History is adorned with extraordinary political leaders who captured the hearts and minds of the common people. From Cleopatra VII’s enigmatic charisma to Julius Caesar’s military prowess, from Wu Zetian’s iron-clad leadership to Hatshepsut’s visionary reign, these iconic figures possessed an uncanny ability to connect with the masses. In this article, we delve into the secrets of their enduring appeal, exploring the factors that shaped their mass popularity and the enduring legacy they left behind.
Key Takeaways:

- Popular leaders are seen as ideal and serve as benchmarks for others.
- Politicians use various strategies to appeal to the masses, such as ambiguity and populist rhetoric.
- Leaders appeal to the people in different ways, and unity among the people does not always translate into a unified approach from politicians.
- Younger generations (Millennials and Generation X) generally have more positive views of politicians.
- Popular sovereignty suggests a distinction between the people and elites and acknowledges the people as legitimate sovereigns.
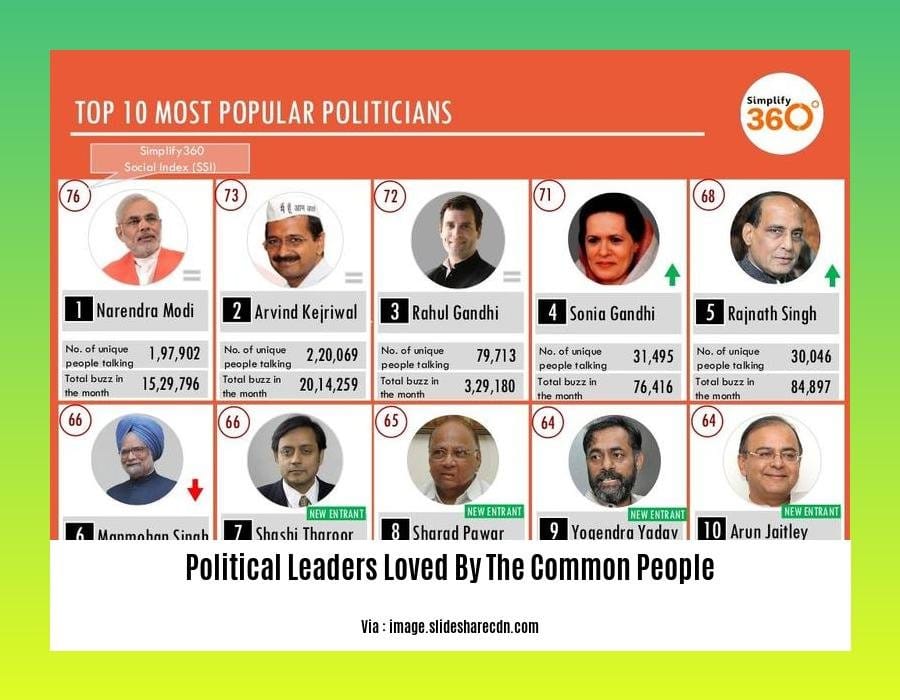
Political Leaders Loved by the Common People
Have you ever wondered what makes certain politicians so beloved by the common people? It’s not always about policies or party affiliation. Often, it comes down to a unique combination of charisma, authenticity, and a genuine connection with the electorate.
Charisma and Likability
Charismatic leaders have a natural ability to connect with people on a personal level. They exude confidence and optimism, making others feel inspired and understood. Likability is also crucial. Voters want to feel a sense of affinity with their leaders, as if they could be friends or neighbors.
Authenticity and Trustworthiness
Authenticity is a powerful force in politics. People are drawn to leaders who they believe are genuine and unscripted. When leaders speak from the heart and connect with their values, it resonates deeply with voters. Trustworthiness is equally important. People want to know they can rely on their leaders to keep promises and act in the best interests of the country.
Connection and Accessibility
The best political leaders loved by the common people make a conscious effort to connect with their constituents. They hold town hall meetings, attend community events, and use social media to engage directly with voters. This personal touch shows that they genuinely care about the people they represent and aren’t just seeking power for its own sake.
Policies That Resonate
While policies alone may not make a leader popular, they can certainly enhance their appeal. If a leader’s policies align with the needs and aspirations of the people, it strengthens their connection and demonstrates that they understand the struggles and hopes of their constituents.
In conclusion, political leaders loved by the common people possess a unique blend of charisma, authenticity, and a genuine concern for the well-being of their constituents. They connect with voters on a personal level, inspire hope, and demonstrate trustworthiness and competence. It’s no wonder that these leaders resonate with the people and earn their enduring admiration.
Discover the captivating stories of leaders adored by the masses, whose charisma and policies have woven their names into the fabric of human history. From beloved leaders of the people who rallied nations to political icons among the populace whose influence transcended borders, explore the lives and legacies of these extraordinary individuals who left an enduring mark on the hearts and minds of the people they led.
Wu Zetian – Empress of China (624–705 C.E.)
Wu Zetian, the only female emperor in Chinese history, ruled from 665 to 705 C.E. Her remarkable journey from empress dowager to emperor transformed the political landscape and left a lasting impact on Chinese society.
Key Takeaways:
- Wu Zetian defied societal norms and established the Wu Zhou dynasty in 690, challenging traditional gender roles.
- She implemented progressive policies, such as promoting education for women and expanding the civil service examination system, benefiting the common people.
- Wu Zetian’s reign marked a shift in political power, as she centralized authority and reduced the influence of aristocratic families.
- Her strong leadership and charisma resonated with the people, solidifying her popularity.
- Despite her accomplishments, Wu Zetian’s legacy remains contested due to her ruthless and ambitious nature.
Citation:
– Wu Zetian, The First Female Empress of China
Hatshepsut – The Female Pharaoh of Egypt (1507–1458 B.C.E.)
Key Takeaways:
- Hatshepsut, Egypt’s first female pharaoh, reigned from 1479-1458 BCE.
- She was a skilled ruler who oversaw ambitious building projects, including the Temple of Deir el-Bahri.
- Hatshepsut adopted the full titles and regalia of a pharaoh, defying societal norms.
Hatshepsut’s Rise to Power
Hatshepsut‘s path to power was not without its challenges. She became regent for her stepson, Thutmose III, after her husband’s death. However, she eventually became the dominant co-ruler, assuming the full power of a pharaoh.
Hatshepsut’s Reign
As pharaoh, Hatshepsut embarked on ambitious building projects, including the construction of the Temple of Deir el-Bahri. This magnificent temple complex showcased her architectural prowess and religious devotion. She also established trade routes, boosting Egypt’s economy and expanding its sphere of influence.
Hatshepsut’s Legacy
Hatshepsut’s reign was marked by stability and prosperity. Her accomplishments as a female pharaoh in a male-dominated society continue to inspire admiration today. Despite attempts to erase her legacy after her death, her achievements stand as a testament to her strength and determination.
Citation:
FAQ
Q1: Who was the first and only female emperor in Chinese history?
A1: Wu Zetian, who ruled from 665 to 705.
Q2: What was the name of the dynasty established by Wu Zetian?
A2: The Wu Zhou dynasty.
Q3: What was the name of the female king of Egypt who reigned from 1479-1458 BCE?
A3: Hatshepsut.
Q4: Who was the Roman dictator who was assassinated in 44 BCE?
A4: Julius Caesar.
Q5: What was the name of the Ptolemaic queen of Egypt who was known for her relationships with Julius Caesar and Mark Antony?
A5: Cleopatra VII.












