Have you ever stopped to think about what makes up everything around us? From the smallest grain of sand to the largest star, it all boils down to chemical elements—the fundamental ingredients of the universe. This comprehensive guide is your personal tour of the periodic table, the ingenious chart that organizes all known elements. We’ll delve into each element, uncovering its unique characteristics and applications. We’ll even explore the fascinating stories behind their discoveries. Whether you’re a student, a science enthusiast, or simply curious about the world, this guide will make learning about the elements engaging and accessible. For more on metallic properties, check out this helpful resource on magnetic materials. Let’s embark on a journey to unlock the secrets of the chemical world!
The Chemical Elements: A Comprehensive Exploration
Prepare for an enthralling expedition into the realm of chemistry! We will explore chemical elements, the essential building blocks of all matter, from the air we breathe to the devices we use daily. We’ll reveal their secrets, trace their histories, and highlight their crucial importance, enriching any chemical compounds list. Consider this your definitive guide to the periodic table, the symbolic map that organizes the elements, revealing their relationships and patterns.
Unlocking the Periodic Table: More Than Just a Chart
The periodic table is more than just a random collection of symbols and numbers; it’s an intelligently designed framework for understanding matter and essential for a proper element list. Each element occupies a unique position determined by its atomic number—the count of protons within its nucleus. This number is key to understanding an element’s behavior. Think of it as a city map, where each location (element) has its unique address (atomic number), and similar areas are grouped together. Elements within the same column, for example, share similar chemical traits. This organization allows scientists to quickly predict the properties and interactions of different elements, making it an indispensable tool in chemistry and materials science.
Exploring the Elements: A Detailed Overview
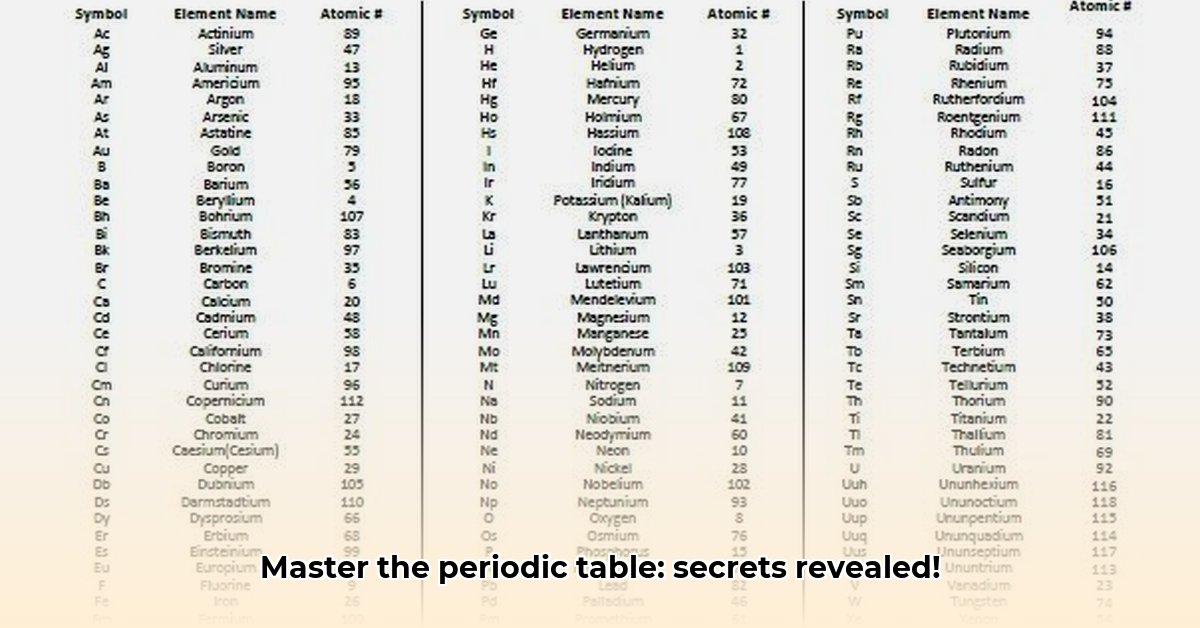
Now, let’s become acquainted with some of the primary elements in this exciting chemical narrative and explore a complete element list. We’ll focus on their unique attributes (properties), origins (discoveries), and significance in the world. Note that the atomic weight of an element can vary due to the presence of different isotopes (versions) of the element in nature.
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Atomic Weight (approx.) | Key Properties and Uses | Discovery Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 1.008 | Lightest element; vital for water, fuels, and organic compounds. | Discovered by Henry Cavendish in 1766. |
| Helium | He | 2 | 4.003 | Inert gas used in balloons, cryogenics, and medical imaging. | First detected in the sun’s spectrum by Pierre Janssen in 1868. |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 16.00 | Essential for respiration and combustion; abundant in Earth’s atmosphere. | Discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Joseph Priestley in the 1770s. |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 12.01 | Foundational element for all known life; forms diverse compounds. | Known since prehistoric times; essential to organic chemistry. |
| Gold | Au | 79 | 196.97 | Valuable metal; excellent conductor; resistant to corrosion. | Known and valued since ancient times. |
| Uranium | U | 92 | 238.03 | Radioactive element; used in nuclear power and weapons. | Discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1789. |
| Iron | Fe | 26 | 55.845 | Strong, abundant metal; used in construction and manufacturing. | Known since ancient times; crucial for industrial applications. |
| Silver | Ag | 47 | 107.868 | Precious metal, excellent electrical conductor, used in jewelry and electronics. | Known since ancient times. |
| Copper | Cu | 29 | 63.546 | Excellent electrical and thermal conductor, used in wiring and plumbing. | Used since prehistoric times. |
| Aluminum | Al | 13 | 26.981 | Lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant metal, used in aerospace and packaging. | Isolated in 1825 by Hans Christian Ørsted. |
This is merely a glimpse into the vast world of elements. Each element has its unique narrative filled with discoveries, surprising characteristics, and various applications.
The Periodic Table: A Dynamic Tool
It’s important to remember that the periodic table is perpetually evolving—a testament to continuous scientific exploration and discovery. Scientists constantly improve our understanding of elements, even discovering new ones. Organizations like the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) regularly update the table, integrating new elements and refining our knowledge of existing ones. Therefore, our present understanding might differ slightly in the future.
The periodic table is more than a list; it represents scientific inquiry, human innovation, and the ongoing quest to comprehend the universe at its most fundamental level. Next time you encounter the periodic table, remember it’s more than just a chart; it’s a key to the fascinating world of chemistry.
Navigating Discrepancies in Element Discovery Dates
Key Points:
- Early element discoveries lack precise dates because of limited historical records; archaeological evidence helps fill these gaps in the chemical element list.
- Simultaneous, independent discoveries create ambiguity; assessing independent claims is crucial for maintaining an accurate elements list.
- Modern discoveries use advanced technologies, providing robust documentation and reducing ambiguity within the list of all elements.
- Resolving discrepancies requires collaboration between historians of science and chemists, ensuring the list of elements is accurate.
The Role of Ancient Civilizations
Before chemistry became a formal science, elements such as gold and copper were discovered naturally. Pinpointing the exact moment of their initial observation is difficult. Navigating discrepancies in element discovery dates for ancient elements relies on archaeological evidence: tools, jewelry, and artifacts. Their usage indicates their understanding, providing contextual clues. Determining a specific “discovery date” remains challenging.
The Rise of Scientific Methods
The discovery of elements saw major advancements in the 17th and 18th centuries. The development of scientific methods led to enhanced documentation. However, navigating discrepancies in element discovery dates continued to be a challenge. Scientists sometimes made similar discoveries concurrently, which introduced ambiguity regarding who should receive credit within the list of chemical compounds. Resolving these issues requires analyzing independent research, publications, and correspondence.
Contemporary Discovery Protocols
Modern element discovery employs sophisticated techniques such as particle accelerators. These experiments are meticulously documented, minimizing ambiguity. Results undergo peer review and international validation, ensuring reliable updates for the list of all elements. This contrasts with the often-uncertain accounts of ancient times, making navigating discrepancies in element discovery dates more manageable.
Intersection of Disciplines
Addressing historical disputes requires a comprehensive approach. Historians analyze historical evidence, while chemists assess the scientific validity of claims. A collaborative effort between these disciplines is essential for providing an accurate timeline and a reliable list of elements. This collaboration is crucial for ensuring that the periodic table remains an up-to-date depiction of scientific comprehension.
The Periodic Table as an Evolving Chronicle
The periodic table is dynamic; it evolves with our understanding of chemistry, providing a constantly updated chemical element list. Addressing historical inconsistencies reflects the scientific method’s dedication to accuracy and improved understanding of the chemical world. The aim is to refine our narrative of developing this fundamental tool for organizing and understanding the elements list.
Periodic Table Trends and Their Applications in Material Design
Key Takeaways:
- The periodic table reveals predictable trends in atomic properties which are vital for a chemical element list.
- These trends are crucial for predicting element reactivity and chemical behavior to populate an elements list.
- Exceptions to general trends exist due to electron configurations, but don’t invalidate the project of compiling list of all elements.
- Understanding Periodic Table Trends and Their Applications in Material Design is crucial for material science, helping organize the list of elements.
- Future research will focus on exploring the properties of period 8 elements, expanding the frontier of the list of chemical compounds.
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
The periodic table charts elements based on atomic number, revealing trends that determine how elements behave, which is valuable for constructing a chemical elements list. These patterns govern atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character across rows and columns. This organization provides scientists with a means to predict elemental properties.
Deciphering Atomic Radius Trends
Atomic radius, or atomic size, typically decreases across a period (left to right) because of increased nuclear charge. Conversely, it increases down a group (top to bottom) due to the addition of electron shells. This key property influences how atoms interact and form materials.
Ionization Energy Explained
Ionization energy, the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom, generally increases across a period, driven by increased nuclear attraction. It decreases down a group as outer electrons
- Uncover the Verna Garver Timeline: A Life Beyond Hollywood - July 20, 2025
- Uncover Verna Garver’s Untold Story: A Life Beyond Headlines - July 20, 2025
- UPCI Missions Japan History: Lucas Family’s 30-Year Impact - July 20, 2025