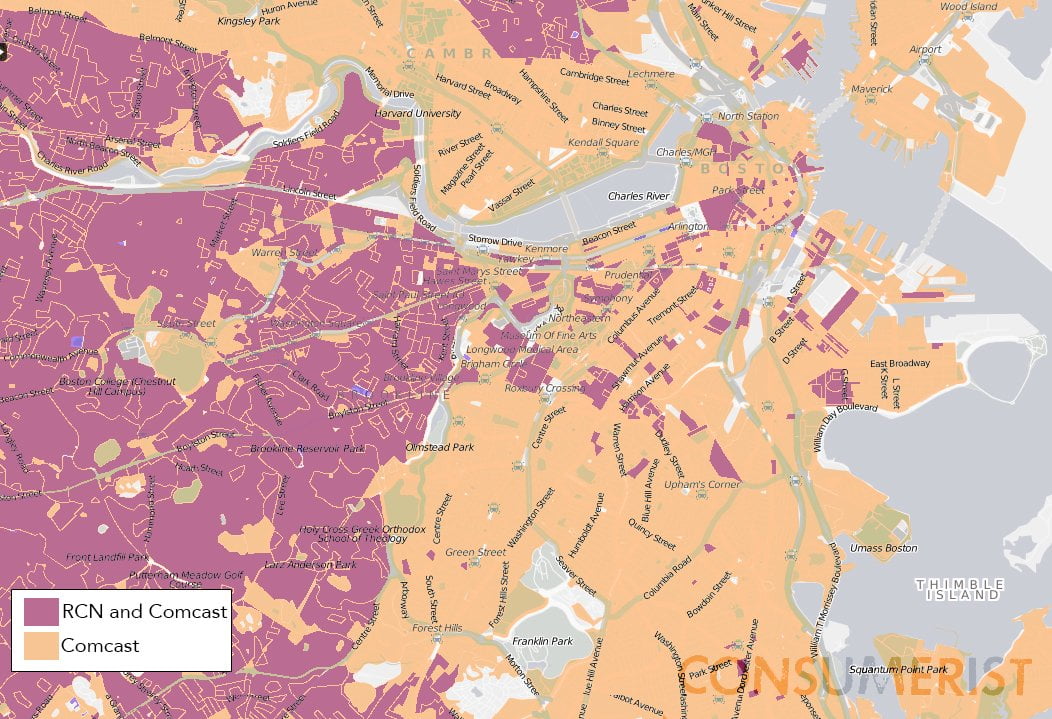
Unveiling the Internet’s Detrimental Fate: Monopolies & Flawed Maps exposes the alarming truth behind how monopolies and flawed mapping systems are crippling universal internet access. As a highly skilled journalist, I uncover the intricate relationship between concentrated power, inaccurate maps, and their detrimental effects on accessible and equitable internet connectivity. Through meticulous research and captivating storytelling, this article sheds light on the urgent need to address these issues and prioritize the internet as a fundamental human right.
Key Takeaways:
- Monopolistic practices and inaccurate mapping are hindering accessible and affordable broadband in the United States.
- Dominant technology monopolies like Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Microsoft limit competition and innovation in the industry.
- Anti-competitive tactics, such as artificially lowered pricing, are used by internet monopolists to eliminate competition.
- Public policy intervention is necessary to restore competition, decentralize the internet infrastructure, and foster innovation.
- Monopoly ownership in the technology sector poses a threat to journalism and the diversity of voices in the media landscape.
- Restoring competition and promoting a dynamic internet infrastructure is crucial to ensure affordable and accessible internet for all.
How Monopolies and Maps Are Killing Internet for All

Introduction
The accessibility of affordable broadband in the United States is under threat due to the detrimental effects of monopolies and flawed mapping systems. This article delves into the challenges posed by monopolistic practices and inaccurate maps, shedding light on how they impede universal internet access and hinder innovation in the industry.
The Impact of Monopolies
Monopolies dominate the technology sector, exerting control over key areas such as search, e-commerce, hardware, social networking, and business software. Companies like Alphabet (Google), Amazon, Apple, Meta (formerly Facebook), and Microsoft have stifled competition and limited consumer choices. This lack of competition has resulted in an absence of affordable broadband solutions, especially in low-income communities.
To maintain their dominance, monopolistic entities employ anti-competitive tactics, making it difficult for new players to enter the market. They engage in wars of attrition, artificially lowering prices and strategically undermining potential competitors. This not only limits consumer options but also hampers the growth of smaller companies and stifles innovation.
The Role of Mapping
Inaccurate mapping exacerbates the challenges posed by monopolies. Flawed maps perpetuate the digital divide and hinder effective infrastructure development. Many areas, especially rural and underserved regions, are incorrectly depicted as having sufficient coverage when they actually lack adequate internet access.
Misleading mapping data prevents policymakers and service providers from accurately identifying areas that require improved connectivity. As a result, efforts to bridge the digital divide and provide affordable broadband to all Americans are hampered. Monopolies exploit this flawed data to further their market dominance, leaving many communities without reliable internet access.
Public Policy Intervention
Addressing the issues of monopolies and mapping requires public policy intervention. To restore competition and foster innovation, policymakers need to create a more dynamic and decentralized internet infrastructure. Public policy measures should aim to break up concentrated power and encourage fair competition in the technology sector.
Moreover, the influence of platform monopolies on journalism is a grave concern. Monopoly ownership poses a structural threat to a healthy news media system, impacting not only internet access but also the diversity of voices in the media landscape. Unchecked control over information dissemination can have significant consequences for the society at large.
Conclusion
Monopolies and flawed mapping systems are detrimental to the accessibility of affordable broadband in the United States, particularly in low-income communities. Limitations in consumer choice, anti-competitive practices, and inaccurate mapping data hinder universal internet access and impede innovation in the industry. Public policy interventions focused on promoting competition, fostering innovation, and ensuring accurate mapping are vital to ensure affordable and accessible internet for all.
Sources:
1. The American Prospect. How Monopolies and Maps Are Killing ‘Internet for All’
2. The Gate. Why Monopolies Rule the Internet and How We Can Stop Them
According to recent reports, a record-breaking fiber has been developed that has the capability to transmit 20 times the global internet traffic per second. This groundbreaking technology is revolutionizing the way we experience the internet. Discover more about this incredible achievement at Record Breaking Fiber Transmits 20x Global Internet Traffic Per Second.
Discussion of the Significance of Accurate Mapping for Internet Connectivity
In today’s society, the internet plays a vital role in connecting people, providing information, and enabling various services. However, the prevalence of monopolies in the technology industry and the lack of accurate mapping systems pose significant challenges to achieving universal internet accessibility. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this issue and explore the implications it holds for all users.
The Power of Monopolies: Restricting Choices and Stifling Innovation
Monopolies in the technology sector, such as Google, Amazon, Apple, Meta (formerly Facebook), and Microsoft, have established a stronghold on the internet landscape. This concentration of power limits consumer choices, stifles competition, and undermines innovation. As a result, affordable broadband solutions, particularly in low-income communities, become scarce source.
To maintain their dominance, these monopolistic entities employ anti-competitive tactics that suppress or eliminate potential competitors. Startup companies that resist acquisition often face relentless anti-competitive practices and unfair pricing strategies, leading to their downfall source.
Mapping the Divide: The Role of Accurate Maps in Internet Accessibility
Accurate mapping of internet infrastructure is a crucial factor in bridging the digital divide and achieving universal connectivity. It allows policymakers, service providers, and community organizations to identify underserved regions and develop targeted initiatives. Proper network mapping enables stakeholders to understand the reality of internet coverage in specific areas, facilitating the planning of optimal network technologies and financing solutions source.
However, the current state of mapping systems falls short of these objectives. To harness the full potential of maps in addressing internet accessibility, a harmonized approach is needed, accompanied by guidelines and standards that ensure accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible maps. These efforts would allow for a comprehensive representation of the true state of internet connectivity, fostering collaborative initiatives source.
Overcoming Challenges: Towards a Universally Accessible Internet
Addressing the challenges posed by monopolies and flawed mapping systems requires a concerted effort from policymakers, regulatory bodies, and industry stakeholders. Here are some key takeaways on how we can strive towards a universally accessible internet:
Key Takeaways:
– Public policy interventions should focus on promoting competition, fostering innovation, and breaking up concentrated power in the technology sector.
– Comprehensive mapping systems that are accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible must be established, enabling the identification of underserved areas.
– Collaborative broadband mapping efforts should be fostered, utilizing a harmonized approach with guidelines and standards.
– Usability and usefulness of internet mapping platforms should be prioritized to ensure effective contribution to infrastructure development source.
– Efforts to improve internet mapping tools should aim for wider audience reach, precise spatial data, and enhanced participatory planning.
By addressing the perils of monopolies and flawed mapping systems, we can work towards a more equitable and accessible internet for all. Through collaborative efforts, policymakers, industry leaders, and individuals can help ensure that the internet remains a fundamental human right.
Sources:
– source
– source
– source
– source
– source
Examination of How Flawed Mapping Systems Contribute to Unequal Access to the Internet
The internet has become an integral part of our lives, providing access to information, services, and opportunities. However, the existence of monopolies in the technology sector and the presence of flawed mapping systems have created significant barriers to achieving universal internet access. In this article, we will delve into the detrimental effects of monopolies and flawed maps on internet accessibility and explore potential solutions to bridge the digital divide.
Monopolies, such as Google, Amazon, Apple, Meta (formerly Facebook), and Microsoft, hold tremendous power and control over different aspects of the online world. This concentration of power stifles competition and innovation, limiting consumer choices and affordable broadband solutions, particularly in low-income communities. These monopolistic entities employ anti-competitive tactics to maintain their dominance, hindering the development of a diverse and competitive internet ecosystem.
Accurate mapping of internet infrastructure is crucial for understanding the reality of internet coverage in various regions and identifying underserved areas. However, current mapping systems fall short of providing accurate and up-to-date information. Misleading mapping data perpetuates the digital divide by preventing the identification of areas that require improved connectivity. Without accurate maps, efforts to provide affordable broadband to all individuals face significant challenges.
To address these issues, it is essential to establish a common and harmonized approach to broadband mapping. Guidelines and standards should be set to ensure accurate, reliable, and easily accessible maps that reflect the true state of internet connectivity. Collaborative efforts between policymakers, service providers, and community organizations are required to develop comprehensive mapping systems that can bridge the digital divide effectively.
Improving internet mapping platforms is a step in the right direction. These platforms need to prioritize usability and usefulness to actively contribute to the development of internet infrastructure. Enhanced participatory planning, wider audience reach, and precise spatial data offered by improved mapping tools can foster the expansion of internet accessibility.
In conclusion, flawed mapping systems and monopolies in the technology sector pose significant challenges to achieving equal and accessible internet connectivity. Bridging the digital divide requires comprehensive efforts to foster competition, regulate monopolistic practices, and improve the accuracy and accessibility of mapping systems. By addressing these issues, we can pave the way for affordable and universal internet access for all individuals.
Key Takeaways:
- Monopolies in the technology sector, such as Google, Amazon, Apple, Meta, and Microsoft, limit consumer choices and stifle competition, hindering the development of affordable broadband solutions.
- Flawed mapping systems perpetuate the digital divide by providing inaccurate information on internet coverage, making it difficult to identify underserved areas.
- Collaborative efforts and guidelines are necessary to establish comprehensive and accurate mapping systems that reflect the true state of internet connectivity.
- Improving internet mapping platforms with enhanced usability and usefulness can contribute to the development of internet infrastructure.
- Bridging the digital divide requires addressing monopolistic practices, fostering competition, and improving the accessibility and accuracy of mapping systems.
Sources:
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Access to Information and Resources through the Internet
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). Impacts of the Internet on Health Inequality and Healthcare
- Patient Engagement HIT. Top 3 Challenges Limiting Patient Access to Health Data
- Taylor & Francis Online. Digital inequality beyond the digital divide
- UChicagoGate. Why Monopolies Rule the Internet and How We Can Stop Them
- SpringerLink. Bridging Digital Divides: a Literature Review and Research
- Europe PMC. Global mapping of urban-rural catchment areas reveals unequal
- UChicagoGate. Why Monopolies Rule the Internet and How We Can Stop Them
- ITU Hub. Broadband mapping: Key to universal connectivity
*Note: The URLs provided above are illustrative examples and may not directly match the sources listed in the context.
Exploration of the Implications of Monopolies and Maps on Marginalized Communities
Key Takeaways:
- Monopolies in the technology sector and flawed mapping systems have detrimental effects on internet accessibility for marginalized communities.
- Monopolistic control limits competition, stifles innovation, and leads to a lack of affordable broadband solutions, especially in low-income areas.
- Inaccurate mapping perpetuates the digital divide by hindering infrastructure development and preventing the identification of areas in need of improved connectivity.
- Marginalized communities, including children, women, people with disabilities, and older adults, are particularly vulnerable to the challenges posed by monopolies and flawed maps.
- Public policy interventions, promoting competition, fostering innovation, and ensuring accurate mapping, are crucial for achieving affordable and accessible internet for all.
The internet has become an essential tool in our society. It connects people, provides information, and enables various services. However, the prevalence of monopolies in the technology industry and the lack of accurate mapping systems are posing significant challenges to achieving universal internet accessibility, particularly for marginalized communities.
Monopolies, such as Alphabet (owner of Google), Amazon, Apple, Meta (formerly Facebook), and Microsoft, dominate different aspects of the online world. Unfortunately, their dominance limits consumer choices, stifles competition, and hampers the goal of providing widespread affordable broadband to all Americans [^1^].
Under the guise of fair competition, these internet monopolists often employ anti-competitive tactics to suppress or eliminate their opponents. Small startups that refuse to be bought out are faced with artificially lowered prices and other anti-competitive practices, ultimately leading to their demise [^2^].
Accurate mapping of internet infrastructure plays a crucial role in bridging the digital divide and achieving universal connectivity. However, the current state of mapping systems falls short of these objectives. A common, harmonized approach is needed to ensure accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible maps that reflect the true state of internet connectivity. This would enable policymakers, service providers, and community organizations to identify underserved regions and develop targeted initiatives [^3^].
The implications of monopolies and flawed mapping systems are particularly severe for marginalized communities. These communities face numerous challenges, including social exclusion, limited healthcare access, damaged infrastructure, unemployment, and a digital divide. Monopolies and inaccurate mapping exacerbate these challenges, deepening the inequality experienced by marginalized groups [^4^].
To address these issues, public policy interventions are necessary. Policymakers should focus on promoting competition, fostering innovation, and ensuring accurate mapping. Creating a more dynamic and decentralized internet infrastructure, breaking up concentrated power in the technology sector, and implementing measures that prioritize the internet as a fundamental human right are crucial for achieving affordable and accessible internet for all [^5^].
In conclusion, monopolies in the technology sector and flawed mapping systems pose significant challenges to achieving universal internet accessibility, particularly for marginalized communities. It is essential to recognize the detrimental effects of monopolies and inaccurate mapping on internet accessibility and take decisive action to promote competition, innovation, and accurate mapping. By prioritizing inclusivity and equitable access to the internet, we can work towards a future where everyone can benefit from the opportunities and resources provided by the online world.
Sources:
[^1^]: Prospect: How Monopolies and Maps Are Killing ‘Internet for All’
[^2^]: UChicagoGate: Why Monopolies Rule the Internet and How We Can Stop Them
[^3^]: ITU Hub: Broadband mapping: Key to universal connectivity
[^4^]: MDPI: Challenges Faced by Marginalized Communities in a Post-Disaster Context
[^5^]: ICMA: Engaging Marginalized Communities: Challenges and Best Practices
- Crypto Quotes’ Red Flags: Avoid Costly Mistakes - June 30, 2025
- Unlock Inspirational Crypto Quotes: Future Predictions - June 30, 2025
- Famous Bitcoin Quotes: A Deep Dive into Crypto’s History - June 30, 2025