In today’s rapidly interconnected world, the global spread of ideas, technologies, and challenges has become an undeniable force shaping our societies. As boundaries blur and communication channels expand, we find ourselves navigating a complex web of interconnectedness, where the exchange of knowledge, innovation, and adversity transcends geographical borders. From the dissemination of scientific discoveries to the proliferation of social movements, from the adoption of emerging technologies to the challenges of global crises, the global spread profoundly influences our lives. Understanding its dynamics and implications is crucial for navigating the complexities of this interconnected world.
Key Takeaways:
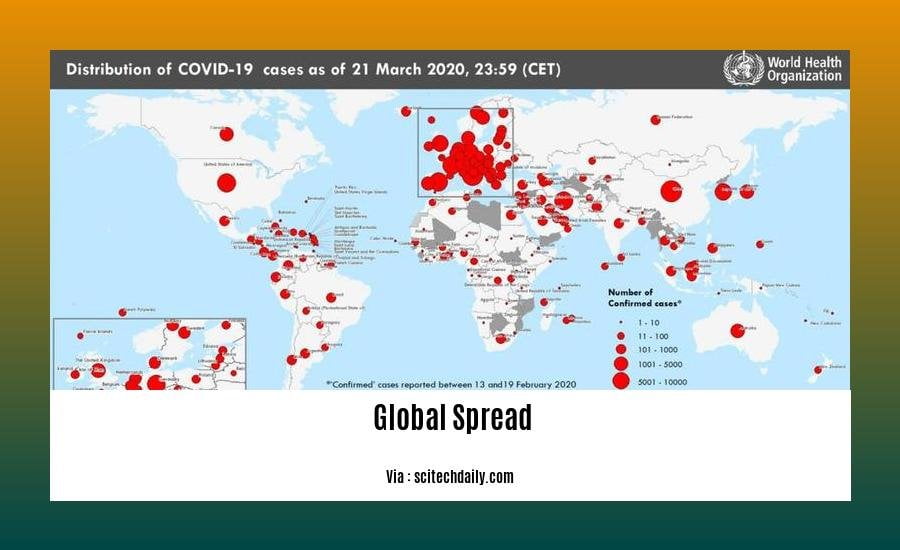
- Global COVID-19 cases rose in January 2022, while deaths remained stable.
- Over 500 million people have been infected with COVID-19 since early 2020, and new variants continue to emerge.
- The Omicron variant of COVID-19 spread rapidly worldwide in late 2021.
- Factors contributing to the uneven global distribution of COVID-19 include differing country policies, healthcare systems, and social factors.
The Global Spread of Ideas, Technologies, and Challenges

The global spread of ideas, technologies, and challenges has profoundly impacted our world. Let’s explore how interconnectedness, trade, and migration have shaped our societies:
Ideas
Ideas spread rapidly through the internet, social media, and global travel. This has fostered an exchange of perspectives, leading to both cultural enrichment and heightened awareness of global issues.
Technologies
Technological advancements, such as smartphones and artificial intelligence, have globally spread, connecting people and facilitating the flow of information and products. While it has improved our lives, it has also raised concerns about privacy and technological inequality.
Challenges
The global spread also comes with challenges. Uneven distribution of resources, disparities in healthcare systems, and climate change pose threats to human development. Addressing these issues requires global cooperation and equitable solutions.
Case in Point: COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic vividly illustrates the global spread of challenges. The virus spread rapidly, exposing weaknesses in healthcare systems and highlighting the importance of international coordination.
The Way Forward
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, we must navigate the global spread of ideas, technologies, and challenges with wisdom and collaboration. By understanding these interconnected dynamics, we can harness the benefits and mitigate the risks to create a more equitable and sustainable world.
- Learn the fascinating history of pizza and its origins in Naples, Italy. Find out how pizza became a beloved food worldwide by discovering its journey through popular culture.
- History of Pizza
- Neapolitan Origins
- Pizza in Popular Culture
Migration patterns and their effects on societies
Migration has been a defining characteristic of human history, as people have always moved from one place to another in search of better opportunities or for escaping conflict. In recent decades, migration has become increasingly globalized, with people moving between countries on all continents.
Causes of Migration
There are many factors that drive people to migrate, including:
- Economic factors: People may migrate to find better jobs or higher wages.
- Political factors: People may migrate to escape war, persecution, or other forms of political instability.
- Environmental factors: People may migrate to escape natural disasters or climate change.
- Social factors: People may migrate to reunite with family or friends who have already migrated.
Impacts of Migration
Migration can have a significant impact on both the sending and receiving countries.
Sending countries
- Positive impacts: Migration can reduce population pressure, increase remittances, and foster the transfer of skills and knowledge.
- Negative impacts: Migration can lead to brain drain, as skilled workers leave the country in search of better opportunities. It can also disrupt social networks and community cohesion.
Receiving countries
- Positive impacts: Migration can boost the economy by providing labor, increasing consumer demand, and fostering innovation. It can also bring new cultures and ideas to the receiving country.
- Negative impacts: Migration can lead to social tensions, as migrants may compete with native-born workers for jobs and resources. It can also strain public services, such as schools and hospitals.
Key Takeaways:
- Migration is a complex phenomenon with both positive and negative impacts.
- The causes of migration are varied and include economic, political, environmental, and social factors.
- Migration can have a significant impact on both the sending and receiving countries.
Sources:
- International Migration: Trends, Determinants, and Policy Effects
- International Migration and Development: The Changing Impact of Migration
Spread of Technologies and Their Influence on Cultural Dynamics

In the interconnected world we live in, the spread of technologies has profoundly shaped cultural dynamics. From the printing press to the internet, technological advancements have spurred a constant evolution of societies, connecting people, ideas, and cultures in unprecedented ways.
Impact on Cultural Diffusion
Advancements in transportation, communication, and media have accelerated the spread of technologies across borders, facilitating the exchange of ideas and cultural practices. This has led to the diffusion of elements from one culture to another, resulting in a blending and diversification of cultural expressions.
For example, the introduction of smartphones in developing countries has provided access to global communication networks, allowing people to engage with different cultures and perspectives, influencing local customs and social norms.
Cultural Transformation
The spread of technologies has also led to cultural transformations within societies. For instance, the widespread adoption of social media platforms has fostered new forms of social interaction, reshaping communication patterns and the way people express themselves.
Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to further transform cultural dynamics by automating tasks, creating new employment opportunities, and challenging traditional ways of thinking.
Challenges and Opportunities
The spread of technologies presents both challenges and opportunities for cultural preservation and innovation. While it enables the exchange and appreciation of diverse cultural expressions, it can also lead to the erosion of local traditions and languages.
To navigate these challenges, it is crucial to foster cultural dialogue and promote the coexistence of different cultural perspectives. By harnessing the power of technology to connect people and ideas, we can create a more inclusive and vibrant global society.
Key Takeaways:
- Technological innovations accelerate cultural evolution and drive the exchange of ideas.
- The spread of technologies has facilitated the diffusion and blending of cultural practices.
- Advancements in communication and media have transformed social interaction and cultural expression.
- The spread of technologies presents both opportunities and challenges for cultural preservation and innovation.
- Balancing cultural exchange and preservation is essential for fostering a diverse and inclusive global society.
Relevant URL Sources:
- The Role of Technology in Cultural Diffusion: A Case Study of the Internet
- Technological Change and Cultural Dynamics: The Impact of the Internet on Cultural Diffusion and Transformation
The Emergence of Global Governance and its Challenges
Globalization has shattered barriers, redistributing power and influence across borders. Yet, this interconnectedness presents significant challenges to global governance.
The Rise of Non-State Actors
Multinational corporations, international organizations, and NGOs increasingly wield power on the world stage. However, their accountability and transparency remain unclear, posing challenges to democratic decision-making.
Inequality and Polarization
Economic disparities and political polarization weaken the social fabric and undermine global cooperation. Addressing inequality and fostering inclusiveness are essential for effective governance.
Climate Change and Terrorism
Transboundary issues like climate change and terrorism require collaborative responses. Global governance mechanisms must adapt to address these pressing challenges.
Collaboration and Trust
Effective global governance relies on cooperation among states, international organizations, and stakeholders. Trust and transparency are paramount to foster collaboration and address global challenges. Lack of trust in political leaders and partisan politics can hinder progress.
Key Takeaways:
- Non-state actors: Their growing influence requires clear accountability and transparency mechanisms.
- Inequality: Addressing economic disparities and fostering inclusiveness is crucial for global governance stability.
- Climate change and terrorism: Collaborative responses are essential for transboundary challenges.
- Collaboration: Effective governance requires trust, transparency, and cooperation among all stakeholders.
- Trust and legitimacy: Political leaders and governance mechanisms must foster trust to enhance legitimacy and global cooperation.
Relevant URL Sources:
- The Challenges of Global Governance
- The Future of Global Governance
FAQ
Q1: How has globalization impacted the spread of diseases like COVID-19?
A1: Globalization has facilitated the rapid spread of diseases like COVID-19 due to increased travel and interconnectedness. However, uneven spread may result from country-specific policies, healthcare systems, and social factors.
Q2: What are the main drivers behind the spread of technological innovations globally?
A2: Technological innovations spread through socio-psychological processes, network effects, and individual learning. Globalization has accelerated this spread, benefiting emerging markets and promoting knowledge flows.
Q3: How has globalization influenced migration patterns around the world?
A3: International migration has remained stable, with main migratory shifts being directional rather than global. Despite a decline in its overall impact, migration continues to play a significant role, with 34% of global migrants residing in industrialized countries.
Q4: What are the key challenges to effective global governance in the face of globalization?
A4: Globalization has shifted power dynamics, introducing challenges like non-state actors, inequality, climate change, and terrorism. Effective global governance requires collaboration and trust among states, international organizations, and stakeholders.
Q5: How has globalization impacted the interplay of sameness and difference in global culture?
A5: Globalization has fostered both cultural homogenization and diversification, creating tensions between sameness and difference. Cultural exchanges have influenced local traditions and values, while also preserving distinct cultural identities.
- Unveiling Bernhard Caesar Einstein’s Scientific Achievements: A Legacy in Engineering - July 15, 2025
- Uncover who is Jerry McSorley: CEO, Family Man, Business Success Story - July 15, 2025
- Discover Bernhard Caesar Einstein’s Scientific Contributions: Unveiling a Legacy Beyond Einstein - July 15, 2025