Delve into the captivating origins of England in “The Enduring Origins of England.” This article explores the enigmatic arrival of the Anglo-Saxons and the profound impact of the Norman Conquest, uncovering the intricate socio-cultural dynamics that shaped the nation’s early history.
Key Takeaways:
- The origins of England can be traced back to the Roman conquest in 43 AD.
- Anglo-Saxon settlement laid the foundation for the English people and the name “England.”
- England emerged from the unification of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
- Viking invasions disrupted the political landscape of early England.
Origins in England
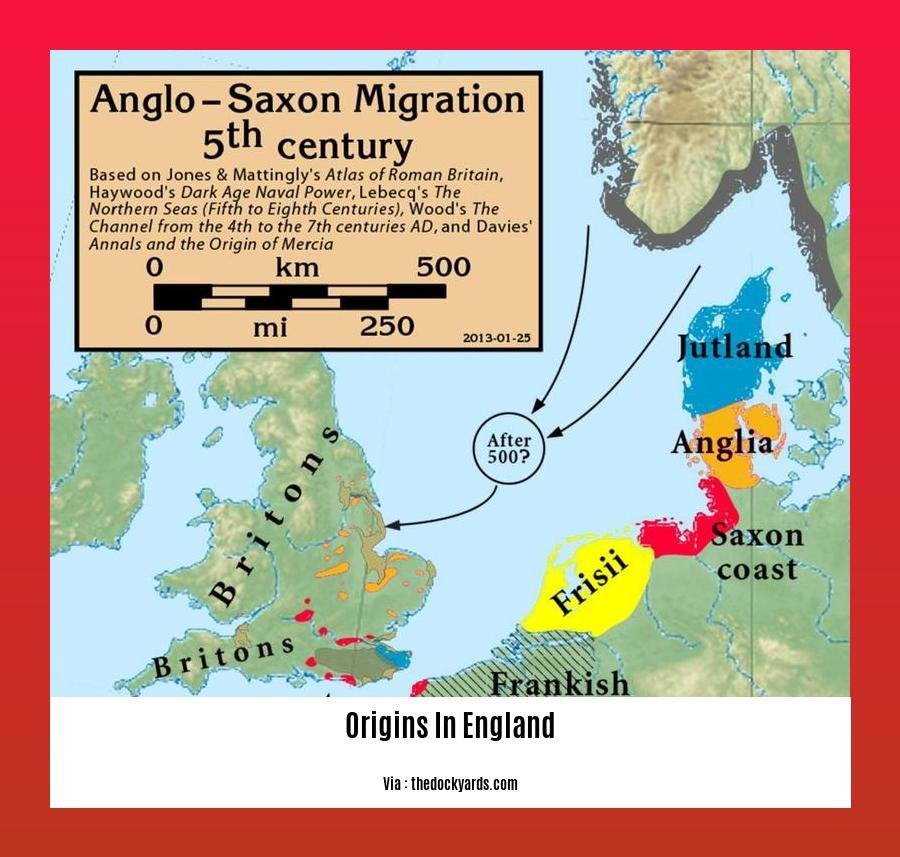
England’s story begins with Origins in England by the Romans in 43 AD. They left an enduring legacy, shaping the landscape with roads, towns, and villas.
Then came the Anglo-Saxons after the Roman withdrawal, bringing their language and customs, forging the foundation of modern-day English identity. The name “England” itself echoes their legacy, meaning “land of the Angles.”
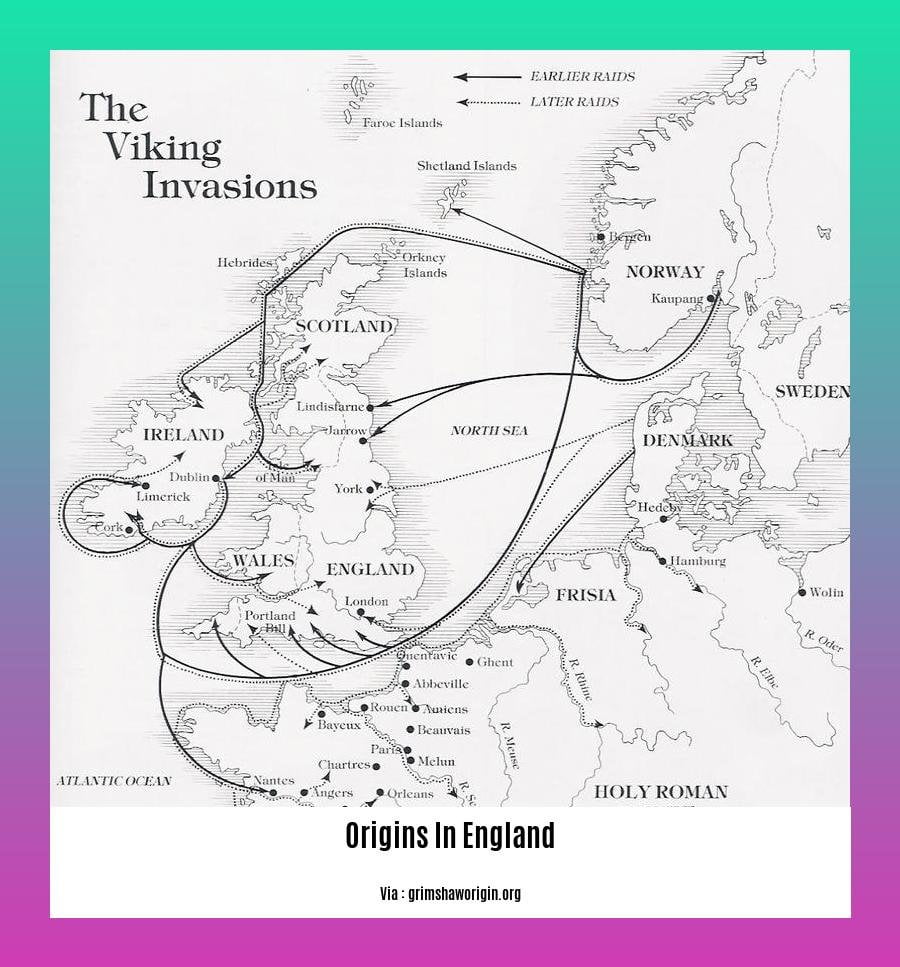
Around the 9th century, Vikings raided England, leaving a complex imprint. They plundered and settled, influencing everything from place names to genetic makeup.
Through alliances and conquests, the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms coalesced into a unified England under King Athelstan in the 10th century. Yet, their dominance was short-lived.
In 1066, the Normans invaded, bringing a profound transformation. Their victory at the Battle of Hastings ushered in a new era of feudalism, architecture, and language, shaping England’s destiny forever.
Timeline of Origins in England:
| Event | Time |
|---|---|
| Roman Conquest of Britain | 43 AD |
| Anglo-Saxon Settlement | 5th-6th centuries |
| Viking Invasions | 9th century |
| Unification of England | 10th century |
| Norman Conquest | 1066 |
From Roman roads to Norman castles, the Origins in England are a tapestry woven through time, shaping the nation’s identity and leaving an enduring legacy that continues to resonate today.
Immerse yourself into the riveting history of cricket, tracing its evolution from humble beginnings to the global phenomenon it is today.
Delve into the captivating evolution of the Ashes series, uncovering the intense rivalry between England and Australia that has shaped the sport for over a century.
Relive the unforgettable moments and key players in the proud history of the ICC World Cup, the pinnacle of international cricket.
The Norman Conquest and its transformational effects
The Norman Conquest of 1066 marked a pivotal moment in English history, leaving an enduring legacy that shaped the nation’s identity, language, and culture. Led by William the Conqueror, the Norman invasion forever altered the political and social landscape of England.
Key Takeaways:
- The conquest established a Norman ruling class that replaced the Anglo-Saxon elite.
- The Norman French language became the language of the court and aristocracy, influencing the development of modern English.
- The Norman introduction of feudalism transformed land ownership and social structure.
- The conquest linked England more closely with mainland Europe, fostering cultural and economic exchanges.
Transformational Effects:
The Norman Conquest had far-reaching consequences for English society.
- Political upheaval: The conquest destroyed the Anglo-Saxon aristocracy and replaced it with Norman lords, who brought with them a new system of government based on feudalism.
- Cultural assimilation: The Norman conquerors gradually assimilated into English society, adopting the language, customs, and traditions of their subjects. However, Norman influence remained strong in the upper echelons of society, particularly in the areas of law, government, and the Church.
- Economic changes: The conquest led to the introduction of new agricultural techniques and land management practices, which increased productivity and improved living standards for many.
The Norman Conquest stands as a testament to the enduring power of conquest and the transformative effects it can have on a nation’s destiny. Its legacy continues to resonate in the English language, institutions, and culture today.
Citations:
The evolution of English language and culture
Our enthralling tale begins with the enigmatic Anglo-Saxons, seafaring warriors who crossed the North Sea to forge a new realm in the 5th century. Their influence seeped deep into the English language, bestowing upon us words like “home” and “king,” shaping the very fabric of our speech.
Centuries later, the thunderous arrival of the Vikings in the 9th century left an enduring imprint on our lexicon. “Berserk” and “skull” are mere echoes of their formidable presence, woven into the tapestry of our language.
But it was the Norman Conquest of 1066 that transformed England’s destiny, heralding a new era of feudalism, architectural marvels, and linguistic fusion. French, the tongue of the conquerors, intertwined with the Anglo-Saxon vernacular, giving birth to a rich and expressive language that flourished in the centuries that followed.
Key Takeaways:
- The Anglo-Saxons laid the foundations of the English language, leaving a lasting legacy in our vocabulary.
- The Vikings left their mark on English through words like “berserk” and “skull.”
- The Norman Conquest infused the English language with elements of French, shaping its modern form.
Relevant URL Sources:
- The Evolution of the English Language
- A History of English
The emergence of feudalism and its influence on society
Feudalism was a complex web of social and political relationships that emerged in Europe during the Middle Ages. At its core, it was a system of land tenure and military service. This system had a profound impact on the development of European society, shaping everything from the structure of government to the lives of ordinary people.
Feudalism emerged in the 9th century as a response to the political and economic instability that followed the collapse of the Carolingian Empire. In the absence of a strong central authority, local lords began to offer protection and justice to their tenants in exchange for military service and other forms of support. Over time, these relationships became formalized, and feudalism became the dominant form of political organization in Europe.
Feudal society was hierarchical, with the king at the top, followed by nobles, knights, and peasants. The king granted land to his nobles, who in turn granted land to knights. Knights were responsible for providing military service to their lord, while peasants worked the land and paid rent to their lord.
Key Takeaways:
- Feudalism was a socio-political system that emerged in Western Europe during the Middle Ages.
- It was a system of land tenure and military service.
- Feudal society was hierarchical, with the king at the top, followed by nobles, knights, and peasants.
- Feudalism had a profound impact on the development of European society, shaping everything from the structure of government to the lives of ordinary people.
Relevant URL Sources:












