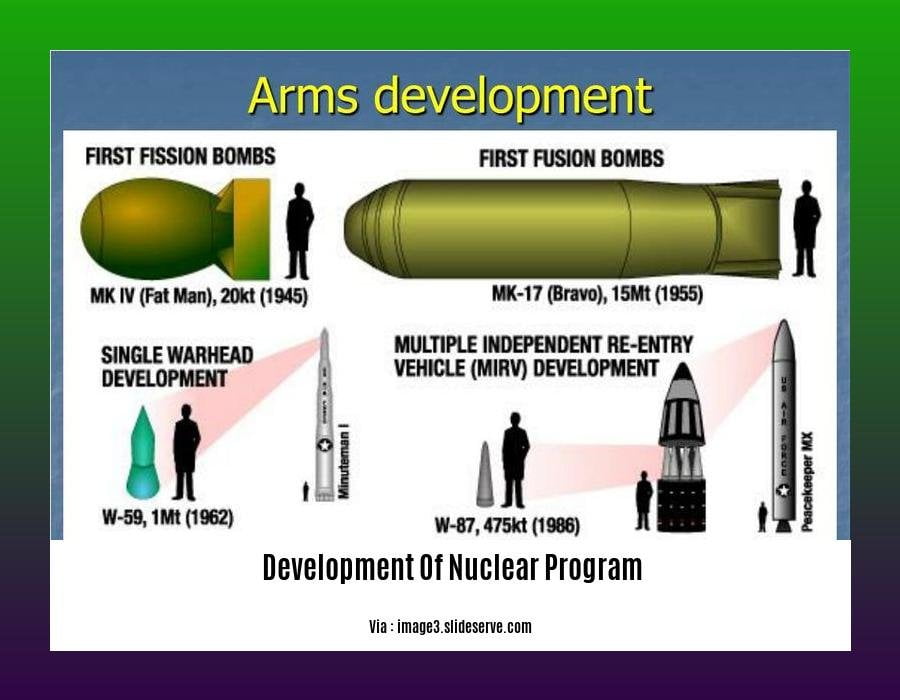
[- Development of nuclear program: assessing risks and opportunities]. The development of nuclear programs presents both opportunities and risks that require careful assessment. The potential benefits of nuclear energy, such as low-carbon electricity generation and medical isotopes production, must be weighed against the risks associated with nuclear waste management, proliferation, and safety concerns. Understanding the technical complexities and policy implications is crucial for making informed decisions about the future of nuclear energy.
Key Takeaways:
- Launching a nuclear program entails careful planning, investment, and long-term commitment (100 years).
- Preparatory work typically spans 10-15 years.
- Key milestones in a nuclear power project include knowledge commitment, bid invitation/negotiation, and commissioning/operation.
- Government, NEPIO (Nuclear Energy Programme Implementing Organization), and regulatory bodies play crucial roles in program implementation.
- Developing nuclear power infrastructure involves establishing national institutions, legal frameworks, human resource and financial strategies, waste management, and stakeholder engagement.
- The planning timeframe from initial consideration to plant operation is approximately 10-15 years.
**Development of nuclear program **

There’s a lot to consider when developing a nuclear program. It’s not a decision to be made lightly, and it requires a long-term commitment. But for countries looking to meet their energy needs while reducing their carbon footprint, nuclear power can be a viable option.
Planning and Preparation
The first step in developing a nuclear program is careful planning and preparation. This involves:
- Establishing a clear policy framework
- Identifying potential sites for nuclear power plants
- Developing a workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge
- Putting in place a regulatory framework to ensure safety
Construction and Operation
Once the planning is complete, the next step is to construct and operate the nuclear power plants. This is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the plants.
Waste Management
One of the biggest challenges associated with nuclear program is the management of radioactive waste. This waste must be safely stored and disposed of to protect the environment and public health.
Public Engagement
It is important to engage the public in the development of a nuclear program. This will help to build trust and support for the program, and it will also help to address any concerns that the public may have.
The Future of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is a low-carbon source of energy that can help to meet the world’s growing energy needs. However, it is important to develop nuclear programs in a safe and responsible manner. With careful planning and preparation, nuclear power can be a valuable part of the global energy mix.
If you seek to delve into the rich tapestry of Pakistan’s past, unveil the History of Pakistan, a chronicle that paints a vivid picture of its evolution.
Witness the pivotal moment in South Asian history with the Partition of British India, a cataclysm that shaped the geopolitical landscape of the region.
Explore the tumultuous legacy of the Indo-Pak wars, conflicts that have profoundly impacted the relationship between these neighboring nations.
Nuclear Waste Management Strategies

Waste management is and should be a top priority in the nuclear industry. It’s less glamorous than reactor development or fusion research, but it’s critical for the safe and sustainable development of nuclear power. Many countries are developing nuclear waste management strategies to deal with the radioactive waste produced by nuclear power plants. Let’s take a closer look at what these strategies entail.
Components of Nuclear Waste Management Strategies
Nuclear waste management strategies typically include a combination of the following components:
- Geological repositories: These are deep underground facilities where radioactive waste is stored for long periods of time.
- Fuel reprocessing: This process separates the reusable materials from the waste, reducing the volume of waste that needs to be disposed of.
- Interim storage: This is a temporary storage facility where radioactive waste is stored before it is disposed of in a geological repository.
- Multinational storage facilities: These are facilities where radioactive waste from multiple countries is stored.
Progress and Techniques in Nuclear Waste Management
Significant progress has been made in the development of safe and effective nuclear waste management strategies. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has developed a set of safety standards for the management of radioactive waste. A number of countries have also implemented successful waste management programs.
The main techniques used for the management of radioactive waste include:
- Reprocessing: Separates the reusable materials from the waste.
- Interim storage: Stores the waste temporarily, until it can be disposed of in a geological repository.
- Geological storage: Stores the waste in deep underground facilities for long periods of time.
Full Responsibility in Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is unique in that the industry assumes full responsibility for the management and costs of its waste, including financial provisions. This is in contrast to other industries, which often pass on the costs of waste management to the public.
Key Takeaways:
- Different nations have adopted distinct nuclear waste management strategies.
- Strategies may include geological repositories, fuel reprocessing, interim storage, and multinational storage facilities.
- Progress has been made in safe and effective radioactive waste management, according to IAEA.
- Accepted techniques include reprocessing, interim storage, and geological storage.
- Nuclear power is unique in assuming full responsibility for its waste management and costs, including financial provisions.
Relevant URLs:
- ScienceDirect: Nuclear Waste Management Strategies
- World Nuclear Association: Radioactive Waste Management
Safety Considerations and Risk Assessment
Evaluating safety considerations and risk assessment is crucial in ensuring the safe operation of nuclear power plants.
Key Takeaways:
- Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) is a comprehensive method for identifying and quantifying risks in nuclear power plants.
- The Level 1 PRA standard provides guidance for risk assessment processes.
- The Nuclear Safety Review 2020 report highlights global trends and priorities for strengthening nuclear safety.
Risk Assessment Methods
PRA is a systematic approach that involves:
- Identifying potential hazards
- Estimating the probability of occurrence
- Evaluating the consequences of each hazard
The Level 1 PRA standard (ANSI/ANS-58.21-2014) defines the minimum requirements for PRA in nuclear power plants. It provides a common framework for assessing risks across different facilities.
Safety Standards and Regulations
The Nuclear Safety Review 2020 report from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) provides insights into global trends and identifies areas for improvement in nuclear safety. The report emphasizes the importance of:
- Establishing clear safety standards
- Implementing robust regulatory frameworks
- Fostering a culture of safety within organizations
By adopting these best practices, we can enhance the safety and reliability of nuclear power plants worldwide.
Safety Measures
In addition to PRA and other risk assessment techniques, nuclear power plants implement various safety measures, including:
- Redundant safety systems
- Emergency response plans
- Continuous monitoring and surveillance
These measures provide multiple layers of protection to ensure that any potential incidents are promptly detected and mitigated.
Conclusion
Safety considerations and risk assessment are essential aspects of nuclear program development. By implementing comprehensive safety measures and adopting best practices, we can ensure the safe and responsible operation of nuclear power plants, contributing to a low-carbon energy future.
Citations:
- Development of risk assessment for nuclear power: insights
- Nuclear Safety Review 2020 – International Atomic Energy Agency
**Policy Implications and Decision-Making Framework for Program Development**
Nuclear power programs are major undertakings with long-term implications, requiring careful consideration of policy implications and decision-making frameworks. Several factors influence these decisions, including:
- Energy policy objectives
- Economic feasibility
- Infrastructure development
- Political buy-in
- Regulatory frameworks
Planning Framework:
Nuclear power program development follows a sequential approach:
– Conceptualization
– Feasibility studies
– Site selection
– Plant design and construction
– Operation and maintenance
– Decommissioning
Policy Considerations:
Clear policy frameworks are essential to guide decision-making, addressing issues such as:
– Energy Security: Nuclear power can enhance energy independence and security.
– Environmental Protection: Nuclear energy has minimal carbon emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation.
– Nuclear Safety: Robust safety regulations and emergency preparedness measures ensure public safety.
– Waste Management: Comprehensive waste management strategies ensure responsible disposal of spent nuclear fuel.
– Public Acceptance: Engaging the public through transparent communication and education is vital.
Decision-Making Framework:
A comprehensive decision-making framework should consider:
– Technical Feasibility: Assessing the feasibility of proposed reactor designs, fuel cycles, and waste management plans.
– Economic Viability: Evaluating the costs of construction, operation, and decommissioning, as well as potential revenue streams.
– Safety and Risk Assessment: Conducting thorough safety assessments to identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
– Policy Alignment: Ensuring that the program aligns with national energy policies and meets regulatory requirements.
– Stakeholder Engagement: Involving stakeholders throughout the decision-making process, including government agencies, industry experts, and the public.
Key Takeaways:
- Nuclear power programs require careful planning and decision-making to ensure safety, economic viability, and public acceptance.
- Clear policy frameworks and a comprehensive decision-making framework guide the development of nuclear power programs.
- Factors such as energy security, environmental protection, safety, waste management, and public engagement influence policy implications and decision-making.
Sources:
– IAEA: Nuclear Power Programme Planning: An Integrated Approach
https://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/TE_1259_prn.pdf
– ScienceDirect: Nuclear Power Plant Development