Embark on a cinematic journey through time with “Of Silver Screens and Time: A Historical Timeline of Cinema’s Evolution.” From the flickering shadows of the silent era to the immersive spectacles of modern blockbusters, this comprehensive timeline unveils the remarkable transformation of the silver screen. Prepare to delve into a century of innovation, artistry, and storytelling that has captivated audiences worldwide.
Key Takeaways:
Film history can be divided into the Pre-Film Era, the Nascent Film Era, and various film movements.
Techniques for taking pictures and early experiments with film theory marked the Pre-Film Era.
Early 20th-century film movements like Dadaism and German Expressionism challenged traditional narratives and explored new cinematic expressions.
The Golden Age of Hollywood led to the rise of major film studios and iconic stars.
The New Hollywood era shifted toward more personal and experimental filmmaking.
Digital technology revolutionized filmmaking, offering new special effects, editing, and distribution possibilities.
Of Silver Screens and Time: A Historical Timeline of Cinema’s Evolution [history of cinema timeline]
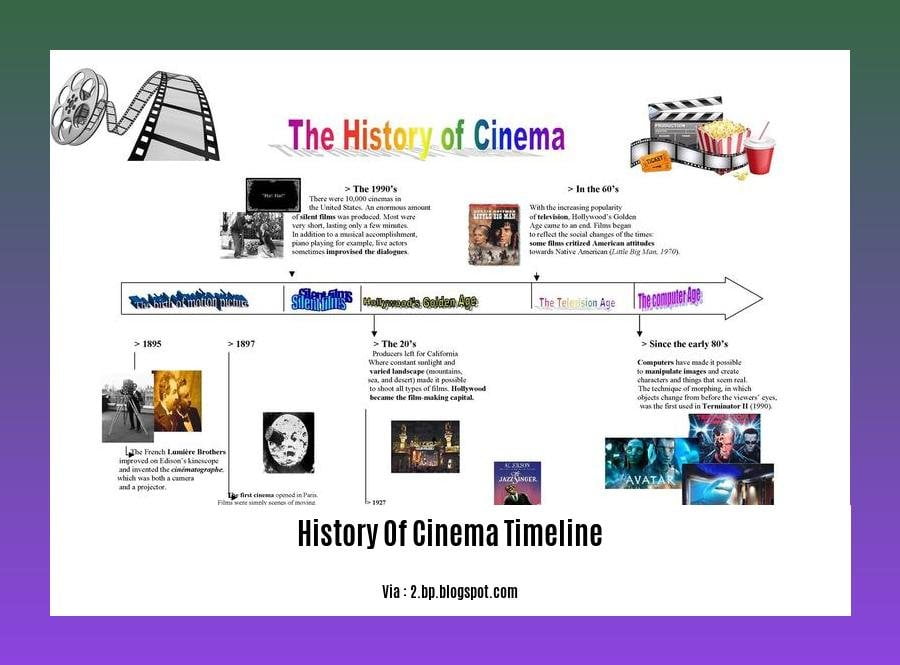
Cinema, the art form that has captivated audiences for over a century, didn’t just appear overnight. It underwent a remarkable journey, evolving from a novelty to a global phenomenon. Let’s explore the milestones that shaped the history of cinema timeline.
Embracing Shadows: The Pre-Film Era (1870s-1910)
- This era laid the groundwork for cinema’s birth.
- Inventions like the thaumatrope and the phenakistoscope created the illusion of movement.
- Eadweard Muybridge’s experiments with motion photography brought us closer to capturing life in motion.
Birth of an Industry: The Nascent Film Era (1910-1920s)
- The first narrative films emerged, introducing storytelling to the silver screen.
- Trailblazers like Georges Méliès pushed boundaries with special effects and fantastical narratives.
- The American film industry took shape, with Hollywood becoming a hub for filmmaking.
Cinema Finds Its Voice: The Silent Film Era (1920s-1930s)
- Silent films reached their zenith, captivating audiences with visual storytelling and expressive acting.
- Charlie Chaplin and Buster Keaton became icons of the era, using physical comedy to convey emotions.
- The rise of film studios led to a surge in production and distribution.
Sound Takes Center Stage: The Golden Age of Hollywood (1930s-1960s)
- The introduction of sound revolutionized filmmaking, adding a new dimension to storytelling.
- Hollywood’s golden age saw the emergence of iconic studios like Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer and Warner Bros.
- Classic films from this era, like Casablanca and Gone with the Wind, left an indelible mark on cinema history.
A New Wave of Creativity: The New Hollywood Era (1960s-1980s)
- The 1960s marked a shift towards more personal and experimental filmmaking.
- Directors like Martin Scorsese and Francis Ford Coppola challenged conventions and pushed creative boundaries.
- New Hollywood films addressed social and political issues, reflecting the changing times.
Digital Revolution: The Modern Era (1990s-Present)
- The advent of digital technology transformed filmmaking processes.
- Computer-generated imagery (CGI) opened up new possibilities for visual effects and storytelling.
- Indie films gained prominence, challenging Hollywood’s dominance.
- Streaming services revolutionized distribution, making films more accessible than ever.
Where Does Cinema Go From Here?
As we look to the future, the history of cinema timeline continues to unfold. What new innovations and stories will grace the silver screen? Only time will tell, but one thing is for sure: cinema’s journey is far from over.
To delve deeper into the roots of the vibrant bachata dance, read the intriguing account of its history here.
Keen on learning how bachata music evolved? Discover the fascinating tale of its enchanting beats.
Embark on a journey through time and explore the captivating history of badminton in the Philippines by clicking here.
Step into the court of history and witness the evolution of basketball rules in this enthralling narrative by Clicking here.
New Wave Cinema (1960-1980): A Revolution in Storytelling

Oh, hello there, cinema enthusiasts! Welcome to a journey through the disruptive era of New Wave Cinema that shook the industry to its core from the ’60s to the ’80s. It was a time when audacious filmmakers thumbed their noses at Hollywood conventions and reshaped the narrative landscape forever!
Breaking the Mold of Traditional Cinema
Before we dive into the New Wave revolution, let’s rewind a bit. In the ’50s, Hollywood was all about conformity and safety. The old guard was churning out predictable stories that were more concerned with box-office success than artistic expression.
The Birth of a New Era
It all began with the Paramount Case in 1948, which shattered the ironclad grip of the studio system. Independent filmmakers saw their chance to break free from those studio shackles and tell stories that truly mattered. Inspired by European pioneers like Truffaut and Godard, these risk-takers challenged conventional filmmaking techniques.
Key Ingredients of New Wave Cinema
Realism and Grit: These films traded glossy sets for the gritty realities of everyday life, shedding light on taboo topics and embracing a more documentary-like style.
Auteurs Take Center Stage:** Directors became the visionaries, asserting their personal styles and perspectives into their work. New Wave cinema was all about the art of filmmaking, not just churning out commercial successes.
Experimental Techniques:
From jump cuts and freeze frames to unconventional camerawork, nothing was off-limits. These filmmakers weren’t afraid to push boundaries and subvert expectations.
The New Wave Legacy
A Lasting Impact:
The New Wave revolution didn’t just shake things up; it changed Hollywood forever. It set the stage for a new era of personal, auteur-driven filmmaking that still influences cinema today.New Wave Icons:
François Truffaut, Jean-Luc Godard, Woody Allen, Martin Scorsese, and Francis Ford Coppola stand as just a few of the visionaries who led the charge.A Global Phenomenon:
The New Wave Movement wasn’t confined to Hollywood. It spread like wildfire across the globe, inspiring filmmakers worldwide to challenge norms and create groundbreaking works of art.
Key Takeaways:
New Wave Cinema emerged during the ’60s and ’80s as a response to the conformist Hollywood studio system.
It championed realism and grit over artificiality, with directors injecting personal styles into their work and embracing experimental techniques.
New Wave Cinema had a profound impact on the film industry, ushering in an era of auteur-driven filmmaking and inspiring a global movement of cinematic innovation.
Notable New Wave directors include François Truffaut, Jean-Luc Godard, Woody Allen, Martin Scorsese, and Francis Ford Coppola.
Sources:
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Hollywood
[2]
Blockbuster Era (1980-2000): The Age of Tentpole Films
The 1980s marked a tectonic shift in the film industry, ushering in an era where spectacle, marketing, and merchandise sales reigned supreme—the Blockbuster Era. This period witnessed the birth of tentpole films, cinematic behemoths designed to attract massive audiences and shatter box office records.
Gone were the days of intimate, character-driven stories. Instead, the big screen was dominated by larger-than-life action sequences, eye-popping special effects, and star-studded casts. Films like “Star Wars,” “Indiana Jones,” and “Jaws” redefined what it meant to go to the movies, transforming cinema into a global phenomenon.
Key Moments in the Blockbuster Era:
- 1975: The release of “Jaws” marked a turning point, showcasing the potential of high-concept films with mass appeal.
- 1977: “Star Wars” took the world by storm, becoming a cultural phenomenon and paving the way for a new era of science fiction blockbusters.
- 1982: “E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial” touched hearts worldwide, cementing Spielberg’s status as a master storyteller and setting new box office records.
- 1993: “Jurassic Park” pushed the boundaries of visual effects, becoming the first film to gross over $900 million worldwide.
Key Takeaways:
- The Blockbuster Era was marked by a shift towards big-budget, crowd-pleasing films designed to appeal to a wide audience.
- Spectacle, marketing, and merchandise sales became key components of the blockbuster formula.
- Tentpole films, such as “Star Wars” and “Indiana Jones,” dominated the box office and redefined the movie-going experience.
- The Blockbuster Era had a profound impact on the film industry, shaping the way movies are produced, marketed, and consumed.
Sources:
- The Blockbuster Era: How Hollywood Changed in the 1980s
- The 25 Highest-Grossing Movies of the 1980s
Digital Revolution (2000-Present): The Transformation of Cinema
The dawn of the new millennium heralded a seismic shift in the world of cinema—the Digital Revolution. It was an era marked by a fundamental transition from traditional film-based methods to a fully digital filmmaking process. This technological revolution brought about a kaleidoscope of changes in the creation, distribution, and consumption of motion pictures, leaving an indelible mark on the cinematic landscape.
The Digital Revolution: Turning Points in Cinema
The Advent of Digital Cinema Cameras
The advent of digital cinema cameras marked the beginning of a new era in filmmaking. These cameras, unlike their film-based predecessors, captured images using digital sensors, eliminating the need for physical film stock. The digital format offered a host of advantages, including ease of use, lower production costs, and the ability to manipulate footage with greater precision.
Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) and Visual Effects (VFX)
The digital revolution opened the door to a realm of boundless visual possibilities. Computer-generated imagery (CGI) and visual effects (VFX) emerged as powerful tools, enabling filmmakers to create stunning and realistic visuals that were previously unimaginable. From the fantastical worlds of “The Lord of the Rings” to the groundbreaking motion capture technology in “Avatar,” digital technology revolutionized the way we experience cinema.
Digital Distribution and Streaming Services
The digital revolution extended its reach beyond the production process, transforming the distribution and consumption of films. The rise of digital platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Hulu disrupted the traditional theatrical release model, making movies more accessible than ever before. Streaming services offered viewers the convenience of watching films on demand, from the comfort of their own homes.
The Democratization of Filmmaking
The reduced costs associated with digital filmmaking democratized the filmmaking process, allowing aspiring filmmakers to create and distribute their own works without the constraints of traditional film production. This led to a surge in independent filmmaking, giving rise to diverse and unique voices that enriched the cinematic landscape.
Key Takeaways:
The digital revolution brought about a paradigm shift in filmmaking, transitioning from film-based to digital methods.
Digital cinema cameras offered advantages such as ease of use, lower costs, and greater control over footage manipulation.
CGI and VFX revolutionized visual storytelling, enabling filmmakers to create stunning and realistic effects.
Digital distribution platforms like streaming services transformed film consumption, making movies more accessible and convenient.
The democratization of filmmaking empowered independent filmmakers, leading to a surge in diverse and unique cinematic voices.
References:
[1]
[2]
FAQ
Q1: What were the major eras in the history of cinema?
A1: The major eras in the history of cinema include the Pre-Film Era, the Nascent Film Era, the Golden Age of Hollywood, the New Hollywood Era, and the rise of digital technology.
Q2: What were some of the first film movements?
A2: Some of the first film movements were Dadaism and German Expressionism, which emerged during the early 20th century and challenged traditional storytelling techniques.
Q3: What was the New Hollywood movement, and how did it impact the film industry?
A3: The New Hollywood movement was a period in American film history from the mid-1960s to the early 1980s characterized by a generation of young filmmakers challenging the traditional Hollywood studio system. It had a lasting impact on the industry by ushering in a new era of more experimental and challenging films.
Q4: How has technology transformed the filmmaking process?
A4: The evolution of technology in cinema has led to advancements like CGI, VFX, digital filmmaking, and motion capture technology, transforming the filmmaking process from film to digital.
Q5: How did the introduction of color, animation, and sound impact the development of film?
A5: The introduction of color, animation, and sound played a significant role in the development of film, enhancing storytelling and creating a more immersive experience for audiences.