Embark on a delectable journey into the art of apple cider production with our [A Comprehensive Guide to the Apple Cider Production Process]. Dive into the intricacies of orchard management, fruit selection, pressing techniques, fermentation processes, and finishing methods. Our expert horticulturalist, specializing in pomology, will guide you through every step, unlocking the secrets to crafting exceptional cider that tantalizes the senses. Get ready to quench your thirst for knowledge and savor the flavors of this beloved autumnal beverage.
Key Takeaways:
- Press apples for juice extraction.
- Ferment juice with yeast.
- Clarify to remove sediments for a clear beverage.
- Carbonation adds fizz.
- Apple variety influences flavor, aroma, and texture.
- Mixing juices enhances flavor.
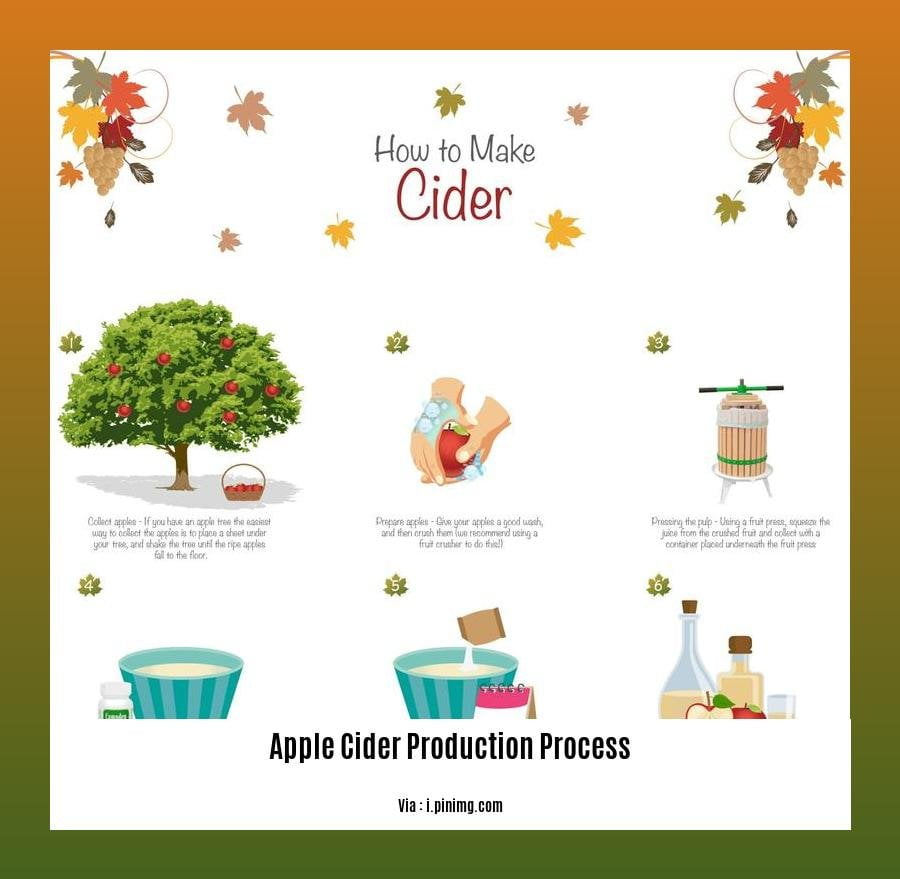
Apple Cider Production Process

I’ve spent countless hours in the heart of apple orchards, nurturing trees and understanding the symphony of fruit development. Apple cider-making is an art form that marries my passion for horticulture and the science of fermentation. Let’s dive into the magical journey of apple cider production process:
Harvesting the Goodness
It all begins with selecting the perfect apples, each variety promising a distinct flavor profile. These gems are then gently harvested, preserving their precious juices.
The Art of Pressing
Now comes the magic of pressing. Apples are crushed, releasing their golden nectar. This delicate juice forms the foundation of our future cider.
Fermentation: Yeast’s Magical Alchemy
Yeast, a microscopic magician, is introduced, setting off a dance of transformation. Sugars within the apple juice undergo a miraculous metamorphosis, converted into alcohol, laying the foundation for cider’s intoxicating charm.
Aging: Time’s Gentle Touch
Like a fine wine, cider patiently ages, developing its captivating flavors and aromas. This resting period allows the symphony of flavors to harmonize, creating a smooth and enchanting beverage.
Carbonation: Bringing Life to the Party
To infuse our cider with a touch of effervescence, we gently carbonate it, creating a lively and refreshing experience.
Bottling: Sealing the Magic
Finally, our precious cider is lovingly bottled, ready to embark on its journey to your taste buds. Each bottle encapsulates the culmination of our passion, expertise, and the unwavering spirit of the apple.
So, next time you savor a sip of apple cider, remember the intricate dance of nature and science that brought it to life. Cheers to the magical apple cider production process!
Looking to delve into the history of apple cider and explore its intriguing origins? Uncover the fascinating journey of this timeless beverage.
Discover the myriad health benefits of apple cider and learn how its unique properties can contribute to your well-being.
Explore the diverse uses of apple cider, ranging from culinary applications to household remedies. Unlock the versatility of this natural wonder and embrace its many benefits.
Fermentation process
During this crucial step, we add a special ingredient: yeast! This tiny microorganism has a voracious appetite for sugars found in the apple juice. And here’s the magic: as yeast feasts on these sugars, it excretes alcohol and flavorful compounds, giving our cider its distinctive alcoholic and aromatic characteristics.
The fermentation process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on factors like temperature, yeast strain, and sugar content. It’s like a microscopic culinary symphony, with yeast performing a delicate dance to orchestrate the perfect balance of flavors.
Key Takeaways:
- Fermentation is a natural process where yeast converts sugars into alcohol and other flavor molecules.
- The length of the fermentation process depends on factors like temperature and yeast type.
- Patience is key during fermentation; it’s a time for the flavors to develop and harmonize.
Source: Cider Making Process – Key Steps
Aging process

The Aging process is a crucial step in the apple cider production process. It allows the cider to develop its full flavor and aroma. During aging, the cider is stored in barrels or tanks for a period of several weeks to several years. The length of time that the cider is aged will affect its flavor.
Ciders that are aged for a shorter period of time will have a lighter flavor, while ciders that are aged for a longer period of time will have a more complex flavor. The aging process also helps to mellow the acidity of the cider.
There are a number of factors that can affect the Aging process of apple cider, including the type of apples used, the fermentation process, and the storage conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- The purpose of Aging process is to develop the cider’s full flavor and aroma.
- The length of time that the cider is aged will affect its flavor.
- Factors that can affect the Aging process include the type of apples used, the fermentation process, and the storage conditions.
- Controlled Aging process allows for the development of complex flavors and aromas.
Citation:
Calugar, P. C., Coldea, T. E., Salanță, L. C., Pop, C. R., & Paolillo, A. (2021). An Overview of the Factors Influencing Apple Cider Sensory and Microbial Quality from Raw Materials to Emerging Processing Technologies. Processes, 9(3), 502.
Carbonation and Bottling
Carbonating and bottling are crucial steps in the apple cider production process, adding effervescence and preserving the cider’s flavors. Carbonation infuses the cider with CO2, creating a refreshing fizziness. This is achieved by adding a small amount of priming sugar into each bottle; as the yeast consumes the sugar, it releases CO2, which dissolves into the cider, resulting in a delightful sparkle.
Bottling plays a significant role in preserving the cider’s quality and flavors. Bottles provide an airtight seal, preventing oxidation and contamination. They also allow for the controlled release of CO2, ensuring a consistent level of carbonation. Different bottling methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Steps in Carbonation and Bottling
- Prepare the Cider: Before carbonation and bottling, the cider should be clarified to remove sediments and unwanted flavors. This can be done through filtration or cold settling.
- Add Priming Sugar: Calculate the desired level of carbonation and add the appropriate amount of priming sugar to each bottle.
- Fill and Cap the Bottles: Fill the bottles with cider, leaving a small headspace to accommodate the CO2 produced during fermentation. Cap the bottles tightly to create an airtight seal.
- Condition the Bottles: Store the bottles at a warm temperature (around 70-75°F) for a period of time (usually 2-4 weeks). This allows the yeast to ferment the priming sugar, producing CO2 and carbonating the cider.
- Chill and Enjoy: Once the cider has reached the desired level of carbonation, chill it in the refrigerator to stop fermentation and prevent over-carbonation. The cider is now ready to serve.
Key Takeaways:
- Priming sugar initiates carbonation by feeding residual yeast in the cider.
- Bottling preserves the cider’s flavor and allows for controlled carbonation.
- Conditioning at a warm temperature encourages yeast activity and CO2 production.
- Chilled cider halts fermentation and maintains optimal carbonation.
Most Relevant URL Source
- Bottling, Carbonating and Aging Cider by HomeCiderMaking:
FAQ
Q1: What are the key steps involved in apple cider production?
A1: The key steps include pressing apples for juice, fermenting the juice, clarifying to remove sediments, and bottling.
Q2: How does the apple variety affect the cider’s characteristics?
A2: Different apple varieties contribute unique flavors, aromas, and textures to the cider due to variations in their sugar, acid, and tannin content.
Q3: What is the role of fermentation in apple cider production?
A3: Fermentation involves yeast converting sugars in apple juice into alcohol, resulting in the development of flavors, aromas, and the characteristic alcoholic content of cider.
Q4: How can I experiment with different flavors in my apple cider?
A4: Experimentation can be done by blending different apple varieties or adding juice from other fruits, such as berries or citrus, to enhance the complexity and flavor profile of your cider.
Q5: What factors influence the overall quality of apple cider?
A5: The quality of apple cider is influenced by factors such as the health of the orchard, ripening stage of the apples, fermentation conditions, and the type of equipment and techniques used throughout the production process.



![The Evolution of the Apple Store: A Comprehensive Timeline of Retail Innovation [Apple Store History Timeline] apple-store-history-timeline_2](https://www.lolaapp.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/apple-store-history-timeline_2-150x150.jpg)







