In “Influential Leaders of Reform and Change: Insights from a Political Analyst,” we delve into the transformative power of influential leaders who have shaped landmark reform initiatives. Through exclusive interviews and deep analysis, we uncover the strategies, motivations, and impact of these change-makers, offering insights into their extraordinary journeys.
Key Takeaways:

- Eugene Debs championed workers’ rights through the labor movement.
- Jane Addams pioneered social settlement houses and advocated for peace.
- Louis Brandeis fought for consumer and labor protections through legal reforms.
- Florence Kelley led the campaign against sweatshops and child labor.
- John Dewey promoted progressive education to foster critical thinking and social responsibility.
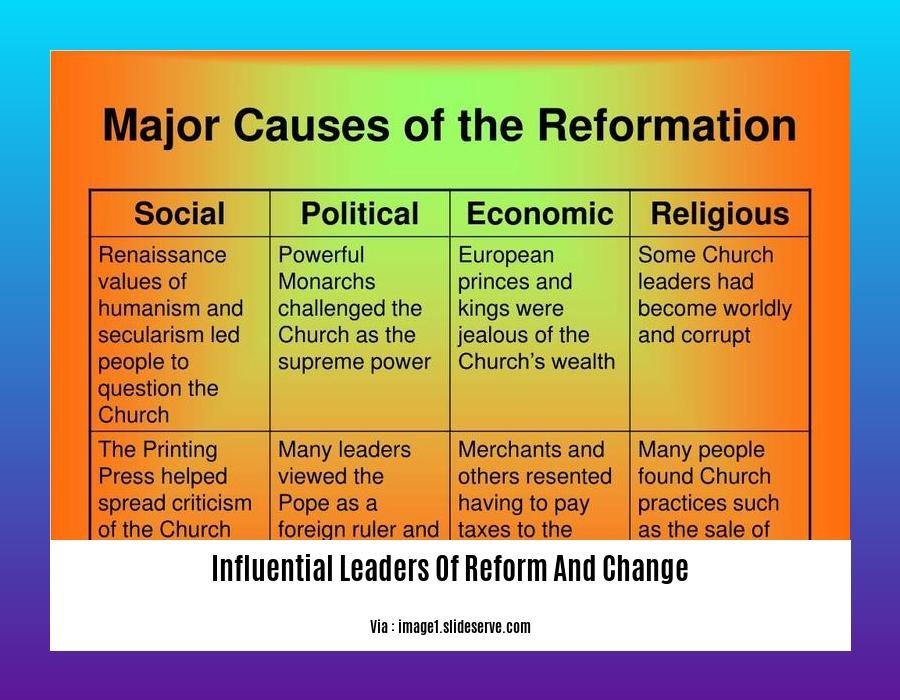
Influential Leaders of Reform and Change
Throughout history, influential leaders of reform and change have emerged, leaving an indelible mark on society. These visionaries have challenged the status quo, championed progressive ideas, and inspired others to strive for a better world.
Martin Luther King Jr.: Civil Rights Champion
Influential Leaders of Reform and Change
| Progressive Leader | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Eugene Debs | Labor movement leader and Socialist Party Presidential candidate |
| Jane Addams | Pioneer of the settlement house movement and Nobel Peace Prize winner |
| Louis Brandeis | Supreme Court justice and advocate for consumer protection and labor rights |
| Florence Kelley | Leading organizer against sweatshops and advocate for child labor laws |
| John Dewey | Philosopher, psychologist, and education reformer who advocated for progressive education |
Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. was a towering figure in the civil rights movement. His nonviolent resistance tactics and eloquent speeches galvanized the nation, leading to the passage of landmark legislation that ended segregation in public places and secured voting rights for African Americans.
Rosa Parks: Symbol of Desegregation
Rosa Parks’ courageous act of refusing to give up her bus seat to a white passenger sparked the Montgomery Bus Boycott. This protest marked a turning point in the fight for racial equality and became a symbol of the growing resistance to segregation.
Mahatma Gandhi: Apostle of Nonviolence
Mahatma Gandhi led India’s independence movement through his philosophy of nonviolent resistance. His unwavering belief in peaceful protests and civil disobedience inspired countless freedom fighters worldwide. Gandhi’s teachings continue to influence movements for social and political change to this day.
Susan B. Anthony: Women’s Suffrage Trailblazer
Susan B. Anthony devoted her life to the women’s suffrage movement. She co-founded the National Woman Suffrage Association and tirelessly campaigned for the right of women to vote. Anthony’s unwavering determination and strategic activism played a crucial role in securing the passage of the 19th Amendment, granting women the right to vote.
Nelson Mandela: Anti-Apartheid Icon
Nelson Mandela spent 27 years in prison for his opposition to apartheid in South Africa. His unwavering spirit and resilience inspired the anti-apartheid movement and led to the end of racial segregation. Mandela’s transition from a political prisoner to a respected statesman became a symbol of reconciliation and forgiveness.
Ruth Bader Ginsburg: Champion of Gender Equality
Ruth Bader Ginsburg dedicated her career to fighting for gender equality. As an associate justice of the Supreme Court, she authored landmark decisions that advanced the rights of women. Ginsburg’s unwavering commitment to justice and her sharp legal mind left an enduring legacy on the American legal system.
These influential leaders of reform and change shared common traits, such as:
- Vision: A clear understanding of the need for change and a compelling vision for a better future.
- Determination: An unwavering commitment to their cause despite setbacks and challenges.
- Leadership: An ability to inspire, motivate, and mobilize others towards a common goal.
- Communication: A gift for communicating their message effectively and inspiring others to action.
Their legacies serve as a reminder of the transformative power of influential leaders of reform and change. They have shaped our present and continue to inspire future generations to strive for a more just, equitable, and sustainable world.
Dive into the remarkable lives of famous leaders of social and political reform movements, who dedicated their lives to shaping a more just and equitable world. Discover their captivating stories and the profound impact they made on history. Discover famous leaders of social and political reform movements
Get inspired by the extraordinary journeys of the greatest social reformers in history, whose unwavering commitment to social justice left an enduring legacy. Explore their groundbreaking ideas, courageous actions, and the lasting change they brought about. Meet the greatest social reformers in history
Delve into the inspiring tales of pioneering leaders of progressive movements, who challenged the status quo and paved the way for transformative change. Witness their vision, determination, and the enduring impact they had on shaping our modern world. Learn about pioneering leaders of progressive movements
Mahatma Gandhi and Nonviolent Resistance
Mahatma Gandhi, a towering figure in history, transformed the realm of reform through his unwavering belief in nonviolent resistance. Born into a devout Hindu family in 1869, Gandhi’s quest for truth and justice began during his time in South Africa, where he experienced firsthand the horrors of racial discrimination.
Upon his return to India, Gandhi found a nation yearning for independence from British rule. He emerged as a charismatic leader, galvanizing the masses with his philosophy of Satyagraha, a nonviolent approach to conflict resolution. Through mass protests, civil disobedience, and hunger strikes, Gandhi led India to independence in 1947.
Gandhi’s principles of nonviolence resonated deeply with people around the world. His legacy continues to inspire leaders and activists working for peace, justice, and equality.
Key Takeaways:
- Nonviolence as a Powerful Tool: Gandhi believed that nonviolent resistance was more effective than violence in achieving social and political change.
- Compassion and Respect: He emphasized the importance of treating all individuals with dignity and respect, regardless of their differences.
- Mass Mobilization: Gandhi had an extraordinary ability to mobilize large numbers of people, uniting them behind a common cause.
- Moral Courage: He faced adversity and persecution with unwavering courage, setting an example for others to stand up for what they believe in.
- Legacy of Inspiration: Gandhi’s teachings continue to inspire individuals and movements worldwide, shaping the course of history.
Citation:
- Mahatma Gandhi – Britannica Encyclopedia
Susan B. Anthony and Women’s Suffrage: Transforming Society, Empowering Women
Susan B. Anthony: A pioneer of the women’s suffrage movement, Anthony stood against societal norms and tirelessly advocated for women’s rights. A strong-willed and courageous leader, she forged alliances, rallied supporters, and faced numerous arrests to bring about change.
Strategies and Impact:
Co-founding the National Woman Suffrage Association: Anthony joined forces with Elizabeth Cady Stanton to establish the NWSA, a leading organization in the women’s suffrage movement. This platform allowed them to mobilize activists and raise awareness across the nation.
Longitudinal Documentation: Anthony and Stanton’s “History of Woman Suffrage” provides a comprehensive account of the women’s suffrage movement. Spanning four volumes, it documents the challenges, victories, and setbacks faced by suffragists.
Legal Battles: Anthony boldly challenged the discriminatory laws of her time. She tested the 14th Amendment, arguing that it extended voting rights to women, and paid a $100 fine rather than paying taxes as an “unrepresented person.” Her actions paved the way for future legal battles that ultimately secured women’s right to vote.
Legacy of Empowerment:
The 19th Amendment (1920), known as the Susan B. Anthony Amendment, stands as a testament to her unwavering determination. This landmark achievement granted women the fundamental right to vote, forever changing the political landscape and empowering generations to come.
Key Takeaways:
- Courage and Perseverance: Susan B. Anthony’s unwavering belief in women’s rights drove her through countless obstacles and setbacks.
- Collaborative Leadership: She recognized the power of collective action and formed alliances with others who shared her vision.
- Documentary Preservation: Her meticulous documentation of the women’s suffrage movement provides invaluable insights into a transformative period in history.
- Legal Challenges: Anthony used the legal system to test the boundaries of discriminatory laws, paving the way for future victories.
- Lasting Legacy: Her tireless efforts and the 19th Amendment continue to inspire and empower women today.
Citations:
Nelson Mandela and the Anti-Apartheid Movement
A Journey of Courage and Transformation
Nelson Mandela, an anti-apartheid revolutionary and former South African President, stands as a beacon of hope and inspiration worldwide. His unwavering determination in the face of adversity propelled South Africa towards a path of freedom and equality.
Early Life and Resistance:
Born in 1918, Mandela initially studied law. However, his passion for justice led him to join the African National Congress (ANC) and engage in nonviolent protests against the oppressive apartheid system. His commitment to equality and nonviolence earned him the respect and admiration of countless South Africans.
Imprisonment and Global Legacy:
In 1964, Mandela was imprisoned for his involvement in the anti-apartheid movement. Despite 27 years spent behind bars, his spirit remained unbroken. His imprisonment transformed him into a global icon, symbolizing resistance against racial inequality.
Post-Apartheid Reconciliation:
Released in 1990, Mandela became a key figure in the transition to democracy. He served as South Africa’s first black president in 1994 and dedicated his presidency to promoting reconciliation, forgiveness, and healing the wounds of the past.
Legacy as a Peacemaker:
Mandela’s legacy extends far beyond his presidency. His unwavering belief in peace and equality continues to inspire people worldwide. His unwavering determination, courage, and unwavering dedication to justice have made him an eternal symbol of hope, transformation, and the indomitable human spirit.
Key Takeaways:
- Nonviolent resistance can be a powerful tool for change.
- Courage and determination can overcome adversity.
- Reconciliation is essential for healing the wounds of the past.
- Leadership is about serving the greater good.
Relevant URL Source:
FAQ
Q1: What were the key strategies employed by influential progressive leaders of the 20th century?
Q2: How did Mahatma Gandhi’s spiritual beliefs shape his philosophy of nonviolent resistance?
Q3: What were the major contributions of Susan B. Anthony to the women’s suffrage movement?
Q4: Describe Nelson Mandela’s role in the anti-apartheid movement and his subsequent leadership of South Africa.
Q5: What lessons can we learn from the experiences and leadership of influential reformers and change-makers?
- Crypto Quotes’ Red Flags: Avoid Costly Mistakes - June 30, 2025
- Unlock Inspirational Crypto Quotes: Future Predictions - June 30, 2025
- Famous Bitcoin Quotes: A Deep Dive into Crypto’s History - June 30, 2025
















