Introducing the Pioneers of Autonomous Systems and Automation: Meet the visionaries who are revolutionizing the future of work and unlocking the limitless potential of automation.

Key Takeaways:
- Early Automation: Water clocks and the Antikythera Mechanism demonstrated early advancements in timekeeping and mechanical devices.
- Modern Automation: Automated soap dispensers, virtual assistants, and supply chain management systems have revolutionized everyday practices and industries.
- Gutenberg Press: The invention of the printing press in the mid-1400s sparked a transformation in information dissemination and book production.
Pioneers of Autonomous Systems and Automation
The pioneers of autonomous systems and automation have transformed the way we live and work. From the early days of programmable looms to the modern era of self-driving cars, these innovators have pushed the boundaries of what’s possible.
Early Pioneers
The quest for automation dates back centuries. Jacques de Vaucanson‘s mechanical duck in the 18th century was an early example of a programmable machine. Joseph Jacquard‘s loom, developed around the same time, revolutionized the textile industry.
20th-Century Advancements
In the 20th century, the field of automation took off. Norbert Wiener‘s work on cybernetics laid the foundation for feedback control systems. John von Neumann‘s stored-program computer made automation more flexible and efficient.
Contemporary Innovations
Today, pioneers like Elon Musk (Tesla, SpaceX) and Sebastian Thrun (Waymo) are leading the charge in autonomous vehicles and AI. Rodney Brooks (MIT) is a pioneer in robotics, developing robots inspired by biological systems.
Their inventions have sparked a revolution in industries like manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. As technology continues to evolve, the legacy of these pioneers will continue to shape the future of our world.
If you’re looking for ways to innovators who automated manual processes, you’ll want to read about scientists and engineers who invented self-driving cars, automated manufacturing, and robotic vacuum cleaners. And if you’re interested in eliminating human toil through pioneering automation, you’ll find fascinating examples ranging from autonomous checkout at grocery stores to surgical robots in hospitals. Read more about breakthrough self-operating innovations that have transformed industries and improved our lives.
Contemporary Innovations
In the realm of Contemporary Innovations, a brilliant tapestry of minds has woven the threads of progress in autonomous systems and automation. These visionaries have reimagined the very fabric of our world, transforming industries and shaping the future we inhabit.
Early Pioneers
- Jacques de Vaucanson: The “father of industrial automation,” whose mechanical creations amazed the world with their lifelike movements.
- Joseph Jacquard: His programmable loom revolutionized textiles, automating intricate patterns.
- Charles Babbage: The “father of computing,” whose Analytical Engine laid the groundwork for modern automation.
20th-Century Advancements
- Norbert Wiener: The pioneer of cybernetics, who introduced feedback control systems, the brains behind automation.
- John von Neumann: The father of the stored-program computer, enhancing automation’s flexibility.
- George Devol: The inventor of the industrial robot, automating repetitive tasks in manufacturing.
Contemporary Innovations
In the 21st century, the pace of innovation has accelerated, with visionaries pushing the boundaries of Contemporary Innovations.
- Elon Musk: The driving force behind Tesla and SpaceX, leading the charge in autonomous vehicles and space exploration.
- Sebastian Thrun: The Stanford professor who co-founded Google’s self-driving car project, now Waymo.
- Rodney Brooks: The MIT roboticist whose bio-inspired robotics mimics natural systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Automation has revolutionized numerous industries, from manufacturing to transportation to healthcare.
- The pioneers of automation have left an indelible mark on our world, shaping the future of technology.
- Contemporary Innovations in autonomous systems continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, transforming our lives in countless ways.
Citation:
TechHQ: What is an autonomous robot? History and the future
Applications and Impact
Autonomous systems and automation have revolutionized our world, from self-driving cars to automated manufacturing processes. These advancements have transformed the way we work, live, and interact with technology.
Early Pioneers
The roots of autonomous systems can be traced back to the early days of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics.
- Jacques de Vaucanson‘s mechanical duck (18th century) demonstrated programmable machines.
- Joseph Jacquard‘s loom revolutionized the textile industry.
20th-Century Advancements
Norbert Wiener‘s cybernetics laid the foundation for feedback control systems, while John von Neumann‘s stored-program computer enhanced automation flexibility and efficiency.
Contemporary Innovations
In recent years, Elon Musk (Tesla, SpaceX) and Sebastian Thrun (Waymo) have driven advancements in autonomous vehicles and AI. Rodney Brooks (MIT) pioneered bio-inspired robotics.
Applications and Impact:
- Automation has revolutionized manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare.
- Autonomous systems are making our lives easier and more efficient.
- The legacy of these pioneers continues to shape the future of technology and society.
Key Takeaways:
- The development of autonomous systems and automation has a long and rich history.
- Early pioneers laid the groundwork for modern advancements.
- Contemporary innovations continue to push the boundaries of automation.
- Applications and Impact: Automation has revolutionized industries and improved our lives.
- The future of autonomous systems and automation holds endless possibilities.
Most Relevant URL Source:
Future Trends: Pioneers of Autonomous Systems and Automation
Delve into the groundbreaking world of autonomous systems and automation, where visionaries have revolutionized how we interact with technology. From self-driving cars to automated manufacturing processes, these pioneers have shaped the future trends of our world.
Early Trailblazers
These early innovators laid the foundation for modern automation:
- Jacques de Vaucanson: His mechanical duck amazed audiences with its intricate movements.
- Joseph Jacquard: His programmable loom transformed the textile industry.
- Charles Babbage: His Analytical Engine paved the way for modern computing.
20th-Century Innovations
The 20th century witnessed a surge in advancements:
- Norbert Wiener: Defined the field of cybernetics, enabling feedback control systems.
- John von Neumann: His stored-program computer revolutionized automation and computing.
- George Devol: Invented the industrial robot, a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Contemporary Visionaries
In our era, these pioneers have pushed the boundaries of automation:
- Elon Musk: Driving advancements in autonomous vehicles (Tesla) and space exploration (SpaceX).
- Sebastian Thrun: Co-founded Google’s self-driving car project (now Waymo).
- Rodney Brooks: Developed principles for autonomous robots inspired by biology.
Key Takeaways:
- Pioneers in autonomous systems and automation have revolutionized industries.
- Early advancements in mechanical automata and programmable looms set the stage for modern technologies.
- 20th-century innovations in cybernetics, computing, and robotics laid the groundwork for contemporary breakthroughs.
- Contemporary visionaries are pushing the boundaries of autonomous technology, shaping the future trends of our world.
Most Relevant URL Source:

FAQ
Q1: Who invented the first autonomous robot?
A1: The first autonomous robots were developed in the early 1940s. However, the specific inventor or inventors are not widely known.
Q2: What are the key challenges facing autonomous systems and automation?
A2: Some key challenges include safety and liability concerns, ethical considerations, and the potential displacement of human jobs.
Q3: What are the potential benefits of autonomous systems and automation?
A3: Potential benefits include increased efficiency, productivity, and safety, as well as the ability to perform tasks that are dangerous or impossible for humans.
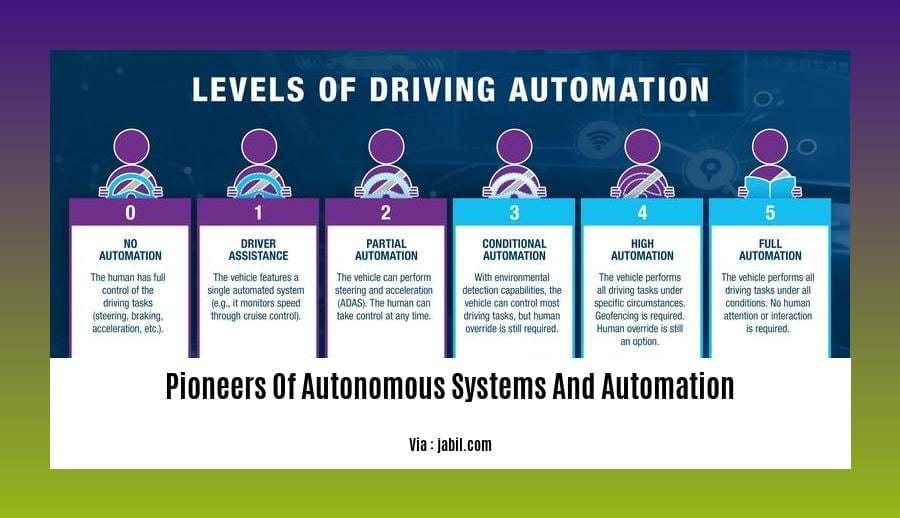
Q4: What are the different levels of autonomous enterprises?
A4: There are five levels of autonomous enterprises, ranging from basic automation to fully autonomous systems that can operate without human intervention.
Q5: How can businesses prepare for the adoption of autonomous systems and automation?
A5: Businesses can prepare by identifying potential use cases, addressing ethical and safety concerns, and developing a workforce strategy that includes training and reskilling employees.
- Crypto Quotes’ Red Flags: Avoid Costly Mistakes - June 30, 2025
- Unlock Inspirational Crypto Quotes: Future Predictions - June 30, 2025
- Famous Bitcoin Quotes: A Deep Dive into Crypto’s History - June 30, 2025