Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey through the annals of computing history in our article, “Computing History Milestones: A Journey Through Technological Transformations.” Join us as we explore the pivotal moments that have shaped the digital realm, from the dawn of electronic computers to the cutting-edge innovations that continue to redefine our technological landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- 1946: ENIAC – First electronic computer
- 1981: IBM PC – Personal computing introduced
- 1984: Macintosh – Graphical user interface (GUI) made computing accessible
- 1985: Microsoft Windows – Dominant operating system
- 1989: World Wide Web – Internet revolution
- 1994: Home video game consoles – Immersive gaming
- 2000s: Broadband Internet – Rich online experiences
- 2000s: Connected Living – Home automation and convenience
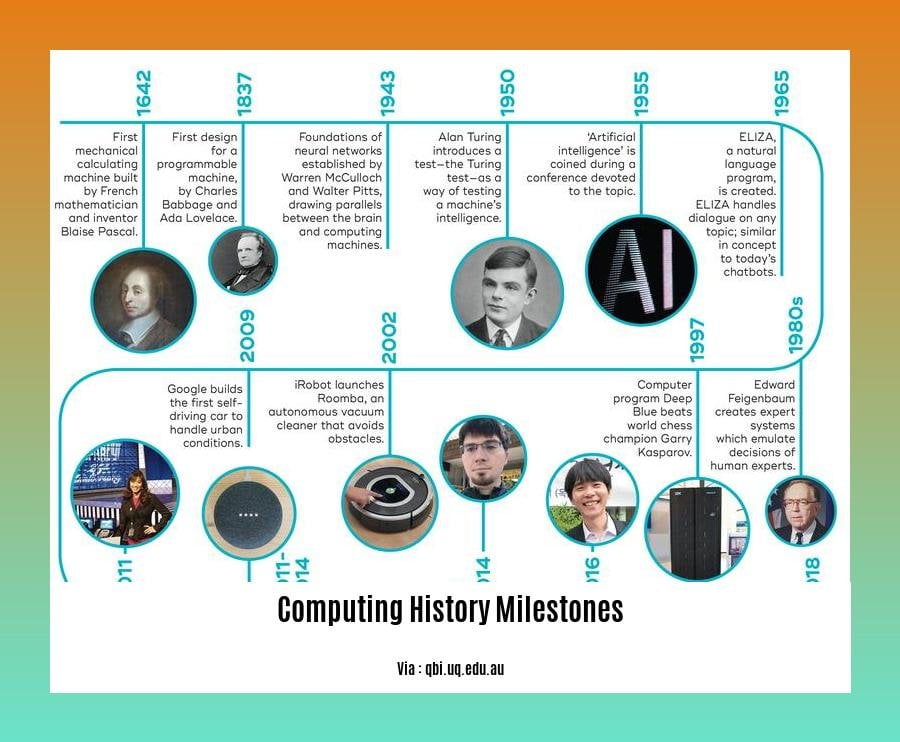
Computing History Milestones

Hey there! Let’s dive into the captivating computing history milestones that have reshaped our world.
The Early Days: Laying the Foundation
From the mechanical calculator to the Analytical Engine, early inventors laid the groundwork for computational marvels.
The Rise of Electricity: Powering Innovation
Morse and Bell’s communication breakthroughs paved the way for electrical systems that transformed computing.
The Dawn of the Computer Age: Birth of the Digital Era
ENIAC ushered in the modern age, followed by stored-program computers that revolutionized data processing.
The Modern Era: Miniaturization and Connectivity
Transistors and integrated circuits miniaturized devices, while PCs and the internet connected the world.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Computing
Quantum computing and AI are on the horizon, promising even more transformative potential.
Timeline of Key Events:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1642 | Pascaline (mechanical calculator) invented |
| 1804 | Jacquard loom uses punched cards |
| 1822 | Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine designed |
| 1837 | Samuel Morse invents the telegraph |
| 1876 | Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone |
| 1946 | ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) |
| 1947 | Transistor invented |
| 1958 | Integrated circuit (IC) developed |
| 1971 | Intel 4004 microprocessor released |
| 1981 | IBM’s Personal Computer introduced |
Dive into the captivating history of computers! Explore the evolution of computing devices over time, from the earliest abacuses to the modern marvels we use today. Trace the computer evolution history and uncover the breakthroughs that shaped our digital world. Delve into the history of computer to appreciate the transformative role technology has played in society.
The birth of electronic computers and the dawn of the digital age

In the realm of human technological advancements, the birth of electronic computers and the subsequent dawn of the digital age stand as transformative milestones. The evolution of computing from its humble beginnings to the sophisticated systems we rely on today has profoundly reshaped our world.
The Precursors
The seeds of computing were sown in the 17th century with mechanical calculators and the visionary Analytical Engine of Charles Babbage. These early inventions laid the foundation for the concept of automated computation.
The Electrical Revolution
The advent of electricity in the 19th century accelerated the development of computing. Innovations such as the telegraph and telephone enabled long-distance communication, while the work of Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla paved the way for electrical power systems.
The Birth of Electronic Computers
The birth of electronic computers marked a watershed moment in computing history. In 1946, the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) emerged as the first fully electronic, programmable computer. This groundbreaking invention opened the door to complex calculations and laid the groundwork for modern computing.
The Digital Age
The development of transistors in the 1950s revolutionized computing by enabling miniaturization. Integrated circuits (ICs) further reduced the size and cost of computers, making them accessible to a wider range of applications. This ushered in the dawn of the digital age, characterized by the rise of personal computers (PCs) and the internet.
Key Takeaways:
- The birth of electronic computers, such as ENIAC, marked a significant shift in computing capabilities.
- The digital age was driven by the miniaturization of transistors and ICs, making computers more accessible.
- Computing advancements have continuously accelerated, shaping our lives in countless ways.
Citation:
MIT Technology Review: A Timeline of MIT Computing Milestones
The transistor revolution and the rise of modern computing
In the realm of technology, it’s hard to overstate the significance of the transistor revolution and the rise of modern computing. It’s a story of innovation, miniaturization, and the democratization of computing power.
The transistor, invented in 1947, replaced bulky and power-hungry vacuum tubes. Its compact size and low power consumption paved the way for smaller, more efficient electronic devices. This breakthrough was the catalyst for the development of integrated circuits and microchips, further shrinking devices while simultaneously boosting their capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- The transistor replaced bulky vacuum tubes, leading to more compact and efficient electronic devices.
- Integrated circuits and microchips further miniaturized devices and increased their capabilities.
- The transistor revolution catalyzed the development of personal computers and the internet, fundamentally altering our lives.
The impact of the transistor revolution extended far beyond the realm of electronics. It gave rise to personal computers in the 1980s, putting computing power in the hands of individuals. The internet, enabled by the interconnectedness of computers, revolutionized communication and information sharing.
Today, transistors continue to be the cornerstone of modern electronics, powering everything from smartphones to supercomputers. Their relentless miniaturization and increased performance have fueled the exponential growth of digital technology, transforming industries, and shaping the way we live.
Source:
The future of computing: Quantum, AI, and beyond
The steady march of technological progress has brought us to the cusp of an unprecedented era in computing, where quantum computing and artificial intelligence (AI) stand poised to revolutionize our world. These transformative technologies hold the potential to solve complex problems, automate tasks, and empower us with new capabilities that were once unimaginable.
Section 1: Quantum Computing
Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations that are exponentially faster than classical computers. This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize fields such as:
-
Drug Discovery: Quantum algorithms can accelerate the development of new drugs by simulating molecular interactions and predicting their effects with far greater accuracy.
-
Materials Science: By simulating the behavior of atoms and molecules, quantum computers can aid in the design of new materials with enhanced properties.
-
Financial Modeling: Quantum algorithms can analyze complex financial data and predict market trends with greater precision, leading to improved decision-making.
Section 2: Artificial Intelligence
AI involves the creation of intelligent systems that can learn, reason, and make decisions like humans. This technology has already made significant strides in:
-
Natural Language Processing: AI-powered systems can understand and generate human language, enabling us to interact with computers in a more natural way.
-
Image Recognition: AI algorithms can analyze images and videos with remarkable accuracy, making them invaluable for tasks such as object detection and surveillance.
-
Machine Learning: AI systems can learn from data and improve their performance over time, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as fraud detection and medical diagnosis.
Key Takeaways:
- Quantum computing and AI are poised to transform various industries.
- Quantum computers excel in complex calculations, while AI excels in learning and decision-making.
- The convergence of these technologies holds boundless possibilities for the future.
Citation:
FAQ
Q1: What was the first general-purpose electronic computer?
A1: ENIAC, developed in 1946.
Q2: Which invention introduced the concept of personal computing?
A2: IBM’s Personal Computer, introduced in 1981.
Q3: Who invented the transistor?
A3: William Shockley, John Bardeen, and Walter Brattain, awarded the Nobel Prize in 1956.
Q4: What is the fundamental difference between quantum and traditional computers?
A4: Quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits) instead of binary bits, leveraging superposition, entanglement, and parallelism for more efficient calculations.
Q5: When was quantum supremacy first claimed?
A5: In 2019, Google claimed to achieve quantum supremacy by performing complex calculations in 200 seconds.
- Unraveling Einstein’s Legacy: Who Inherited His Genius? - July 14, 2025
- Unlock Einstein’s Family Tree: Bernhard Caesar & Untold Stories - July 14, 2025
- Unveiling Bernhard Caesar Einstein: His Life & Albert Einstein’s Legacy - July 14, 2025


![A Journey Through the History of Computing: From Its Humble Origins to Modern Innovations [history of computing ss1] history-of-computing-ss1_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/history-of-computing-ss1_2-150x150.jpg)


![Unveiling Apple's Legacy: A Comprehensive Timeline of Innovation [apple company history timeline] apple-company-history-timeline_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/apple-company-history-timeline_2-150x150.jpg)









