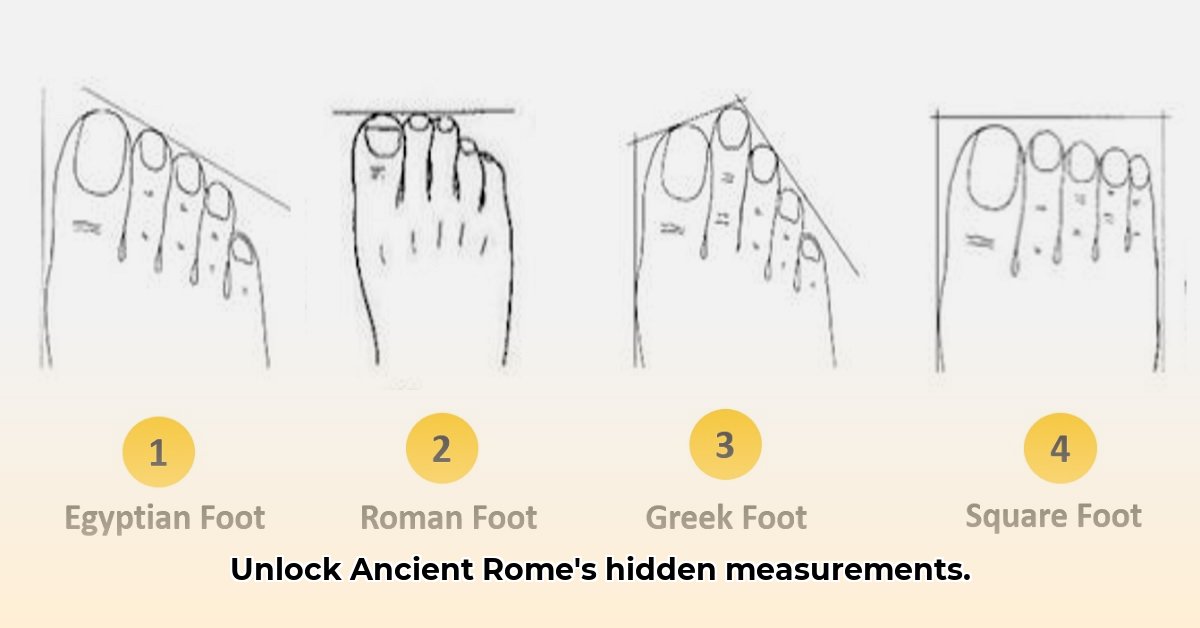
Ever wonder how the Romans measured things back in the day? Their “foot,” or pes, wasn’t just any old foot—it was a pretty important piece of their world. This article will take you on a journey through the Roman measurement system, from understanding exactly how long their foot was to seeing how it affected everything from building magnificent structures to everyday shopping. We’ll explore the variations and what they meant, because even the Romans adapted their measurements to different needs! For a deeper dive into Roman feet, check out this helpful resource: Roman foot details. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind this ancient unit of measure and how it laid the foundation for measurements we still use today.
The Roman Measurement System: A Foundation of Empire
The Roman foot, or pes, was more than just a unit; it was fundamental to the Roman Empire’s success. Consider the architectural marvels—the Colosseum, the vast network of roads, and the ingenious aqueducts—all meticulously planned and constructed using this basic unit. The consistency in measurement facilitated trade, construction, and even military planning across the vast empire. The pes enabled incredible feats of engineering and organization, allowing the Romans to project their power and influence far and wide. How did a standardized system of measurement contribute to Rome’s administrative and logistical capabilities?
Defining the Pes: Units and Subdivisions
The pes was primarily divided in two ways: into twelve unciae (inches) or sixteen digiti (fingers). The division into twelve unciae is strikingly similar to our modern foot, while the digitus offered an even finer level of precision. Romans also commonly used the palmus (palm), equivalent to four digiti. Roman builders and surveyors would use these varied units to accommodate a wide array of tasks, from large-scale construction to detailed craftsmanship. This adaptable system highlights their practical approach to measurement. How did these subdivisions contribute to the versatility of the Roman measurement system?
The Challenge of Standardization: Regional Variations
The story of the Roman pes isn’t without its complexities. Archaeological evidence suggests that the length of the pes could vary from region to region and even change over time. The pes monetalis, often considered the standard “money foot,” also exhibited slight deviations. These variations pose questions about the level of standardization achieved across the Empire. Were these differences a result of practical compromises or a lack of central control?
The challenge of maintaining consistency across vast distances, diverse cultures, and varying economic conditions was immense. The Romans likely faced the same difficulties in standardization that many empires throughout history have encountered. These inconsistencies highlight the practical challenges of implementing and enforcing a uniform measurement system in the ancient world. How did regional variations in the pes impact trade and construction practices?
Modern Conversion and Interpretation
Converting ancient Roman measurements into modern metric units requires careful consideration of these variations. Historians and metrologists have developed approximate conversion factors based on surviving measuring devices, architectural dimensions, and textual references. While a generally accepted value for the pes is around 29.6 cm, the actual length could differ depending on the context. The limitations of ancient measuring tools and the potential for human error further complicate the process. What are the primary sources of uncertainty in converting Roman measurements to modern units?
The Broader System: Beyond Length
The pes was just one component of a comprehensive Roman measurement system. Other units included the libra (pound) for weight, the sextarius for volume, and various units for area, such as the jugerum. These units were interconnected, often based on the duodecimal system, which provided a cohesive framework for commerce, construction, and administration. This system wasn’t just about measuring; it was designed for accuracy and efficiency in a wide range of applications. How did the Roman system of weights and measures contribute to the empire’s economic stability?
Applications in Roman Life
The Roman pes played a pivotal role in numerous aspects of Roman life. Engineers relied on it for designing aqueducts, roads, and public buildings. Military engineers used it for constructing fortifications and planning troop movements. Merchants used it for measuring land and goods, ensuring fair trade. The pes was integral to the functioning of Roman society. How did standardized measurements facilitate military logistics and engineering projects?
Ongoing Research and Discovery
The study of Roman measurements continues to be a vibrant field of research. Archaeologists are constantly uncovering new evidence that sheds light on the nuances of the Roman system. They analyze architectural remains, examine measuring tools, and decipher ancient texts to refine our understanding of Roman metrology. These efforts help us to better appreciate the sophistication and complexity of Roman measurement practices. What recent archaeological discoveries have contributed to our understanding of Roman measurement systems?
A Lasting Impact
Despite the challenges of achieving perfect standardization, the Roman system of measurement left a lasting legacy on Western civilization. The division of the foot into twelve inches, a direct inheritance from the unciae, persists to this day. Understanding the Roman pes provides valuable insights into the engineering, organization, and daily life of one of history’s most influential empires. The enduring influence of the Roman measurement system underscores its importance in shaping our modern world. How does the Roman system continue to influence modern measurement practices?
Converting Ancient Roman Measurements to Modern Units: A Practical Guide
Key Takeaways:
- The Roman pes (foot) was a fundamental unit, but its precise length varied regionally and over time.
- Converting Roman measurements to modern units requires understanding these variations and employing appropriate conversion factors.
- Several methods exist for estimating conversions, each with its own limitations and levels of accuracy.
- Archaeological evidence and historical context are crucial for refining conversion estimates.
Understanding the Roman Foot (Pes)
The Roman foot, or pes, was not a uniform standard like the modern foot. Its length varied across regions and evolved throughout the Roman Empire. This variability is a crucial consideration when attempting to convert ancient measurements to modern units. Scholars continue to debate the precise length of the pes, leading to a range of estimated values. What factors contributed to the variations observed in the length of the Roman pes?
Regional Variations and the Pes Monetalis
One notable variation is the pes monetalis, the “money foot,” which served as the standard for Roman coinage. The weight and dimensions of coins were directly related to this unit, making it a relatively reliable reference point. However, even the pes monetalis exhibited slight deviations, potentially reflecting deliberate adjustments or limitations in manufacturing techniques. How did the Romans attempt to ensure accuracy and consistency in their monetary system?
Subdivisions of the Pes
The pes was further divided into smaller units, including the uncia (inch), palmus (palm), and digitus (finger). These subdivisions, based on the duodecimal system (base-12), provide additional points of reference for conversion. However, the exact values of these subdivisions also varied, adding another layer of complexity to the conversion process. How did the Romans utilize the duodecimal system in their measurement practices, and what advantages did it offer?
Converting to Metric: A Step-by-Step Guide
Because of the variations, there is no single, universally accepted formula. Instead, it involves a careful, multi-step approach:
- Identify the Specific Roman Unit: Determine the exact Roman unit of measurement used (pes, uncia, palmus, etc.).
- Determine Historical Context: Research the period and region in which the measurement was taken, as variations existed across the Empire.
- Choose an Approximate Conversion Factor: Based on scholarly consensus and the historical context, select a suitable conversion factor. A commonly used approximation is 1 pes ≈ 0.296 meters, but this may need adjustment.
- Apply the Conversion: Multiply the Roman measurement by the chosen conversion factor to obtain its metric equivalent.
- Acknowledge Uncertainty: Recognize that any conversion carries an inherent margin of error, particularly when dealing with ancient sources. What are the key sources of uncertainty when converting Roman measurements?
Practical Applications within the Empire
The pes was not simply an abstract unit of measure; it had tangible applications throughout the Roman Empire. It influenced the dimensions of buildings, the layout of roads, and the allocation of land. Understanding the pes provides insights into the practical challenges and solutions faced by Roman engineers, architects, and surveyors. How did the use of the pes directly impact the daily lives of Roman citizens?
Challenges and Ongoing Debate
Archaeological evidence, such as surviving measuring tools and architectural remains, offers valuable clues for understanding Roman measurements. However, the interpretation of this evidence is often complex and subject to ongoing debate among scholars. Accounting for potential errors in ancient texts, variations in materials, and the limitations of ancient technology is crucial for accurate conversion. What specific types of archaeological evidence are most helpful for understanding Roman measurement systems?
Conclusion: A Foundation for Modern Metrology
The study of Roman measurements, including the variations in the pes and the challenges of accurate conversion, continues to inform modern metrology. The Roman legacy in measurement is undeniable, and by refining our conversion methods, we gain deeper insights into Roman civilization. The Roman system laid the groundwork for many of the measurement practices we use today. How does the Roman system continue to influence modern measurement standards and practices?