To embark on an odyssey through time, explore the intricate historical tapestry of Morocco unveiled in our article, “Timeline of Morocco’s History: A Journey Through the Centuries.” Delve into the annals of this captivating nation, uncovering the rich legacy that has shaped its identity and continues to reverberate in its vibrant present. From ancient civilizations to modern-day transformations, this article paints a vivid picture of Morocco’s remarkable journey across the centuries.
Key Takeaways:
- Morocco’s history dates back to the 7th and 8th centuries AD with the introduction of Islam.
- Various dynasties and religious movements ruled Morocco, including the Almoravids, Almohads, and Saadi dynasties.
- In 1912, Morocco became a French protectorate, leading to uprisings and resistance movements like the Rif War.
- After independence in 1956, Morocco faced challenges such as the Western Sahara conflict and the Polisario Front seeking independence for Western Sahara.
- King Hassan II’s passing in 1999 led to King Mohammed VI’s reign, who implemented reforms for modernization and democratization.
- Morocco achieved significant economic growth, becoming a popular tourist destination and regional economic hub.
- Morocco continues to address challenges related to human rights, poverty, and inequality.
History of Morocco Timeline: Unveiling a Tapestry of Empires, Dynasties, and Cultural Heritage
The history of Morocco is a captivating narrative woven with the threads of empires, dynasties, and a rich cultural tapestry. Let’s delve into a timeline that will transport us through the centuries, unveiling the defining moments that have shaped this vibrant nation.
Early Morocco: Laying the Foundation
- 7th-8th Centuries AD: The Arrival of Islam
Umayyad Caliphate establishes Islamic rule in Morocco, introducing a new era of cultural and religious transformation.
8th-11th Centuries AD: Rise of the Idrisid Dynasty
- Morocco’s first independent Islamic dynasty emerges, establishing Fez as its capital and laying the foundation for future Moroccan identity.
The Almoravid and Almohad Dynasties: A Legacy of Conquest and Cultural Flourishing
- 11th-12th Centuries AD: Reign of the Almoravids
Berber dynasty conquers vast territories, stretching from present-day Mauritania to Spain, leaving behind a legacy of architectural wonders like the Koutoubia Mosque.
12th-13th Centuries AD: The Almohad Dynasty’s Golden Age
- Expansion of the empire continues, with conquests in Spain and North Africa, while advancements in science, literature, and architecture flourish.
The Saadi Dynasty: Unveiling the Splendors of the Sahara
- 16th-17th Centuries AD: The Saadian Empire Rises
Morocco’s southern territories expand, securing control over the lucrative Saharan trade routes and establishing Marrakech as the imperial capital.
Architectural Marvels: The Alhambra of Morocco
- The Saadians leave an indelible mark with the construction of the Bahia Palace in Marrakech and the renovation of the Kasbah of the Udayas.
A New Era Dawns: Colonialism and the Path to Independence
- 1912-1956: French Protectorate
Morocco falls under French control, igniting resistance movements. The Rif War of 1921-1926 emerges as a pivotal moment in the struggle for independence.
1956: The Dawn of Independence
- Morocco regains its sovereignty under King Mohammed V, ushering in a new chapter of self-governance and national unity.
Contemporary Morocco: Navigating Challenges and Embracing Development
- 1961: King Hassan II Ascends to the Throne
Morocco faces internal conflicts and regional disputes, including the Western Sahara conflict, while pursuing economic development and modernization.
1999: A New Era under King Mohammed VI
King Mohammed VI introduces reforms to promote human rights, economic liberalization, and social progress.
21st Century: A Hub of Tourism and Economic Growth
- Morocco emerges as a popular tourist destination, showcasing its cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and modern infrastructure.
As we trace the history of Morocco timeline, we witness a land where empires have risen and fallen, where cultural influences have intertwined, and where the spirit of resilience and progress continues to shape its destiny. Morocco’s rich tapestry is an invitation to delve deeper into its past, to appreciate its present, and to anticipate its future with optimism and wonder.
Find out the history of mass media in India and see how it has changed with people’s perspective over time. history of mass media in india.
Learn in detail about Media Law in India, and its development throughout history with important details and case studies. history of media law in india.
Discover the rich historical account of the Mountain Province with its background, people and famous landmarks. history of mountain province.
Foundation of the Idrisid Dynasty
Jumpstarting Moroccan History:
The Foundation of the Idrisid Dynasty [1] marks a pivotal chapter in Morocco’s storied past. This Arab Muslim dynasty reigned over most of present-day Morocco and parts of western Algeria from 788 to 974, leaving an enduring legacy that reverberates to this day.
Key Takeaways:
- The Idrisid dynasty was founded by Idris I, a great-grandson of the Prophet Muhammad.
- Idris I sought refuge in Morocco after fleeing political persecution in the Abbasid Caliphate.
- The dynasty established its capital in Fez, which flourished as a cultural and religious center.
- The Idrisids played a crucial role in the Islamization of Morocco and the Maghreb region.
- The dynasty’s reign ushered in a period of stability and prosperity, marked by trade, agriculture, and architectural achievements.
The Rise of a Sharifian Dynasty:
In the mid-8th century, Idris I, a descendant of the Prophet Muhammad, fled the Abbasid Caliphate in present-day Iraq due to political turmoil. Seeking refuge in Morocco, he found support among the local Berber tribes, who embraced his leadership and religious teachings. In 788, Idris I established the Idrisid dynasty, marking the beginning of a new era in Moroccan history.
Fez: A Cultural and Religious Hub:
Idris I chose the city of Fez as his capital, recognizing its strategic location and potential for growth. Under the Idrisid rule, Fez transformed into a vibrant center of learning, culture, and religion. The city’s famed Al-Qarawiyyin Mosque, founded in the 9th century, became a renowned institution of Islamic scholarship and attracted students from across the Muslim world.
Islamization of Morocco:
The Idrisids played a pivotal role in the Islamization of Morocco and the wider Maghreb region. They actively promoted the Islamic faith and encouraged the adoption of Islamic laws and customs. Their efforts laid the foundation for Morocco’s strong Islamic identity, which persists to this day.
A Legacy of Stability and Prosperity:
The Idrisid dynasty brought a period of stability and prosperity to Morocco. They established a centralized government, maintained peace and security, and fostered trade and agriculture. The dynasty’s architectural achievements, such as the construction of mosques, palaces, and irrigation systems, showcased their commitment to urban development and infrastructure.
The Idrisid dynasty’s reign came to an end in 974, but their legacy lived on. The dynasty’s contributions to Morocco’s political, cultural, and religious landscape were profound and laid the groundwork for the country’s future development.
Sources:
[1] Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopedia. “Idrisid dynasty.” Encyclopedia Britannica, Accessed 14 March 2023.
[2] Wikipedia contributors. “Idrisid dynasty.” Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Idrisid_dynasty&oldid=1144368717. Accessed 14 March 2023.
Almoravid and Almohad Empires: A Legacy of Conquest and Cultural Exchange
In the vast tapestry of Morocco’s rich history, the Almoravid and Almohad Empires stand as beacons of power and influence, leaving an indelible mark on the country’s cultural, political, and architectural landscape.
The Almoravids: A Dynasty Rooted in Reform
Emerging from the Sahara in the 11th century, the Almoravids swept across Morocco like a desert storm, fueled by a zeal for Islamic reform and a thirst for conquest. Their strict adherence to Quranic law and commitment to simplicity won them the support of Berber tribes, uniting them under a single banner.
Led by the charismatic warrior-scholar Yusuf ibn Tashfin, the Almoravids embarked on a mission to spread their puritanical brand of Islam and establish a vast empire that stretched from the Atlantic coast to the gates of Cordoba. Their military prowess and organizational skills propelled them to victory, transforming Morocco into a regional powerhouse.
The Almohads: A Golden Age of Expansion and Refinement
The 12th century witnessed the rise of the Almohads, another reformist movement that emerged from the Atlas Mountains. Inspired by the teachings of Ibn Tumart, a charismatic mystic, the Almohads sought to purify Islam and restore its original principles.
Under the leadership of Abd al-Mu’min, the Almohads overthrew the Almoravids and established a vast empire that spanned Morocco, Algeria, and much of Spain. Their reign ushered in a golden age of cultural and intellectual flourishing, marked by grand architectural achievements, advancements in science and philosophy, and a vibrant artistic tradition.
Architectural Marvels of the Almoravids and Almohads
The Almoravids and Almohads left a lasting legacy in the form of architectural masterpieces that continue to captivate visitors to this day. Their distinctive style, characterized by intricate geometric patterns, graceful arches, and soaring minarets, can be seen in mosques, palaces, and city walls throughout Morocco.
The Almoravids are renowned for the construction of the Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech, a towering edifice that remains one of the city’s most iconic landmarks. With its elegant proportions, exquisite carvings, and a minaret that pierces the sky, the Koutoubia Mosque epitomizes the architectural brilliance of the era.
The Almohads took architectural refinement to new heights, leaving behind a legacy of monumental structures that showcased their mastery of design and engineering. The Hassan Tower in Rabat, an unfinished minaret that would have dwarfed the Koutoubia, stands as a testament to the ambitious vision of the Almohads. Its sheer size and intricate ornamentation evoke a sense of awe and wonder.
The Legacy of Two Empires
The Almoravids and Almohads ruled Morocco for over two centuries, leaving an enduring legacy that shaped the country’s political, cultural, and religious identity. Their military prowess, architectural achievements, and commitment to Islamic reform laid the foundation for Morocco’s emergence as a regional power.
Even after their decline, the Almoravids and Almohads continued to influence Morocco’s history. Their architectural masterpieces remain sources of pride and inspiration, drawing visitors from around the world to marvel at their beauty and grandeur. Their legacy lives on in the vibrant culture, traditions, and historical heritage of modern Morocco.
Key Takeaways:
The Almoravid dynasty, founded by Yusuf ibn Tashfin, arose in the 11th century and established a vast empire rooted in Islamic reform.
The Almohads, led by Abd al-Mu’min, emerged in the 12th century and overthrew the Almoravids, ushering in a golden age of cultural and intellectual flourishing.
The Almoravids and Almohads left an indelible mark on Morocco’s architecture, constructing masterpieces such as the Koutoubia Mosque and the Hassan Tower.
Their empires contributed to the spread of Islamic culture, art, and learning, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to shape Morocco’s identity.
Sources:
[1]
[2] https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/almo/hd_almo.htm
Emergence of the Saadian Dynasty
The rise of the Saadian Dynasty marked a significant shift in Morocco’s history, transitioning from Berber-led empires to Arab Sharifian dynasties. Their story is a captivating blend of resistance, conquest, and architectural splendor.
Muhammad al-Qa’im: A Spark of Rebellion
The Saadian saga began in the Sous valley, where Muhammad al-Qa’im emerged as a beacon of resistance against Portuguese occupation. Leading the tribal forces, he ignited the flame of rebellion, setting the stage for the dynasty’s remarkable ascent.
Conquest and Consolidation: The Reign of Muhammad al-Shaykh
Muhammad al-Shaykh, the successor to al-Qa’im, further cemented the Saadian dynasty’s power. His strategic prowess led to the capture of strategic cities like Agadir from the Portuguese and Fez from the Wattasids, solidifying the dynasty’s control over vast swathes of Morocco.
A Dynasty Divided: The Battle of Ksar el-Kebir
After Muhammad al-Shaykh’s tragic assassination, the dynasty faced internal strife as rival successors clashed for the throne. This culminated in the pivotal Battle of Ksar el-Kebir in 1578, where Portuguese intervention on behalf of one of the claimants ended in defeat.
Ahmad al-Mansur: A Golden Reign
Ahmad al-Mansur emerged triumphant from the chaos, ushering in a golden era for the Saadian Dynasty. Under his rule, the dynasty reached its zenith, expanding its influence and leaving a lasting imprint on Morocco’s architectural landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- Rise against Occupation: Muhammad al-Qa’im ignited the flame of resistance against Portuguese occupiers, marking the beginning of the Saadian Dynasty’s remarkable journey.
- Conquest and Consolidation: Muhammad al-Shaykh’s military prowess expanded the dynasty’s reach, capturing key cities and consolidating their control over Morocco.
- Internal Conflict: After Muhammad al-Shaykh’s assassination, the dynasty faced internal strife as rival claimants battled for power, leading to the pivotal Battle of Ksar el-Kebir.
- Golden Age: Ahmad al-Mansur’s reign marked the apex of Saadian power, leaving a lasting legacy of architectural marvels and expanding the dynasty’s influence.
- Enduring Legacy: The Saadian Dynasty laid the foundation for a new era in Moroccan history, leaving behind a rich legacy and architectural masterpieces that continue to captivate visitors today.
Sources:
- The Saadi Dynasty of Morocco
- Mark Greengrass, Christendom Destroyed: Europe 1517-1648 (Penguin Books, 2014)
FAQ
Q1: What was the significance of the Idrisid dynasty in Moroccan history?
A1: The Idrisid dynasty played a crucial role in the early Islamization of Morocco. Founded by Idris I, a descendant of the Prophet Muhammad, the dynasty established the sharifian tradition and contributed to the linguistic Arabization of parts of northern Morocco.
Q2: How did the Almoravid dynasty come to power in Morocco?
A2: The Almoravid dynasty emerged as a conservative Islamic reform movement led by the Berber tribes of the Sahara. They gained military strength through their infantry armed with spears and swords, and their adoption of the black standard symbolized the religious nature of their political and military movement.
Q3: What were the achievements of the Saadi dynasty in Morocco?
A3: The Saadi dynasty, led by the Arab Moroccan Sharifian dynasty, expanded their rule over most of Morocco by capturing key cities like Agadir and Fez. Under the reign of Ahmad al-Mansur, the Saadians reached the height of their power and established a model of political-religious legitimacy that would be continued by subsequent dynasties.
Q4: What was the impact of the French protectorate on Morocco?
A4: The French protectorate, established in 1912 by the Treaty of Fez, lasted until Morocco’s independence in 1956. During this period, Morocco experienced several uprisings and resistance movements, including the Rif War of 1921-1926. The protectorate had a significant impact on Morocco’s political, economic, and social development.
Q5: What are the main challenges facing Morocco today?
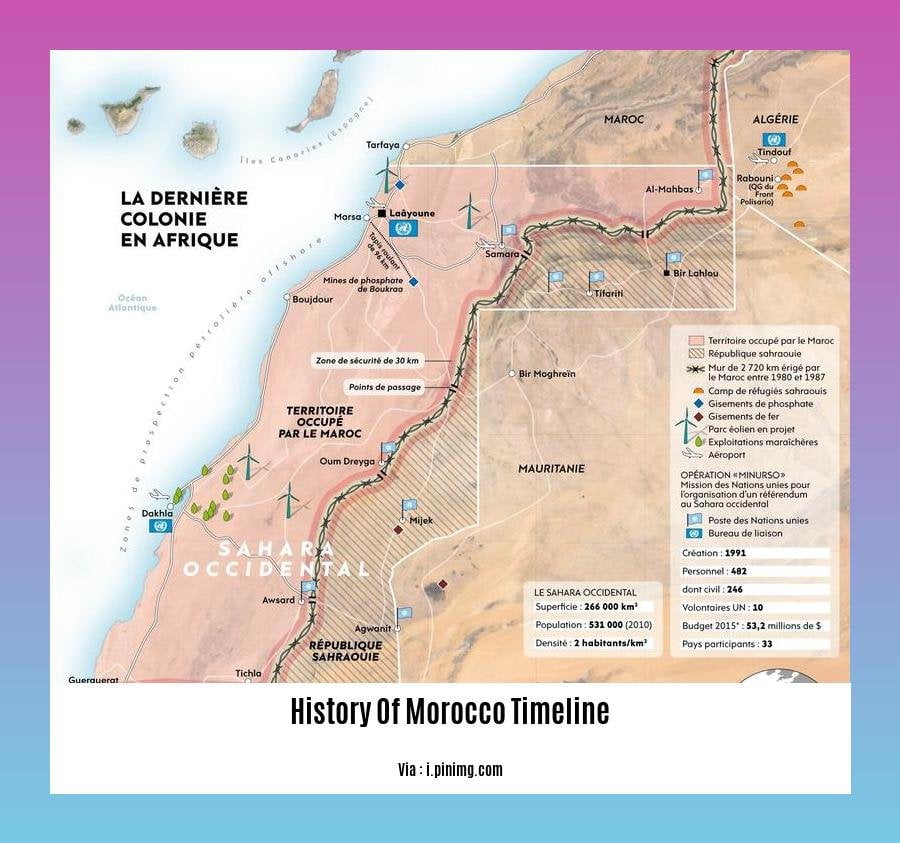
A5: Morocco continues to face several challenges, including human rights issues, poverty, and inequality. The country is also engaged in the Western Sahara conflict, which began in 1975 when Morocco annexed the former Spanish colony. The government is working to address these challenges through various initiatives aimed at promoting economic development, social justice, and human rights.
















