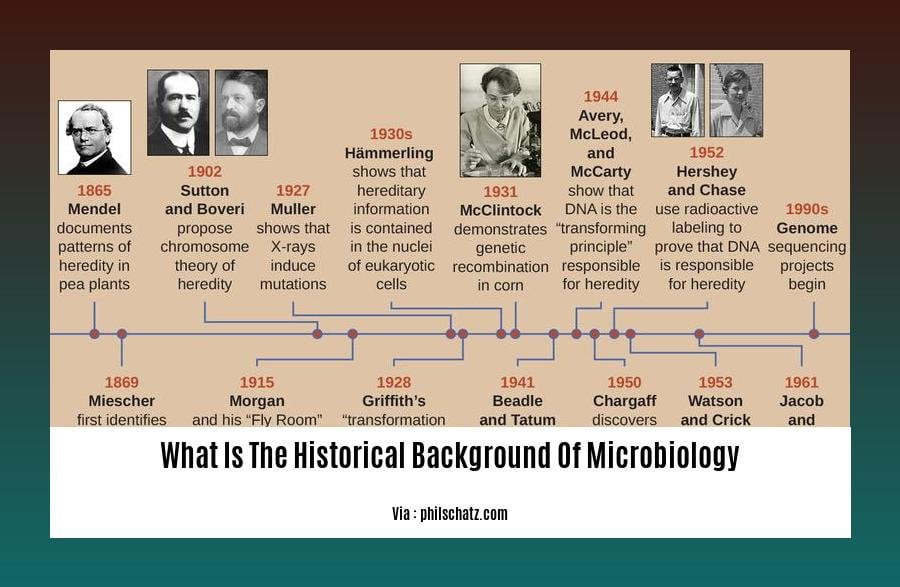
Embark on a captivating journey through the annals of microbiology in [What Is The Historical Background Of Microbiology And Its Impact On Our Understanding Of Life]. This article delves into the remarkable evolution of microbiology, tracing its transformative impact on our comprehension of life’s fundamental principles. Discover how pioneering scientists unraveled the mysteries of microbes, shaping our understanding of health, disease, and the intricate balance of ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, revolutionizing our understanding of life since the 17th century.
Early Greeks believed in abiogenesis, but experiments by Redi and Pasteur challenged this, leading to the acceptance of biotic generation.
Girolamo Fracastoro proposed contagion transmission, while Robert Koch linked specific microbes to diseases, leading to the germ theory and the development of pasteurization.
Advances in laboratory techniques and antibiotics transformed microbiology in the 20th century, along with discoveries in DNA and RNA structure and function, which fueled advances in genetics and molecular biology.
Microbiology has aided biotechnology and the development of vaccines and drugs, and continues to expand our understanding of life.
What Is The Historical Background Of Microbiology?

The Quest to Unravel the Microscopic Realm
Embark on a journey through the remarkable annals of microbiology, a scientific odyssey that has transformed our comprehension of life’s intricacies. From humble beginnings to groundbreaking discoveries, we delve into the historical backdrop that shaped our knowledge of the microbial world, its profound impact on our understanding of life, and the unsung heroes whose dedication paved the way.
Unveiling the Secrets of the Invisible
The story of microbiology begins with the invention of the microscope, a pivotal moment that opened up a hidden universe teeming with microscopic organisms. The pioneering work of Anton van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century revealed a realm of previously unseen creatures, challenging long-held beliefs about the nature of life.
The Battle Against Infectious Diseases
Microbiology’s impact on our understanding of life became strikingly evident in the fight against infectious diseases. The germ theory of disease, championed by Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, revolutionized medicine by establishing the causal link between microorganisms and illness. This breakthrough led to the development of pasteurization and sterilization techniques, saving countless lives.
Advancing Medical Frontiers
Microbiology continued to make significant strides in the 20th century. The discovery of antibiotics, such as penicillin, ushered in a new era of treating bacterial infections. Advancements in microscopy and genetic engineering further illuminated the intricate world of microorganisms, laying the foundation for breakthroughs in biotechnology, immunology, and vaccine development.
Microorganisms in Environmental and Industrial Processes
Beyond their role in health and disease, microorganisms also play pivotal roles in environmental processes and industrial applications. They contribute to nutrient cycling, decomposition, and bioremediation, shaping the delicate balance of ecosystems. In industry, microorganisms are harnessed for fermentation, waste treatment, and the production of biofuels and pharmaceuticals.
Ongoing Explorations and Future Frontiers
The study of microbiology is a constantly evolving field, with ongoing research expanding our knowledge of microbial diversity, microbial interactions, and the complex interplay between microorganisms and their environments. As we continue to probe the secrets of the microbial world, we uncover new insights into life’s origins, evolution, and the potential for harnessing microorganisms for the benefit of humanity.
In summary, the historical background of microbiology is a captivating tale of scientific exploration, groundbreaking discoveries, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. It’s a story of how we came to understand the microbial world, its impact on our lives, and the ongoing quest to unlock the full potential of microorganisms for the betterment of our planet and its inhabitants.
Understanding the evolution of microbiology requires delving into the history of microbiology, shedding light on the pivotal discoveries that shaped our understanding of microbial life.
Embark on a journey through the history of microbiology and uncover the fascinating chronicles of microbial exploration, revealing the milestones and trailblazers that revolutionized our perception of the microscopic world.
Explore the captivating history and vast scope of microbiology in this comprehensive guide. Uncover the origins and milestones that have shaped this field, from the pioneering discoveries of Leeuwenhoek to the cutting-edge advancements of modern microbiology. History and Scope of Microbiology
Work of notable figures like Louis Pasteur, Robert Koch impacted the field

Have you ever wondered how we came to understand the intricate world of microorganisms? Our knowledge of microbiology, the study of microorganisms, has evolved drastically over time, thanks to the groundbreaking work of notable figures like Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch.
A Journey Through History
Microbiology’s journey has been marked by pivotal moments and discoveries that have shaped our understanding of life. In the 19th century, Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch emerged as pioneers in the field, revolutionizing our knowledge of microorganisms and their impact on human health.
Louis Pasteur: Unveiling the Germ Theory of Disease
Pasteur’s meticulous experiments challenged the prevailing notion of spontaneous generation, demonstrating that microorganisms are responsible for fermentation and putrefaction. His work laid the foundation for the germ theory of disease, which revolutionized medicine by establishing the link between microorganisms and illness.
Robert Koch: Defining the Causal Relationship in Disease
Koch’s groundbreaking research further solidified the germ theory of disease. He formulated his famous postulates, known as Koch’s postulates, which provide a framework for establishing a causal relationship between a specific microorganism and a specific disease. This framework has become a cornerstone of microbiology and infectious disease research.
Pioneers of Vaccines and Antiseptics
Pasteur and Koch’s contributions extended beyond the germ theory of disease. Pasteur developed groundbreaking vaccines for rabies, chicken cholera, and anthrax, demonstrating the principle of immunization. His work on sterilization and antisepsis revolutionized surgical practices, reducing the risk of infection. Koch’s research on disinfection and sterilization techniques further contributed to infection control in hospitals and laboratories.
Key Takeaways:
- Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch were pioneering figures in microbiology, revolutionizing our understanding of microorganisms and their impact on human health.
- Pasteur’s experiments challenged spontaneous generation and established the germ theory of disease.
- Koch’s postulates provided a framework for linking specific microorganisms to specific diseases.
- Pasteur developed vaccines and antiseptics, transforming medical practices and reducing infection risks.
- Koch’s research on disinfection and sterilization contributed to infection control in healthcare settings.
Citations:
A Brief History of Microbiology and Immunology
Robert Koch and the ‘golden age’ of bacteriology
Major Discoveries Like Germ Theory of Disease and Antibiotics Revolutionized Microbiology
The Pioneering Leap: How Germ Theory Changed Medical Understanding
The 19th century marked a significant turning point in medical history, thanks to groundbreaking discoveries that revolutionized our understanding of disease and led to life-saving innovations. Central to this transformation were the works of Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch, who played a pivotal role in establishing the germ theory of disease. Their remarkable findings shattered prevailing notions and paved the way for advancements in vaccines, antiseptics, and sterilization techniques, improving public health and hygiene.
The Germ Theory: Unveiling the Microscopic Culprits
Prior to Pasteur and Koch’s work, the prevailing belief was that diseases arose spontaneously from miasma or bad air. Pasteur, through his meticulous experiments, demonstrated that microscopic organisms, such as bacteria, were responsible for fermentation, putrefaction, and, most importantly, disease. Koch further strengthened the case for the germ theory by isolating specific microorganisms and linking them to specific diseases. This paradigm shift revolutionized medical thinking and laid the groundwork for targeted treatments.
Vaccines: A Triumph of Prevention
One of the most significant outcomes of the germ theory was the development of vaccines. Pasteur’s pioneering work on vaccines for rabies, chicken cholera, and anthrax marked a major milestone in medical history. By introducing weakened or attenuated forms of the disease-causing organism, vaccines stimulated the body’s immune system to mount a defense against future infections. This discovery led to the prevention of numerous deadly diseases and saved countless lives.
Antiseptics and Sterilization: Safeguarding Surgical Practices
Pasteur’s and Koch’s work extended beyond vaccines to revolutionize surgical practices. Their discoveries led to the development of antiseptics and sterilization techniques, reducing the risk of infection during surgery. Pasteur’s pasteurization method, which involves heating liquids to kill harmful microorganisms, found applications in food preservation as well. These advancements significantly improved patient outcomes and transformed surgical procedures.
Key Takeaways:
- Germ Theory Revolution: Pasteur and Koch’s work established the germ theory of disease, overturning traditional beliefs and attributing illness to microscopic organisms.
- Vaccines as Lifesavers: Pasteur’s development of vaccines prevented deadly diseases and marked a turning point in medical history.
- Antiseptics and Sterilization: Discoveries in antiseptics and sterilization techniques improved surgical outcomes and revolutionized medical practices.
Additional Resources:
- The Germ Theory of Disease: A Turning Point in Medical History
- Louis Pasteur and the Germ Theory of Disease
Current state of microbiology in modern medicine and biotechnology:
Microbiology has fundamentally altered medical research and practice by aiding in the treatment, prevention, and understanding of diseases. Let’s delve deeper into its captivating journey:
The Golden Age of Discovery:
Microbiology’s golden age witnessed pioneers like Pasteur and Koch unraveling the mysteries of microbial life. Their work laid the cornerstone for modern microbiology, compelling the medical community to embrace the germ theory of disease. This realization revolutionized hygiene practices and led to the development of vaccines, antibiotics, and sterilization techniques.
Current State of Microbiology in Modern Medicine and Biotechnology:
- Antibiotics: The development of antibiotics has been a monumental feat, saving innumerable lives. These drugs combat bacterial infections by hindering their growth or killing them, reducing the severity and duration of illnesses.
- Vaccines: Vaccination has proven to be a powerful tool in preventing infectious diseases. By introducing weakened or inactivated pathogens, vaccines stimulate the body’s immune system to mount a defense, safeguarding individuals from future infections.
- Microbiome Research: The study of the human microbiome – the trillions of microorganisms residing in and on our bodies – has shed light on their pivotal role in health and disease. Understanding these microbial communities opens avenues for novel treatments and therapies.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: The escalating issue of antimicrobial resistance poses a significant threat, as bacteria evolve to withstand antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. Combating this growing challenge demands ongoing research and responsible antibiotic stewardship.
- Microbial Biotechnology: Microbiology has revolutionized biotechnology, leading to advancements in genetic engineering, biofuels, and pharmaceuticals. Harnessing the power of microorganisms enables the production of life-saving drugs, sustainable energy sources, and bioremediation strategies.
Key Takeaways:
- Microbiology’s rich history has illuminated our understanding of life and revolutionized medical practices.
- Antibiotic development has significantly reduced morbidity and mortality rates from bacterial infections.
- Vaccines have proven effective in preventing diseases and improving public health.
- Microbiome research unveils the intricate relationship between microbes and human health.
- Antimicrobial resistance poses a serious threat, necessitating prudent antibiotic use.
- Microbial biotechnology offers promising avenues for drug discovery, renewable energy, and environmental remediation.
Sources:
FAQ
Q1: What drove scientists to challenge the prevailing notion of spontaneous generation?
A1: Spontaneous generation, the belief that life can arise from non-living matter, was challenged by scientists in the 17th and 19th centuries due to experimental evidence suggesting that microorganisms like bacteria are responsible for various phenomena like fermentation and disease.
Q2: What was the contribution of Robert Koch to the advancement of microbiology?
A2: Robert Koch played a significant role in establishing the germ theory of disease, formulating Koch’s postulates, which provide the framework for linking a specific microorganism to a specific disease. His work on anthrax and tuberculosis further solidified the understanding of disease causation.
Q3: How did Louis Pasteur revolutionize the food and beverage industry?
A3: Louis Pasteur developed the process of pasteurization, a technique that uses heat to kill harmful microorganisms in beverages like milk and beer. This discovery transformed the food and beverage industry, reducing the risk of spoilage and contamination.
Q4: What is the legacy of Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch in microbiology?
A4: Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch are considered pioneers in the field of microbiology. Their contributions to the germ theory of disease, vaccine development, and antisepsis techniques revolutionized medical practices, leading to safer surgical procedures and effective treatments for infectious diseases. Their work laid the foundation for modern microbiology and immunology.
Q5: How has the understanding of microbiology changed our perception of the diversity of life on Earth?
A5: Advances in microbiology have revealed the immense diversity of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and protists. This understanding has broadened our comprehension of the complexity of life on Earth and highlighted the fundamental role that microorganisms play in various ecological processes, such as nutrient cycling and decomposition.
- SYBAU See You Baby Meaning: Gen Z Slang Evolves - July 1, 2025
- Unlock Your Inner Youth: Lifestyle Secrets for a Vibrant Life - July 1, 2025
- Decode SYBAU Meaning: Gen Z Slang Explained - July 1, 2025