In the realm of healthcare, intravenous fluid therapy plays a pivotal role in ensuring optimal patient outcomes. [Advances in the Development of Intravenous Fluids: Formulations, Manufacturing, and Regulatory Considerations] explores the latest advancements in this field, providing invaluable insights into the development of innovative formulations, the intricacies of manufacturing processes, and the stringent regulatory frameworks that govern these lifesaving solutions.
Key Takeaways:
- IV fluids are essential for maintaining fluid balance in the body.
- Balanced crystalloids are increasingly used in IV fluid therapy.
- IV fluid administration should be monitored for effectiveness and potential side effects.
- Dehydration can have serious consequences, including organ failure and tissue damage.
- Excessive fluid intake can also be harmful.
Development of Intravenous Fluids: Innovations in Formulation, Manufacturing, and Regulation
Intravenous (IV) fluids play a critical role in healthcare, providing essential hydration and electrolyte balance to patients. Over the years, significant advancements have been made in the development of intravenous fluids to enhance their efficacy and safety.
Formulations: Tailoring to Clinical Needs
IV fluids are formulated with various electrolytes and nutrients to meet specific clinical requirements. Balanced crystalloids, such as lactated Ringer’s solution, have gained popularity due to their ability to closely mimic the body’s natural fluid composition.
Manufacturing: Ensuring Quality Standards
The manufacturing process of IV fluids adheres to stringent quality standards to guarantee sterility, safety, and consistency. Advanced filtration techniques and rigorous testing protocols ensure that fluids are free of contaminants and meet regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Considerations: Safeguarding Patient Well-being
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in overseeing the development of intravenous fluids to protect patient safety. They establish guidelines for formulation, manufacturing, and clinical trials to ensure that IV fluids are safe and effective.
Monitoring for Optimal Outcomes
IV fluid administration requires careful monitoring to assess clinical response and prevent adverse effects. Vital signs, urine output, and electrolyte levels should be closely observed to guide fluid management decisions.
Balanced Approach: Achieving Hydration Without Complications
Dehydration can lead to serious complications, but excessive fluid administration can also be detrimental. Healthcare providers must strike a balance between providing adequate hydration and avoiding fluid overload, which can strain the heart and kidneys.
Table: Key Considerations in the Development of Intravenous Fluids
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Formulation | Tailoring electrolyte composition to clinical needs |
| Manufacturing | Adhering to quality standards, ensuring sterility and purity |
| Regulation | Compliance with regulatory guidelines for safety and efficacy |
| Monitoring | Assessing clinical response and preventing adverse effects |
| Balance | Avoiding both dehydration and fluid overload |
If you are interested in learning more about New Zealand’s historical roots, don’t miss out on our history of New Zealand page.
For those fascinated by the rich traditions and culture of the indigenous Maori people, our Maori culture page offers an in-depth exploration.
If you want to delve into the impact of European colonization of New Zealand, be sure to visit our dedicated page.
To gain insights into New Zealand’s New Zealand in the 20th century and its role in shaping the nation’s present, explore our comprehensive article.
For a deeper understanding of intravenous therapies, their applications, and future prospects, check out our uses of intravenous therapy and the future of intravenous therapy pages.
Role of Intravenous Fluids in Critical Care
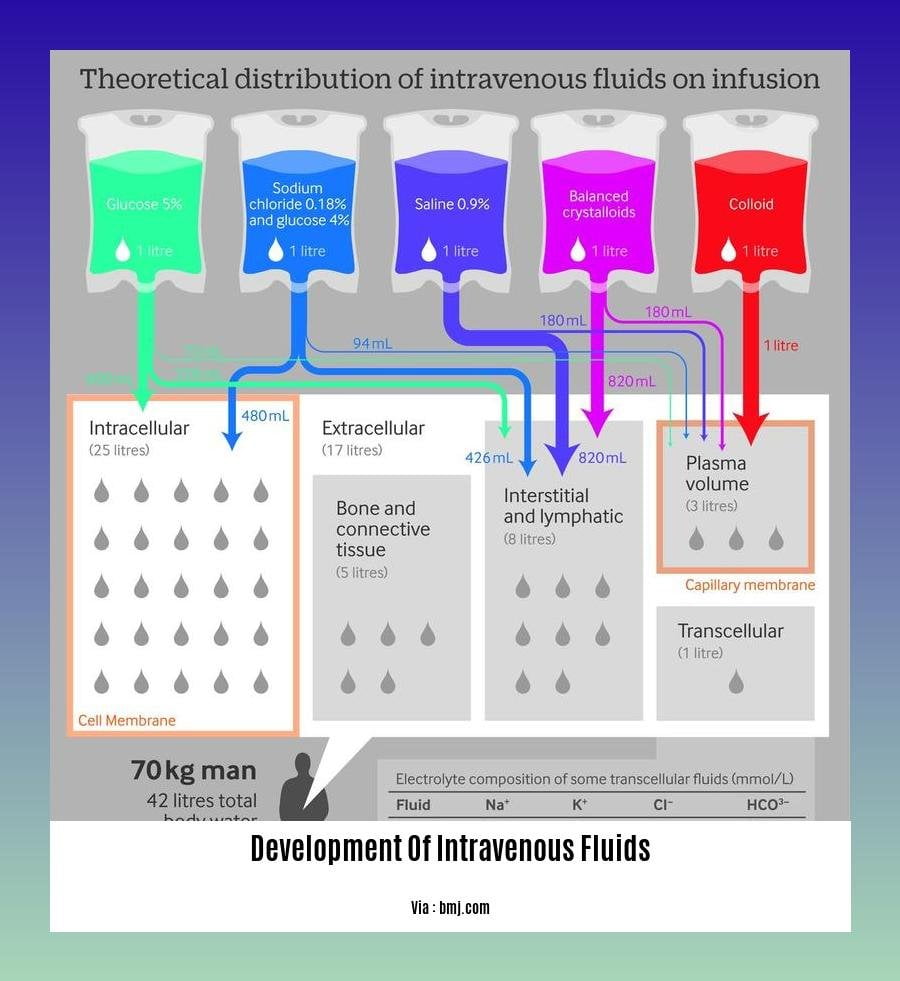
In essence, Intravenous (IV) fluids replenish lost fluids, electrolytes, and nutrients to maintain fluid balance and physiological functions. Their use in Critical Care is pivotal due to altered fluid distribution and accelerated volume losses in critically ill patients.
Indications for Intravenous Fluid Therapy
- Resuscitation: Replenishing fluids rapidly to restore circulation in emergencies.
- Maintenance: Providing fluids to meet ongoing physiological needs.
- Volume Expansion: Increasing intravascular volume to improve organ perfusion.
Key Considerations for Effective IV Fluid Management
- Evaluate Volume Status: Monitor vital signs, urine output, and electrolyte levels to assess fluid needs.
- Monitoring: Closely track fluid intake and output to adjust accordingly.
- Avoid Fluid Overload: Excessive fluid administration can lead to complications.
- Individualize Therapy: Tailor fluid therapy to each patient’s specific needs.
Types of Intravenous Fluids
- Crystalloids: Water-based solutions containing electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride.
- Colloids: Blood-volume expanders that stay in the bloodstream longer than crystalloids.
Key Takeaways:
- IV fluids play a crucial role in managing fluid balance in Critical Care.
- Indications include resuscitation, maintenance, and volume expansion.
- Evaluation of volume status and monitoring are essential for effective IV fluid management.
- Individualizing therapy and avoiding fluid overload are key considerations.
- Crystalloids and colloids are the two main types of IV fluids used.
Most Relevant Source:
- Intravenous Fluid Management in Critically Ill Adults: A Review
Regulatory Considerations and Quality Control
In the realm of healthcare, the safety and quality of intravenous (IV) fluids are of utmost importance. Regulatory Considerations and Quality Control play a critical role in ensuring that these fluids meet the highest standards.
Regulatory Compliance:
Stringent regulatory guidelines are in place to oversee the development, manufacturing, and distribution of IV fluids. These regulations aim to guarantee the safety, efficacy, and quality of these products. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, establish rigorous standards for the formulation, production, and testing of IV fluids. Compliance with these guidelines ensures that fluids meet the prescribed criteria and are safe for patient use.
Quality Control Measures:
Quality control measures are essential in every step of the IV fluid production process. From raw material sourcing to final packaging, manufacturers implement strict quality control protocols to ensure the integrity of the fluids. These measures include:
- Raw Material Inspection: Incoming raw materials undergo thorough inspections to meet established specifications.
- Process Validation: Manufacturing processes are validated to ensure consistent production of high-quality fluids.
- In-Process Testing: Samples are taken throughout the manufacturing process to monitor critical parameters like pH, osmolarity, and sterility.
- Final Product Testing: Finished IV fluids undergo rigorous testing to assess sterility, pyrogenicity, and other safety parameters before release for distribution.
Patient Safety:
The ultimate goal of regulatory compliance and quality control measures is to ensure the safety of patients who rely on IV fluids for various medical treatments. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers and healthcare providers can reduce the risk of adverse reactions and other complications associated with IV fluid administration.
Key Takeaways:
- Regulatory guidelines establish standards for IV fluid development, manufacturing, and distribution.
- Quality control measures ensure the safety and quality of IV fluids throughout the production process.
- Patient safety is the primary objective of regulatory considerations and quality control measures.
Most Relevant URL Source:
- Regulatory Considerations and Quality Control of Intravenous Fluids
Future Directions in Intravenous Fluid Therapy
As we delve into the future of intravenous (IV) fluid therapy, the focus shifts towards precision and personalization.
Tailored Therapies
Future Directions in Intravenous Fluid Therapy:
- Personalized Fluid Regimens: Developing tailored fluid regimens based on individual patient characteristics, such as age, weight, and co-morbidities.
- Targeted Delivery: Utilizing advanced drug delivery systems to deliver fluids directly to specific organs or tissues for targeted therapy.
Novel Formulations
- Bioengineered Fluids: Exploring bioengineered fluids that mimic the composition and properties of human plasma, reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
- Nanoparticle-Based Fluids: Developing nanoparticle-based fluids to enhance drug delivery, reduce side effects, and improve patient outcomes.
Advanced Monitoring and Control
- Real-Time Monitoring: Employing wearable devices and sensors to monitor fluid balance and electrolyte levels in real-time, enabling prompt adjustments.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Implementing closed-loop systems that automatically adjust fluid delivery based on patient data, ensuring optimal hydration.
Artificial Intelligence
- AI-Driven Fluid Management: Utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to analyze patient data and predict fluid needs, leading to more efficient and effective therapy.
- Virtual Reality Training: Employing virtual reality simulations to train healthcare professionals in advanced fluid management techniques, improving patient care.
Key Takeaways:
- Personalized fluid regimens will optimize therapy for individual patients.
- Novel formulations will enhance drug delivery, reduce side effects, and improve outcomes.
- Advanced monitoring and control systems will ensure optimal hydration and patient safety.
- AI and virtual reality will revolutionize fluid management training and decision-making.
Most Relevant URL Source:
FAQ
Q1: What are the key advancements in the development of intravenous fluids?
Q2: How has the manufacturing process of intravenous fluids evolved to ensure safety and efficacy?
Q3: What are the regulatory considerations involved in bringing new intravenous fluid formulations to the market?
Q4: How does the development of novel intravenous fluid formulations address specific clinical needs?
Q5: What are the latest trends and future directions in the field of intravenous fluid therapy?
- SYBAU See You Baby Meaning: Gen Z Slang Evolves - July 1, 2025
- Unlock Your Inner Youth: Lifestyle Secrets for a Vibrant Life - July 1, 2025
- Decode SYBAU Meaning: Gen Z Slang Explained - July 1, 2025



![[History of EMS Timeline]: A Journey from Humble Beginnings to Sophisticated Healthcare history-of-ems-timeline_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/history-of-ems-timeline_2-150x150.jpg)
