Imagine stepping through the bustling Forum, marveling at the colossal Pantheon, or tracing the strategic movements of legions across vast landscapes—all from the comfort of your device. Digital maps of Ancient Rome are transforming this vision into a tangible reality, offering unparalleled access to the Eternal City and its sprawling empire. These sophisticated tools transcend static images, providing dynamic, interactive blueprints that unlock the intricate details of one of history’s most influential civilizations. Consider exploring a labeled Rome map for additional context. This exploration delves into how these digital wonders provide immersive experiences, their commitment to historical accuracy, and the profound benefits they offer to a diverse audience, from scholars to casual enthusiasts.
The Digital Tapestry of Rome: Immersive Exploration
Digital mapping technology weaves a rich tapestry of Ancient Rome, inviting users to embark on an unparalleled journey. From the vibrant heart of the city to the far-flung frontiers of its empire, these interactive platforms bring history to life with breathtaking detail. Imagine zooming in to examine the intricate carvings of Trajan’s Column, virtually navigating the labyrinthine passages beneath the Colosseum, or exploring the layout of a Roman villa, complete with reconstructed rooms and artifacts.
These immersive experiences are powered by a fusion of archaeological data, historical texts, and cutting-edge visualization techniques. High-resolution satellite imagery, ground-penetrating radar, and 3D modeling are meticulously integrated to create highly accurate and visually stunning representations. Unlike static maps, digital versions often feature layers of information, allowing users to toggle between different historical periods, view reconstructed buildings alongside their ruins, or access detailed annotations about specific landmarks. This dynamism provides a comprehensive understanding of historical sites and landmarks through detailed, interactive representations of the Roman world, offering a sense of presence that traditional media cannot match.
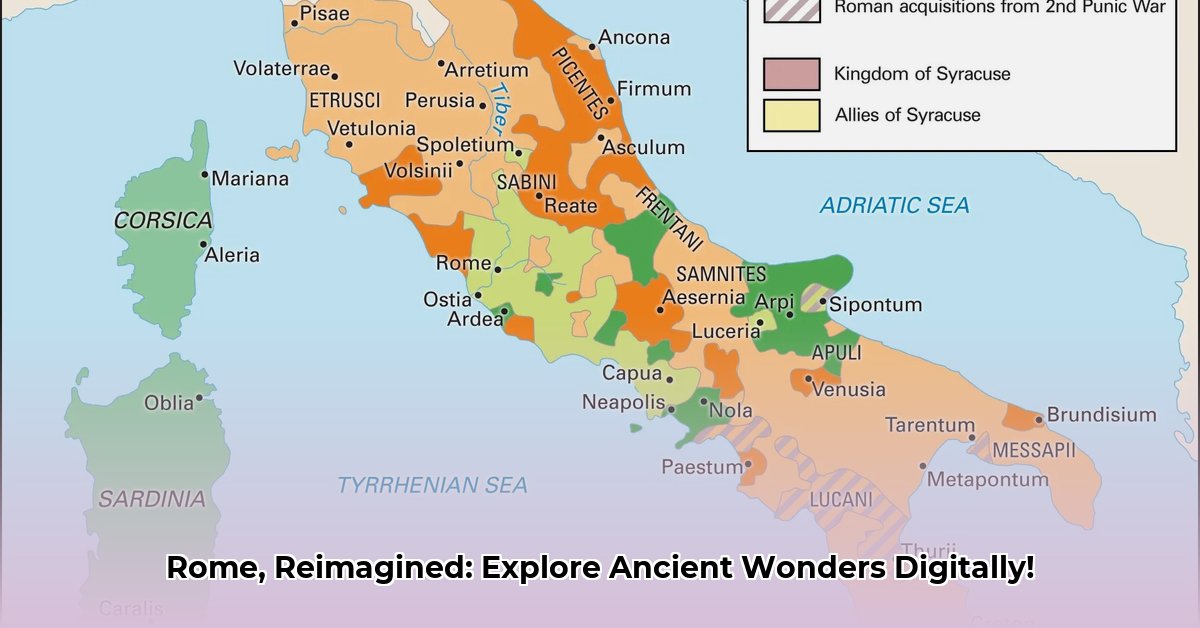
Beyond the urban core, advanced digital resources extend their gaze across the entire Roman Empire. These expansive views illustrate the strategic military campaigns, the elaborate network of trade routes, and the profound dissemination of Roman cultural and religious ideas. Such global perspectives vividly demonstrate the sheer extent of Rome’s enduring influence, providing a crucial contrast to resources that focus solely on the city while still offering detailed insights into urban layouts and iconic structures.
Bridging the Ages: Accuracy, Engagement, and Preservation
The creation of historically accurate digital maps presents a fascinating challenge: balancing the latest archaeological discoveries with compelling user engagement. As new findings continually reshape our understanding of the Roman era, these digital resources must undergo continuous updates to reflect the most current knowledge. The integration of diverse datasets—from ancient texts and epigraphic evidence to modern LiDAR scans and geophysical surveys—necessitates robust quality control mechanisms. Developers often collaborate with historians and archaeologists, emphasizing their ongoing dedication to improvement and actively soliciting user feedback to maintain precision and prevent the spread of inaccurate information. This dynamic process ensures that the interpretation of historical data evolves with scholarship, underscoring the living nature of digital historical cartography.
The true power of these platforms lies in their ability to combine academic rigor with widespread accessibility. Interactive features, meticulously detailed 3D reconstructions, and integrated multimedia elements such as videos and audio guides make history accessible to a broad audience, regardless of their prior knowledge. However, it is essential that these engaging features remain firmly anchored in verifiable historical evidence, ensuring they enhance, rather than overshadow, the core historical substance. This balance ensures that the maps serve as both entertaining educational tools and reliable scholarly resources for exploring Roman civilization.
Furthermore, digital mapping plays a critical role in the preservation of cultural heritage. By creating highly detailed digital twins of archaeological sites and artifacts, these tools offer a safeguard against the erosive effects of time, climate change, and human impact. This digital preservation not only ensures that future generations can access and study these invaluable remnants but also opens new avenues for research, allowing scholars to analyze site relationships and environmental factors with unprecedented precision.
The Evolution of Roman Cartography: From Practicality to Precision
Understanding how Ancient Romans perceived and mapped their world offers crucial context for appreciating modern digital cartography. Unlike some Greek cartographers who pursued abstract geographical precision, the Romans prioritized the practical. Their maps were not merely depictions but functional tools designed to aid in conquering, administering, and connecting their vast empire. This approach was less a quest for mathematically perfect representation and more a logistical imperative, directly tied to maintaining imperial power and control.
For instance, managing an empire stretching from Britannia to the Middle East demanded highly effective navigational aids for moving legions, collecting taxes, and facilitating trade. For the Romans, efficient mapping was synonymous with maintaining their extensive influence and ensuring the smooth operation of their vast network.
Route-Based Realities: Itineraries Over Images
Rather than broad geographical depictions, the Romans favored “itineraries.” These were not maps in the contemporary sense, but detailed route guides—lists of cities and distances crucial for travelers navigating the extensive Roman road network. Often presented as stretched or folded representations, like the famous Peutinger Table (a medieval copy of a Roman original), they prioritized the sequential ordering of locations over accurate spatial depiction. This artifact served as a visual index of the empire’s key roads, eminently practical for moving goods and legions across vast distances, even if it distorted landscapes.
Military planning profoundly shaped Roman cartography. Knowing precise distances, road conditions, and terrain features was critical for the strategic movement of troops and supplies. Roman military leaders relied on “illustrated itineraries” and visual aids that allowed them to choose optimal routes based on complex logistical needs. The widespread and well-maintained Roman road network, facilitated by these detailed itineraries and even rudimentary odometers, allowed troops and information to swiftly reach distant frontiers, underpinning the empire’s enduring strength and expansion.
While their primary focus was on utility, some prominent figures, like Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, demonstrated an interest in the broader geographical context. His Orbis Terrarum, a comprehensive map of the known world intended for public display in Rome, suggests that the Romans were not entirely oblivious to the bigger picture. They understood the necessity of comprehending the world beyond their immediate practical needs.
When assessing the “accuracy” of Ancient Rome’s maps, it’s vital to judge them by their intended utility rather than applying modern cartographic standards of geometric perfection. The Romans developed remarkably effective tools for managing a vast and complex empire. Their maps and itineraries served specific, vital purposes: facilitating travel, promoting trade, supporting military campaigns, and ensuring administrative control. In essence, they valued utility over unwavering, abstract accuracy.
A Historian’s Perspective: Digital Spatial Analysis
The field of Roman Imperial geography is undergoing a radical transformation, largely thanks to advancements in Digital Humanities. This new era moves beyond merely measuring straight-line distances, embracing concepts like cost-based connectivity that paint a far more nuanced picture of the Roman Empire’s intricate networks.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) tools are at the forefront of this revolution. They allow historians to analyze spatial data in ways unimaginable just a few decades ago. Projects like ORBIS, the Stanford Geospatial Network Model of the Roman World (ORBIS), meticulously calculate the true cost—in terms of time, money, and resources—of moving across the ancient world. This reveals the actual arteries of the Roman Empire, illustrating how factors like terrain, season, and mode of transport influenced connectivity. For instance, ORBIS can demonstrate that traveling from Rome to Byzantium via sea was often faster and cheaper than overland, despite longer linear distances.
Digital tools also enable precise dissection of historical texts. Primary sources like Strabo’s Geography and Pliny the Elder’s Natural History come alive when analyzed with advanced text analysis tools. Through this process, researchers can unearth hidden connections, meticulously track ancient trade routes, and gain a profound understanding of the intricate web of Roman power and influence. This approach allows scholars to overlay textual evidence onto geographic models, providing a richer, more integrated understanding of historical phenomena.
This digital revolution in historical studies offers impressively broad benefits, impacting nearly everyone with an interest in the past:
| Stakeholders | How Digital Rome Maps Enhance Engagement and Understanding |
|---|---|
| Educators | Transform history lessons into captivating, immersive experiences through virtual field trips. Students can explore ancient cities, trace military campaigns, and analyze trade networks, sparking critical thinking and enhancing curriculum engagement beyond traditional textbooks. Teachers can integrate interactive maps for dynamic lessons that foster active learning and a deeper understanding of Roman civilization. |
| Researchers | Leverage digital maps for detailed spatial analysis, visually mapping historical data to uncover hidden connections and patterns across the Roman world. This includes conducting cost-time efficiency studies on Roman networks, analyzing socio-economic impact assessments, and identifying previously unnoticed demographic shifts or resource distribution patterns through advanced GIS tools and data visualization. |
| Tourists | Simplify vacation planning with interactive maps, making navigation of historical locations significantly easier. Tourists can personalize itineraries, discover lesser-known sites, utilize augmented reality (AR) experiences on-site to overlay reconstructions onto ruins, and gain a deeper understanding of the historical context of monuments. This transforms a casual visit into an immersive, educational journey. |
| Museums & Cultural Institutions | Elevate visitor experiences with interactive map displays and immersive virtual tours. Digital archives of Roman artifacts and sites can be established, making them accessible to a global audience. Collaborations with researchers to create detailed virtual reconstructions of Roman cities and monuments can focus on both preservation and enhanced public engagement, drawing new audiences and enriching educational programs. |
| Policy Makers & Military Strategists | Study Roman military tactics’ adaptability, resource management strategies, and logistical prowess for insights applicable to modern strategic planning. Analyzing Roman supply lines, defensive fortifications, and campaign routes through digital modeling can provide valuable lessons in efficiency, resilience, and adaptability in complex geopolitical scenarios. |
| City Planners & Civil Engineers | Draw inspiration from Roman engineering designs (e.g., aqueducts, roads, urban layouts). Analyzing historical connectivity, resource management in public works projects, and sustainable urban development principles from ancient Rome can inform contemporary infrastructure and planning, particularly for resilient and efficient urban systems. |
Challenges and Opportunities in the Digital Future
This transformative journey, while promising, is not without its complexities. We must continually grapple with issues of data accuracy, the inherent subjectivity of historical interpretation, and the ethical considerations involved in reconstructing the past. An ongoing question remains: Are we merely enhancing traditional scholarship, or are these digital methodologies fundamentally replacing it? This introspection is crucial for the responsible advancement of the field.
From a historian’s perspective, the potential is immense. The future envisions a landscape where digital tools empower an understanding of the Roman world with unprecedented detail and accessibility. This future allows students, researchers, and the public to explore the past in immersive and deeply engaging ways, pushing the boundaries of historical inquiry and making ancient history more relevant and compelling than ever before.
Mastering Ancient Rome on the Map: Take Your Next Steps
Digital maps are fundamentally revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with Ancient Rome and its vast cultural legacy. These advanced tools offer unique and tailored experiences for educators, tourists, researchers, and the broader community. Understanding Roman military prowess, infrastructural marvels, and complex societal structures offers valuable insights for modern applications. Critically, a comprehensive understanding also requires consideration of the profound ethical implications of Roman expansion and its enduring legacy.
Ready to embark on your own Roman exploration? Here are some actionable steps tailored for different audiences to maximize the potential of digital Rome:
- Explore Digital Resources: Dive into online map resources like ORBIS, the Digital Atlas of the Roman Empire (DARE), or the Pleiades project. Experiment with their various interactive features, layer analysis, and 3D models to discover their full potential for research, education, or personal interest.
- Engage and Discuss: Participate in online forums dedicated to ancient history or digital humanities. Share your experiences with different mapping platforms, discuss insights gleaned from digital spatial analysis, and contribute to a broader community of enthusiasts and scholars. Many digital history projects actively seek user feedback and contributions.
- Critically Assess Information: Always verify information gleaned from digital sources by cross-referencing with multiple, reputable academic and historical sources. Understand that digital reconstructions are interpretations based on current evidence, ensuring your understanding is both accurate and nuanced.
- Integrate into Learning: For educators, integrate these interactive maps directly into your curriculum. Design assignments that require students to use digital tools for spatial analysis or virtual site visits. For travelers, use these maps to pre-plan your visits, understand the historical context of each site, and optimize your on-site experience with virtual overlays.
By combining the transformative power of digital mapping with a critical and nuanced understanding of Roman history, we can unlock unprecedented insights into this endlessly fascinating civilization. This digital renaissance is not just about recreating the past; it’s about forging new pathways to understanding its enduring impact on our present and future.
- Unearth ancient rome roads: Empire’s power and modern highway’s origin - August 15, 2025
- Discover geography of ancient Rome: Empire’s secrets revealed (2024 insights) - August 15, 2025
- Unveiling Ancient Roman Empire Geography: Power & Legacy Secrets - August 15, 2025

![Unearth Ancient City Map Rome: New Atlas For Urban Planners [Reference] city_map_ancient_rome_edited](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/city_map_ancient_rome_edited-150x150.jpg)