Are you prepared to explore the intriguing domain of condensation and evaporation? This article will reveal an abundance of intriguing facts that provide insight into the mechanisms underlying these remarkable natural phenomena. By working together, we shall investigate the scientific principles underlying condensation and evaporation in order to unveil the marvels they conceal. Therefore, settle in for an enthralling exploration of the fascinating realm of condensation and evaporation.
Fascinating Facts: Unveiling the Wonders of Condensation and Evaporation
Evaporation and condensation are two remarkable phenomena that are indispensable to our daily existence. By acquiring knowledge regarding condensation and evaporation, it is possible to decipher the enigmas that surround these intriguing natural occurrences. Therefore, let us immediately delve into the intriguing realm of condensation and evaporation!
“Evaporation: Gas to Liquid”
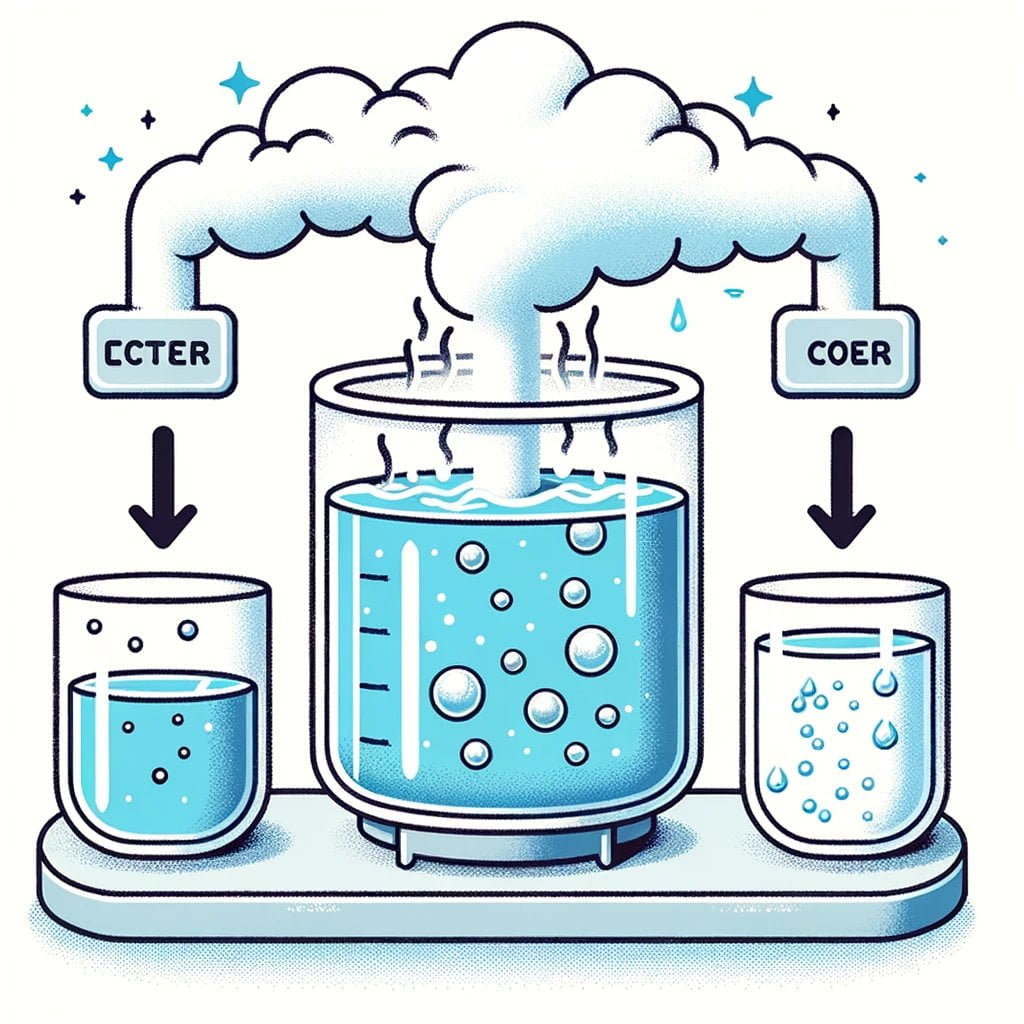
The manner in which matter can change states during condensation and evaporation is among the most intriguing aspects of these processes. Evaporation is the precise term used to describe the transformation of a substance from a liquid state to a gaseous state as a result of an elevated temperature. This marvelous phenomenon enables the transformation of water, for example, into vapor, which then ascends into the atmosphere.
Were you aware? The sun is an indispensable component in the evaporation process. When volumes of water on the Earth’s surface, including puddles, rivers, and lakes, are heated, the liquid molecules acquire sufficient energy to transition from their liquid state to that of gas.
The Condensation Process: Gas to Liquid
Conversely, condensation signifies the transformation of a gas back into its liquid state. This occurs when the gas’s molecules decelerate and become more closely spaced due to a decrease in temperature. The consequence is that the gas molecules lose energy and condense into liquid particles, which adhere to surrounding surfaces.
Have you ever observed water beads forming on the exterior of a chilled beverage? Condensation is at work here! These invigorating droplets form on the surface of the glass as a result of the water vapor in the air being transformed into liquid water droplets due to the glass’s low temperature.
The Water Cycle: A Grand Scale Analysis of Evaporation and Condensation
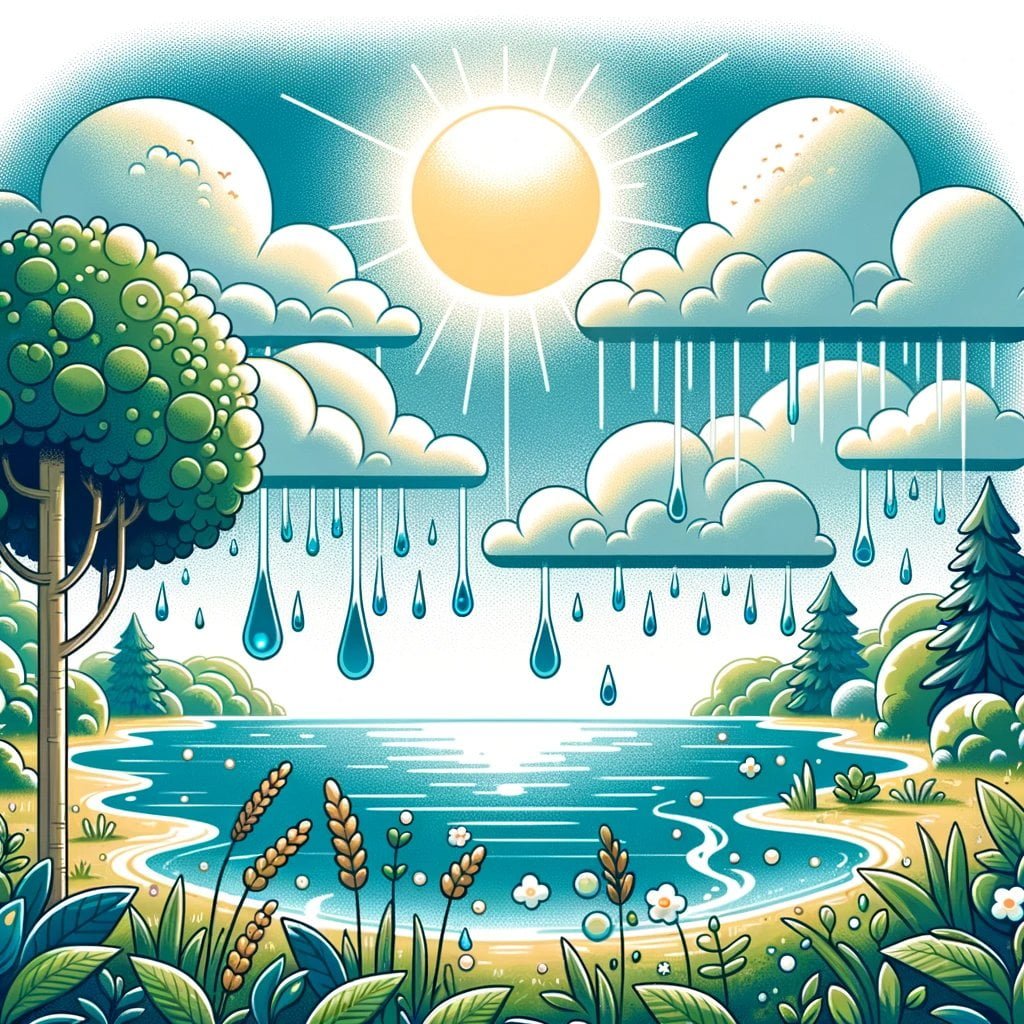
Evaporation and condensation, although captivating in and of themselves, are integral components of the water cycle, a significantly more extensive phenomenon. This cycle encompasses the perpetual motion of water, which undergoes transformations among its various states as a result of the fluctuating energy levels within the Earth’s atmosphere.
The evaporation of water from the Earth’s surface, including lakes, oceans, and vegetation, initiates the water cycle. Water that dissipates into the atmosphere produces clouds composed of vapor. Within these clouds, condensation takes place as the temperature decreases; this process converts the vapor into liquid droplets, which subsequently aggregate to form clouds.
Condensation is a critical component of the water cycle due to its role in cloud formation, which ultimately culminates in the generation of precipitation in the form of snow or rain.
The Consequences of Evaporation and Condensation on Daily Life
In addition to their substantial implications for the water cycle, condensation and evaporation exert a profound influence on the course of our everyday existence. These phenomena, which range from the fog that envelops an urban area to the morning dew that adorns vegetation, all contribute to the dynamic weather patterns and climate fluctuations that occur globally. By gaining knowledge about condensation and evaporation, one can develop an appreciation for the complex mechanisms that govern our environment.
Notably, condensation is a crucial component in the operation of steam turbines. Through the process of steam generation from simmering water, thermal energy can be converted into mechanical work that can be utilized to power a variety of machines and generate electricity.
In summary, the information pertaining to condensation and evaporation reveals an intriguing realm replete with changes and transitions. These phenomena, which include the water cycle, cloud formation, and steam engine propulsion, exert a profound influence on both our planet and our everyday existence. Through an exploration of the phenomena of condensation and evaporation, one can develop a deeper admiration for the splendor and intricacy of the natural world.
Bear in mind that evaporation and condensation are remarkable phenomena that facilitate the transition of matter between distinct states. These transitions—from liquid to gas and back again—influence our surroundings and contribute to the ever-changing quality of our planet. Therefore, the next time you observe the development of clouds or appreciate the steam that rises from your morning coffee, pause momentarily to behold the intriguing information regarding condensation and evaporation that form the basis of these natural occurrences.
Condensation, an intriguing natural phenomenon, is the transformation of water vapor into liquid droplets. If you are interested in discovering additional knowledge regarding this process and the fascinating facts that surround it, please visit our webpage devoted to condensation facts. Gain an understanding of its formation on diverse surfaces, its influence on weather patterns, and its practical implications. Enhance your comprehension of this enthralling process by thoroughly examining the information provided in our all-encompassing guide. So go ahead, satisfy your curiosity, and click here to unravel the mysteries of condensation: facts about condensation.
Facts About Condensation and Evaporation:
Condensation and evaporation are fascinating natural processes that play a crucial role in our everyday lives. If you’ve ever wondered about the science behind these phenomena, we’ve got you covered! Dive into the captivating world of condensation and evaporation with our comprehensive article, “Facts About Condensation and Evaporation”. This informative piece will uncover all the secrets behind these intriguing processes and their impact on the environment. From the water cycle to the formation of clouds, you’ll learn about the essential role that condensation and evaporation play in shaping our world. Don’t miss out on the chance to expand your knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of these amazing scientific processes. Click here to explore “Facts About Condensation and Evaporation” now.
But wait, there’s more! Are you interested in learning more fascinating facts about evaporation? Look no further! Our article, “Facts About Evaporation,” is jam-packed with intriguing information that will satisfy your curiosity. Discover the various factors influencing evaporation rates, from temperature and humidity to surface area. Unearth the surprising ways in which evaporation impacts our environment, from cooling systems to the preservation of food. Soak up all the knowledge and uncover the mysteries behind this essential natural process. Click here to delve into “Facts About Evaporation” and expand your understanding of this incredible phenomenon.
Remember, knowledge is power, and with these two articles, you’ll become an expert on condensation, evaporation, and their fascinating facts. Happy reading!
Explore “Facts About Condensation and Evaporation.”
Delve into “Facts About Evaporation.”
Evaporation vs. Condensation: Understanding the Key Processes of Matter Transformation
An Explanation of Evaporation and Condensation
Evaporation and condensation are intrinsic phenomena that are vital to the process of matter transformation. A comprehensive understanding of these processes is imperative for grasping the complex mechanisms that govern the natural environment that envelops us.
Evaporation is the process by which a liquid substance changes state from liquid to gas or vapor. This phenomenon predominantly occurs when the liquid’s temperature is increased. An instance of this is when the heat generated by the sun’s rays evaporates water from a lake, transforming it into water vapor.
When the liquid assimilates the thermal energy from its environment, the particles acquire sufficient kinetic energy to liberate themselves from the attractive forces that confine them in place. This energy enables the egress of liquid molecules into the atmosphere, resulting in the formation of water vapor.
Conversely, condensation refers to the reverse-phase transition of a gas or vapor back into a liquid state. This is the result of the gas’s molecules decelerating and collapsing due to cooling. As atmospheric water vapor decreases in temperature, it condenses into minuscule water molecules. As an illustration, consider the accumulation of particles on a glass or the exterior of a chilled beverage.
The Functions of Condensation and Evaporation in the Water Cycle
Evaporation and condensation are fundamental constituents of the water cycle, an inherent ecological phenomenon that guarantees the perpetual motion of water across the planet. Evaporation from bodies of water, including oceans and lakes, recirculates water vapor into the atmosphere. As the temperature decreases, this vapor subsequently condenses into clouds comprising liquid particles.
As the condensation particles within the clouds eventually coalesce and enlarge, precipitation such as snow or rain is generated. This process, which is supported by condensation, is vital for sustaining life on Earth and nourishing its ecosystems.
The Influence of Condensation and Evaporation on the Weather and Climate
These two processes exert a substantial impact on variations in climate and weather patterns. Indeed, thunderstorms, characterized as intense convective cyclones, arise precisely from the dynamic interaction of condensation and evaporation.
Warm, moist air ascends into frigid regions of the atmosphere during the formation of thunderstorms. Small water droplets are produced when water vapor within the heated air condenses as the air cools. As a result of the condensation of these particles, cumulonimbus clouds are formed, which precipitate thunderstorms or downpours.
The perpetual succession of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation significantly influences the climate of our planet and is indispensable for preserving its fragile equilibrium.
Other Applications of Evaporation and Condensation Beyond the Water Cycle
Various domains make use of evaporation and condensation in addition to their functions in the water cycle. Steam engines, for example, convert thermal energy into mechanical labor through the utilization of condensation. Through the process of converting steam into liquid water, these engines effectively utilize the liberated heat to execute practical operations.
Furthermore, knowledge of evaporation and condensation enables one to develop an admiration for the splendor and intricacy of the natural environment. These processes exemplify the complex mechanisms through which matter undergoes changes and engages in interactions with its environment.
As our exploration of the intriguing domains of evaporation and condensation progresses, we uncover the marvels of the water cycle, the intricacies of weather systems, and the innumerable interconnections that influence our surroundings.
In summary, evaporation and condensation are intrinsic phenomena that regulate the transition of substances between different states. These are not mere theoretical constructs derived from the physical sciences; rather, they are fundamental components of our planet that have far-reaching consequences, ranging from the viability of life to weather patterns.
“Evaporation and condensation are the dynamic duo that shape our world, moving water from one state to another and driving the vital processes of nature.”
FAQ
To what does discharge refer?
Evaporation is the transformation of substances from a liquid to a gaseous state. It is the process by which the energy of the molecules in a liquid is sufficient to transform them into vapor.
Preface: Define condensation.
The process by which matter transforms from a gaseous to a liquid state is called condensation. It is the result of energy loss by gas molecules, which causes them to combine and form liquid particles.
What is the process by which evaporation takes place?
The process of evaporation takes place when a liquid is subjected to heat, which induces molecular motion and energy gain. The molecules are able to escape into the atmosphere as a gas due to the forces of attraction they surmount due to their increased energy.
What causes condensation to occur?
When a gas is chilled, condensation occurs; this results in the gas’s molecules decelerating and losing energy. The molecules subsequently condense and transform into liquid particles.
How do condensation and evaporation contribute to the water cycle?
Evaporation is a critical component of the water cycle because it facilitates the release of water into the atmosphere from bodies of water, including oceans, lakes, and rivers. Eventually, this atmospheric moisture condenses into clouds. By means of condensation, these clouds subsequently discharge precipitation, including snow or rain, thereby reinstating the Earth’s water supply and completing the water cycle.
- SYBAU See You Baby Meaning: Gen Z Slang Evolves - July 1, 2025
- Unlock Your Inner Youth: Lifestyle Secrets for a Vibrant Life - July 1, 2025
- Decode SYBAU Meaning: Gen Z Slang Explained - July 1, 2025