
Migrants as Catalysts of Cultural Change
Migrants not only adapt to new cultures but also bring their own influences. They mix and change the cultural fabric of host societies, introducing new values, norms, and traditions. This reciprocal exchange fosters cultural diversity and transformation.
Key Takeaways:
- Cultural differences influence migration decisions and patterns.
- Accurate measurement of cultural proximity is crucial for understanding its impact on migration.
- Cultural proximity can vary over time, affecting migration patterns.
- Migrants play a pivotal role in shaping culture through exchange and dissemination.
Relevant URL Sources:
Exploring the influence of globalization on the spread of ideas and values
Cultural Globalization: Key Points As the world grows more interconnected, the spread of ideas, values, and cultural practices across borders is becoming increasingly prevalent. This phenomenon, known as cultural globalization, has significant implications for societies worldwide.
Key Characteristics of Cultural Globalization
– Increased cross-cultural interactions and communication.
– Adoption and integration of foreign cultural elements into existing cultures.
– Intensification of cultural exchange and dissemination of ideas.
Impact of Cultural Globalization on Culture
1. Cultural Imperialism vs. Cultural Sharing: Globalization has led to increased exposure to diverse cultural influences. However, it’s crucial to distinguish between the dominance of one culture over others (cultural imperialism) and the equitable exchange of ideas (cultural sharing).
2. Cultural Homogenization: While globalization exposes cultures to global influences, it does not necessarily lead to a single, worldwide culture. Instead, it fosters cultural diversity and the coexistence of multiple cultural expressions.
Key Takeaways:
- Globalization has accelerated the spread of ideas and values across national borders, fostering cross-cultural interactions and exchange.
- Cultural globalization is characterized by increased social interactions, technological adoption, and intensified cultural exchange.
- The impact of globalization on culture is multifaceted, encompassing both cultural imperialism and cultural sharing, as well as the potential for homogenization and diversity.
Sources:
– Globalization and Culture | SpringerLink [link]
– Cultural globalization | Britannica [link]
Discussing the Challenges and Opportunities Presented by the Global Spread of Phenomena
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, we’ve witnessed the rapid spread of ideas, trends, and events across borders. From the devastating COVID-19 pandemic to the urgent threat of climate change, global phenomena have become a defining feature of our time.
Challenges
Global Crises and Health Emergencies:
Pandemics spread rapidly due to international travel and globalization. The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the interconnectedness of global health systems, highlighting the urgent need for international collaboration and a robust response network.
Climate Change Impacts:
The consequences of climate change are felt worldwide, regardless of a country’s contribution to emissions. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and food security challenges pose significant risks to communities across the globe.
Opportunities
Collaboration and Innovation:
Global crises present opportunities for collaboration among countries and organizations. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the development of vaccines, testing methods, and treatment protocols, showcasing the benefits of international cooperation.
Shared Solutions:
Addressing global challenges can lead to shared solutions. The lessons learned from containing COVID-19 can be applied to mitigating the impacts of climate change, such as developing early warning systems and investing in sustainable infrastructure.
Key Takeaways:
- Global phenomena pose both challenges and opportunities that require a collective response.
- International collaboration and data sharing are crucial for tackling global crises and mitigating risks.
- Shared solutions emerging from global challenges can have lasting positive impacts on society.
Relevant URL Sources:
- Climate Change and COVID-19: Global Challenges and Opportunities
- COVID-19 Pandemic, Global Spread, Issues, and Challenges
FAQ
Q1: How has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced global interconnectedness?
Q2: What role have cultural differences played in the global spread of COVID-19?
Q3: How does cultural globalization affect the transmission of ideas and cultural practices around the world?
Q4: What are the key challenges posed by the global spread of COVID-19?
Q5: What opportunities exist for addressing both COVID-19 and climate change crises through collaboration and innovation?
- Unveiling the Enigma: Mansoureh Khojasteh Bagherzadeh’s Public Appearances & Private Life in Iran - July 18, 2025
- Unveiling the Mystery: Mansoureh Khojasteh Bagherzadeh’s Husband: A Rare Glimpse into a Private Life - July 18, 2025
- Unveiling Masoud Khamenei’s Mother: Power, Influence, and Iran’s Future - July 18, 2025